Introduction & Basics
UMD CP Club Summer CP


Who am I?
Cheng-Yuan (Sam) Lee
.Rising Sophomore
.ICPC Mid-Atlantic 3rd Place
.UMD CP Club President
.Codeforces Master
.AtCoder Rating \(\ge\) 2000
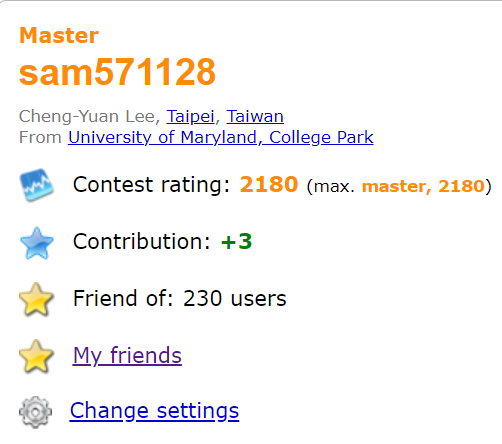
Feel free to discuss problems with me!

What is Competitive Programming

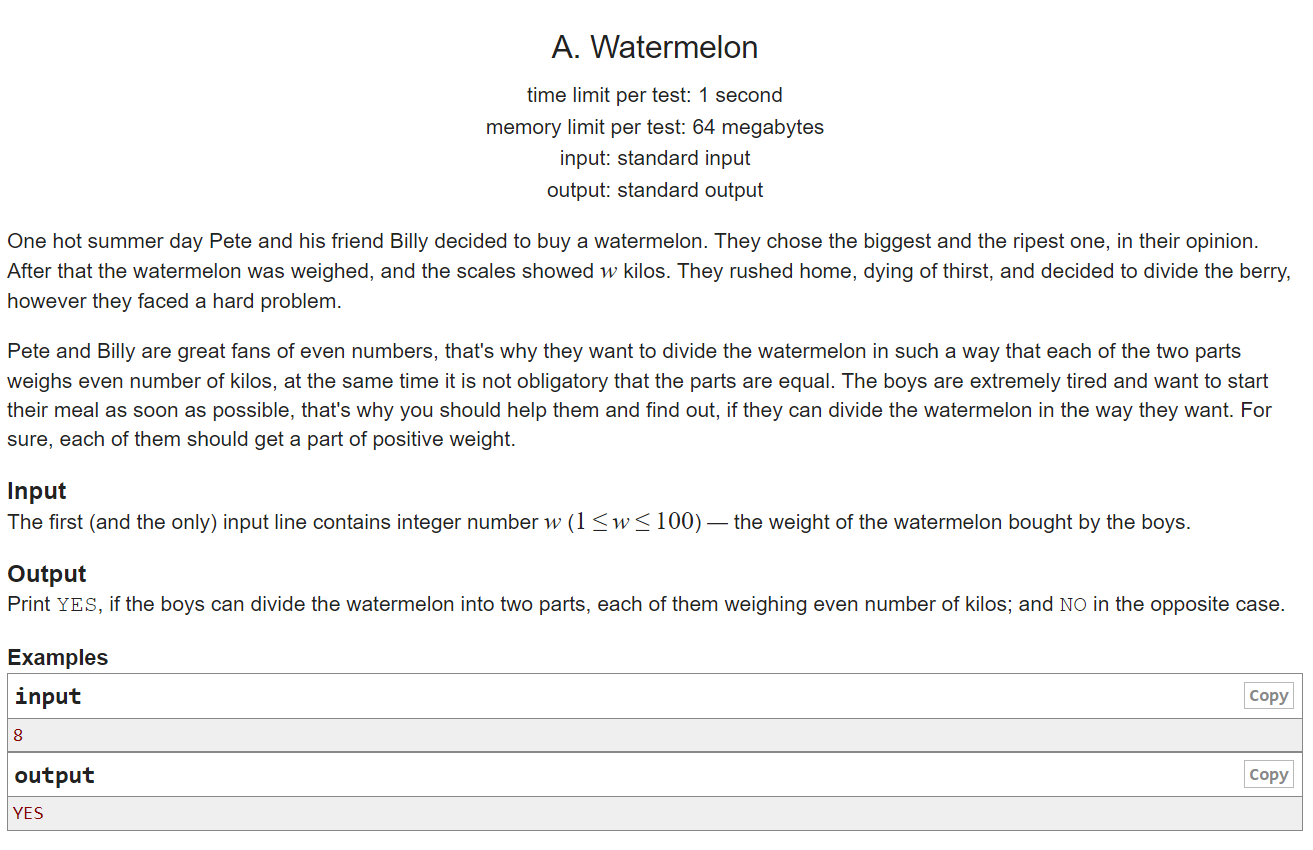

The problems are usually algorithmic
(CMSC351/451)

