Introduction to ARM Cortex M3