You have to come up with an algorithm
and implement It!
There are also two important parts

Time and Space

Time and Space



If Your Code didn't fit in Time

If Your Code didn't fit in Time
You get TLE
(Time Limit Exceeded)

If Your Code didn't fit in Space
You get MLE
(Memory Limit Exceeded)

If Your Code is incorrect
You get WA
(Wrong Answer)

When you finally solved a problem, you get AC !
(Accepted)


Ratings!

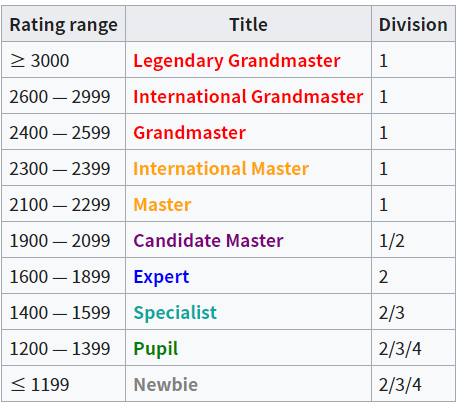



T-Shirt!




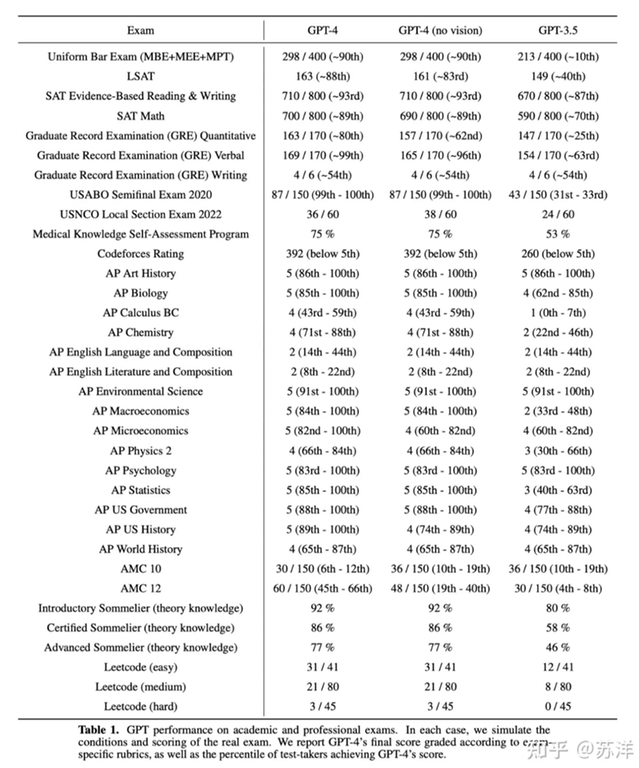
Resources





Time Complexity

In C++

In C++

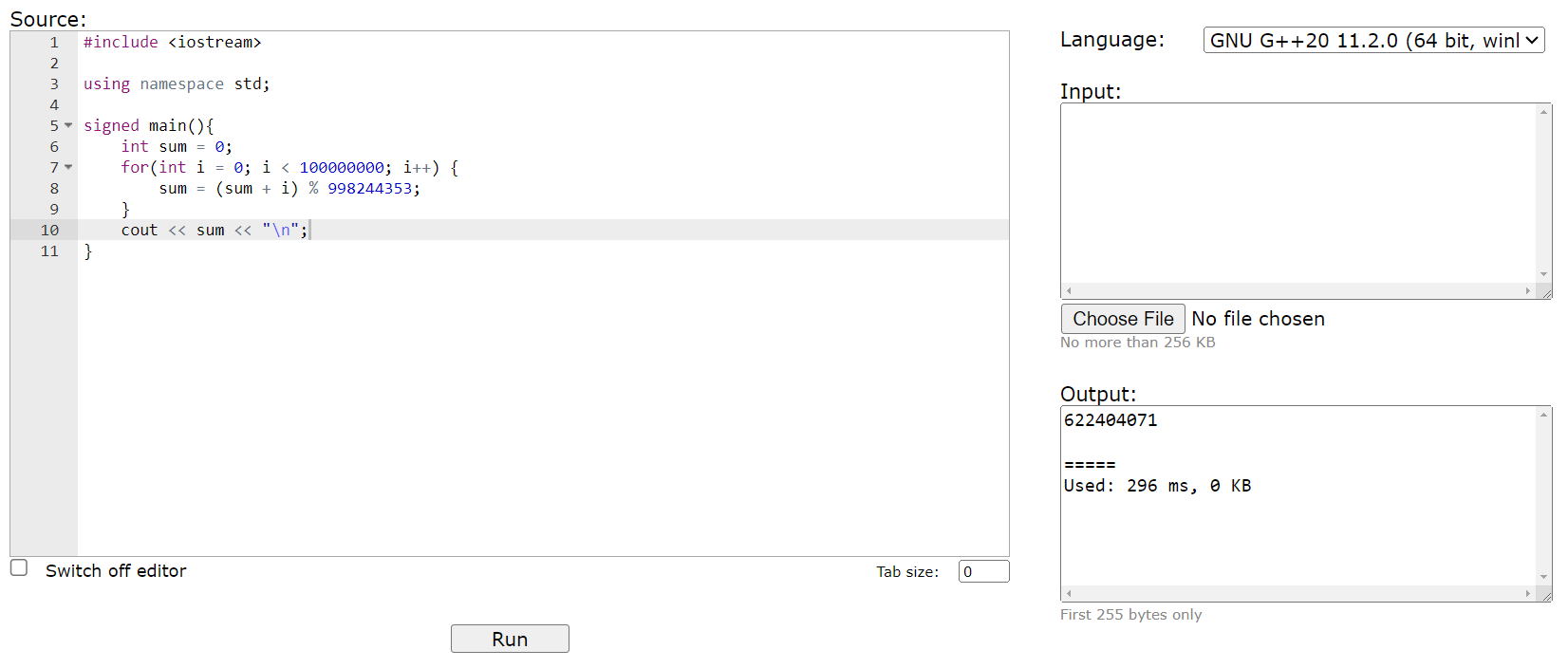
It varies from \(10^8 \sim 5 \times 10^8\)

We need a tool to approximate how many operations our code does!

Big O Notation

Big O Notation
We denote the runtime of an algorithm with
where \(n\) is the input size
\(f(n)\) is the number of operations with respect to \(n\)

Big O Notation
The formal definition of Big O is
if and only if

Big O Notation
The formal definition of Big O is
if and only if
We ignore the constant factor

Big O Notation
The other viewpoint of Big O is
if and only if

Big O Notation
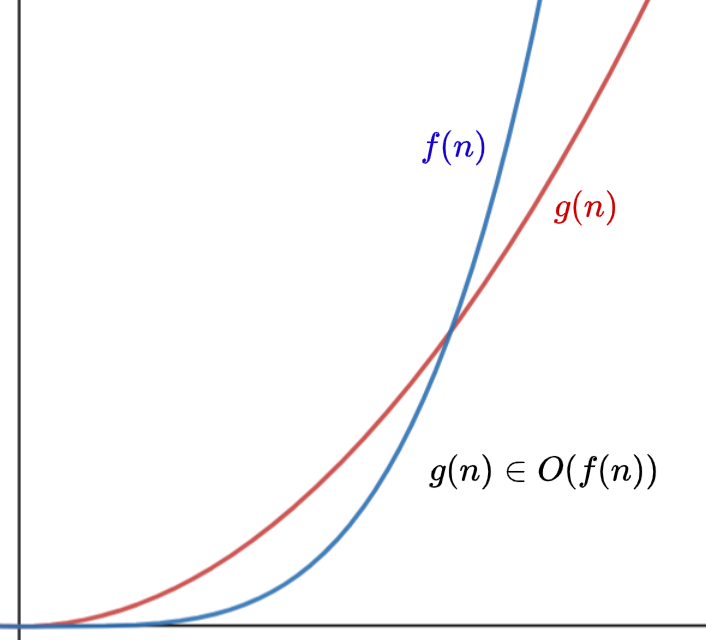

In CP, we usually plug \(n\) in
and divide by \(10^8 \sim 5 \times 10^8\)

1. Counting Loops

for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += i;
}What is the time complexity of this code?
1. Counting Loops

for (int i = 1; i <= 2*n; i++) {
sum += i;
}What is the time complexity of this code?
1. Counting Loops

for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
sum += i * j;
}
}What is the time complexity of this code?
1. Counting Loops

for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 2 * i; j <= n; j += i){
isprime[j] = false;
}
}What is the time complexity of this code?
1. Counting Loops

for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 2 * i; j <= n; j += i){
isprime[j] = false;
}
}What is the time complexity of this code?
1. Counting Loops

2. Recursions

int f(int x){
if (x <= 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return f(x-1) + f(x-2);
}
}What is the time complexity of this code?
2. Recursions

2. Recursions
You will learn different ways to approximate time complexity of recursion in CMSC351
Recursion Tree
Substitution Method
Master's Theorem
Knowing Master's Theorem will be sufficient

Big O Notation
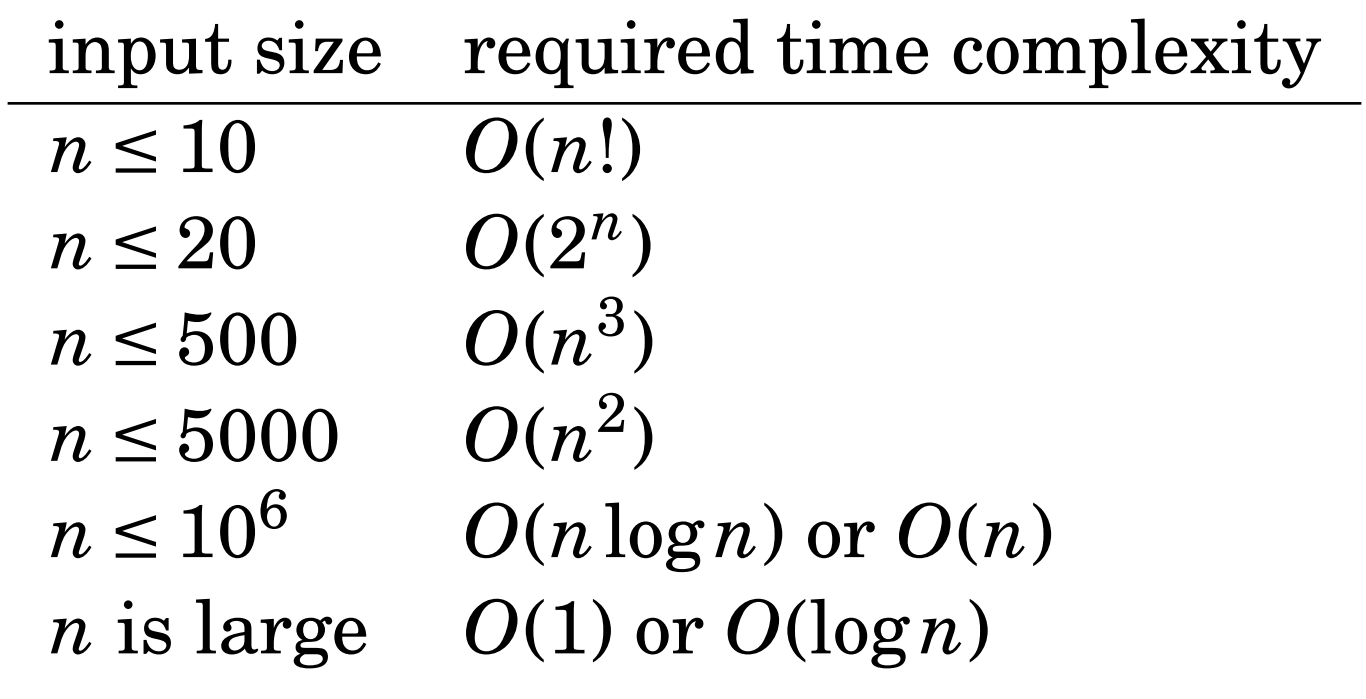

Programming Language

Which Language Should I Use?

In IOI (International Olympiad in Informatics)
The only allowed language is C/C++

In ICPC
The allowed languages are
C/C++, Java, Python, Kotlin

Most Competitive Programmer Uses C++


We will be using C++

Basic C++ Syntax

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << a+b << "\n";
}A+B Code

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
This header includes all the common headers

cin >>
cout <<
The above input things from standard input
The bottom output things to standard output

for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//do something n times
}
while(condition) {
//do something when condition is true
}Loops

The range of int is approxiamtely
\([-2 \times 10^9, 2 \times 10^9]\)
Important!
The range of long long is
|
\([-9 \times 10^{18}, 9 \times 10^{18}]\) |

There was a debate between
cin, cout and scanf(), printf()

cin, cout
are slow!

Try this problem

If you use scanf, printf
You get AC

If you use cin, cout
You get TLE

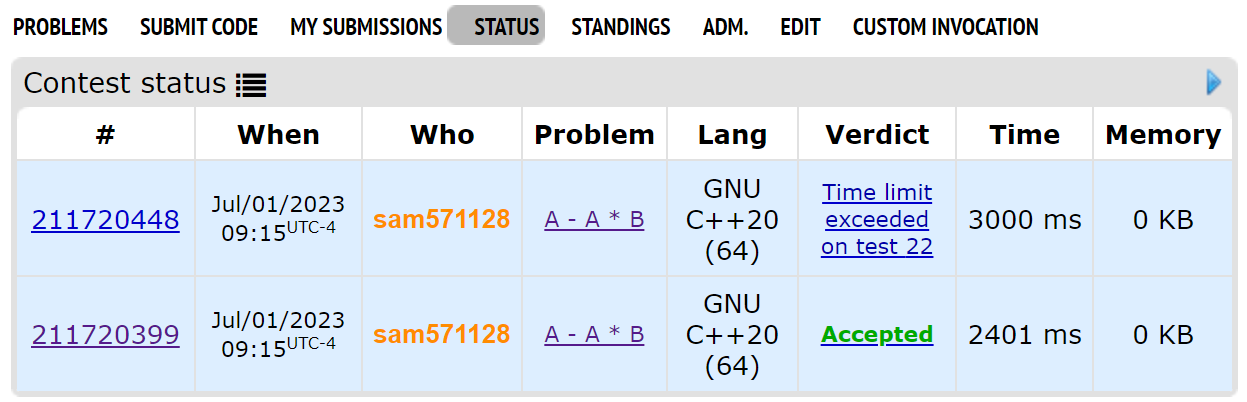

Does that mean you shouldn't use cin, cout?
NO!

ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
Add these two lines to your code!

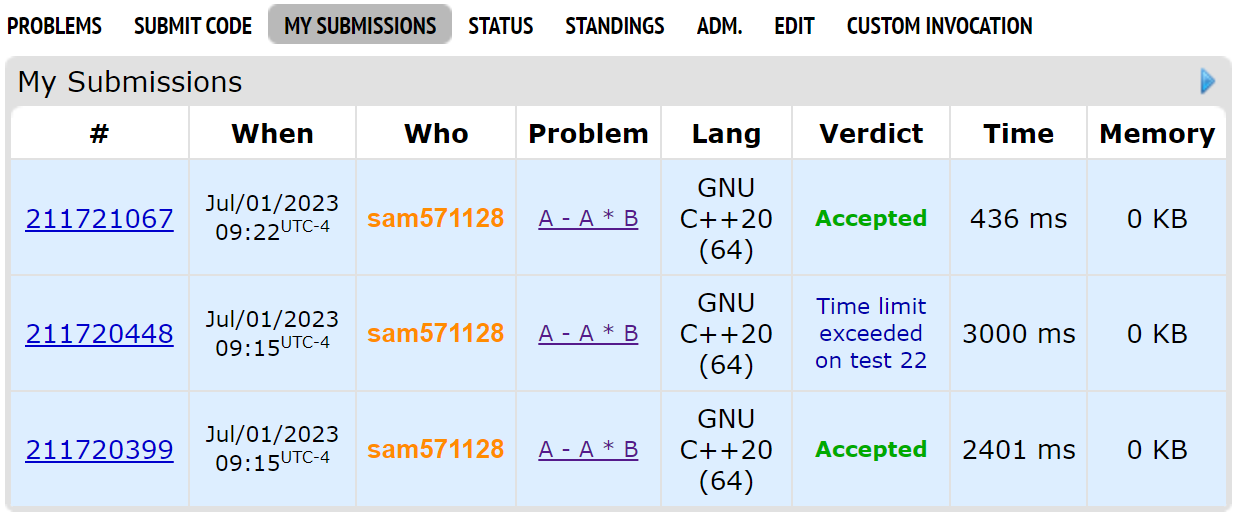
cin, cout is now 6x faster than scanf, printf !

Another Important Thing

Another Important Thing
Use "\n" instead of endl

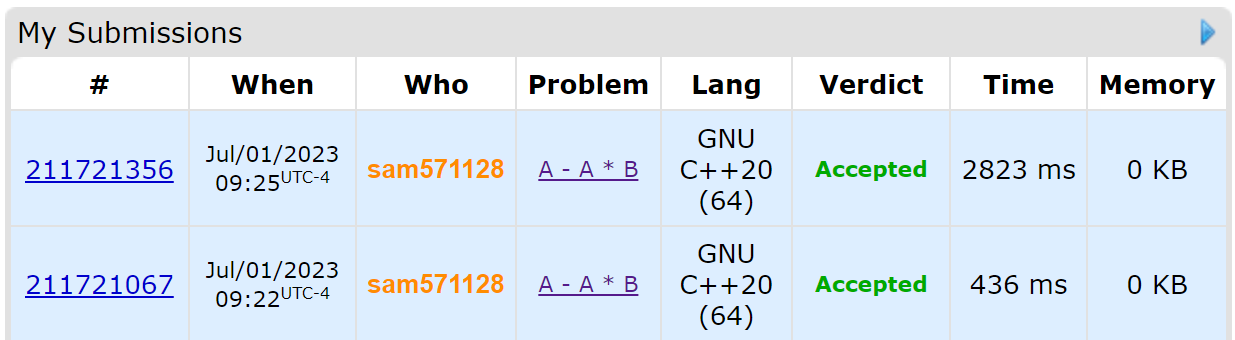
First one uses cin, cout and endl
Second one uses cin, cout and "\n"

C++ STL & Basic Data Structures

Immutable Arrays
int arr[n];
long long arr[n];
char arr[n];
string arr[n];An array is initialized with T arr[length]
where T is some type and length is some integer
The size cannot be changed

Immutable Arrays
int arr[n] = {1, 2, 3};
cout << arr[0] << "\n"; // 1
cout << arr[1] << "\n"; // 2
arr[1] = 0;
cout << arr[1] << "\n"; // 0You can access elements with arr[i]
it is 0-based, the first element is arr[0]

Dynamic Arrays
There are two types of dynamic arrays
vector<T>
deque<T>
vector supports pushing back but not front
deque supports both pushing back and front

Dynamic Arrays - vector<T>
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1); // v = {1}
cout << v[0] << "\n"; // 1
v.push_back(2); // v = {1, 2}
v.pop_back(); // v = {1}
v.push_back(3); // v = {1, 3}
cout << v[1] << "\n"; // 3
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
Dynamic Arrays - vector<T>
vector<int> v(len, x);
//initialize a vector of length len and initial element x
v[i]; //access the ith element
v.push_back(x); //add x to back
v.pop_back(); //remove last element
v.size(); //returns size of the vector
v.empty(); //returns true or false
v.resize(len); //resize the vector to len
v.clear(); //clear the vector
Dynamic Arrays - string
string in C++ is technically just vector<char>
but it also has
string s = "Hello";
s += "World";
cin >> s;
cout << s;
Dynamic Arrays - deque<T>
deque<int> dq;
dq.push_back(1); // v = {1}
cout << dq[0] << "\n"; // 1
dq.push_back(2); // v = {1, 2}
dq.pop_front(); // v = {2}
dq.push_back(3); // v = {2, 3}
cout << dq[0] << "\n"; // 2
for (int i = 0; i < dq.size(); i++) {
cout << dq[i] << " ";
}
Dynamic Arrays - deque<T>
deque<int> dq(len, x);
//initialize a deque of length len and initial element x
dq[i]; //access the ith element
dq.push_back(x); dq.push_front(x);//add x to back/front
dq.pop_back(); dq.pop_front(); //remove last/first element
dq.size(); //returns size of the deque
dq.empty(); //returns true or false
dq.resize(len); //resize the deque to len
dq.clear(); //clear the deque
You might ask, why don't we always use deque?
It has a larger constant!

How to sort an array?
In C++, there are builtin functions that are fast and easy to use!

How to sort an array?
int arr[n] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
vector<int> v = {3, 4, 5, 1, 2};
sort(arr, arr+n);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
std::sort has a time complexity of \(O(n \log n)\)

Other useful methods (requires sort)
lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x);
//return the iterator to first >= x
upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x);
//return the iterator to first > x
unique(v.begin(), v.end());
//if v has k unique elements, set v[0], v[1], v[k-1] to those elementsBoth lower and upper bound takes \(O(\log n)\)
unique takes \(O(n)\)

Other useful methods
swap(&a, &b); //swap the value of a and b
fill(v.begin(), v.end(), x) //make all elements in range x
reverse(v.begin(), v.end()); //reverse the range
max_element(v.begin(), v.end()); //return iterator to maximum element
min_element(v.begin(), v.end()); //return iterator to minimum element
shuffle(v.begin(), v.end()); //random shuffle all elements in rangeswap is \(O(1)\)
others are \(O(n)\)


Pairs
Consider this simple task
You are given \(n\) points on 2d plane,
sort them first by \(x\) then by \(y\)

Pairs
pair<T, T> p;
p.first; //returns first element
p.second; //returns second element
pair<T,T> make_pair(T a, T b); //return a pair {a,b}
{a, b}; //same as above
Pairs
vector<pair<int,int>> v;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
v.push_back({x[i], y[i]});
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());

Stack
It is a Last in First Out Data Structure
stack<int> st;
st.push(x); //push back
st.pop(); //pop back
st.top(); //returns last element
st.empty(); //return true or false
st.size(); //return size of stack


This is monotonic stack, we will focus on it more later

Queue
It is a First in First Out Data Structure
queue<int> q;
q.push(x); //push front
q.pop(); //pop front
q.front(); //returns first element
q.empty(); //return true or false
q.size(); //return size of queue

Queue
This data structure is used for BFS
We will use it more when we talk about it

Priority Queue (Heap)
You can simply used it as a sorted queue
priority_queue<int> pq;
pq.push(x); //push x into the queue
pq.pop(); //pop the largest element
pq.top(); //returns the largest element
pq.empty(); //return true or false
pq.size(); //return size of queuepush and pop are \(O(\log n)\)

Priority Queue (Heap)
You can also create min heap (default is max heap)
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<>> pq;
pq.push(x); //push x into the queue
pq.pop(); //pop the smallest element
pq.top(); //returns the smallest element
pq.empty(); //return true or false
pq.size(); //return size of queue
This data structure is used the most in Greedy algorithms


Binary Search Tree
There are two builtin binary search trees
set<T>
map<K,V>
Both are ordered

set
set<int> st;
st.insert(x); //add x to set
st.erase(x); //remove x from set
st.count(x); //most used as finding x
st.find(x); //it is harder to use than count
st.empty(); //return true or false
st.size(); //return size
st.lower_bound(x); //return iterator to first >= x
st.upper_bound(x); //return iterator to first > x
multiset
multiset<int> st;
st.insert(x); //add x to set, O(log n)
st.erase(x); //remove all x from set, O(log n)
st.count(x); //count the number of x, O(log n)
st.find(x); //find the first x, O(log n)
st.empty(); //return true or false, O(1)
st.size(); //return size, O(1)
st.lower_bound(x); //return iterator to first >= x, O(log n)
st.upper_bound(x); //return iterator to first > x, O(log n)
multiset
If you only want to remove an element
Use st.erase(st.find(x));

map
You can use it as an array for any data type
map<string, int> mp;
mp["hello"] = 1; //O(log n)
mp.insert("a", 2); // O(log n)
cout << mp["a"] << "\n"; // 2
mp.erase("hello"); // O(log n)
//other things are the same as set
mp.erase(Key); //remove Key from map O(log n)
mp.count(Key); //check if Key exists in map O(log n)
mp.find(Key); // O(log n)
mp.lower_bound(key); // O(log n)
mp.upper_bound(key); // O(log n)
unordered_map (hash table)
Same as map, but doesn't support set operations
Everything becomes \(O(1)\) (expected)



These are just the basics, but it is important to know them
We will start discussing actual algorithms in the following weeks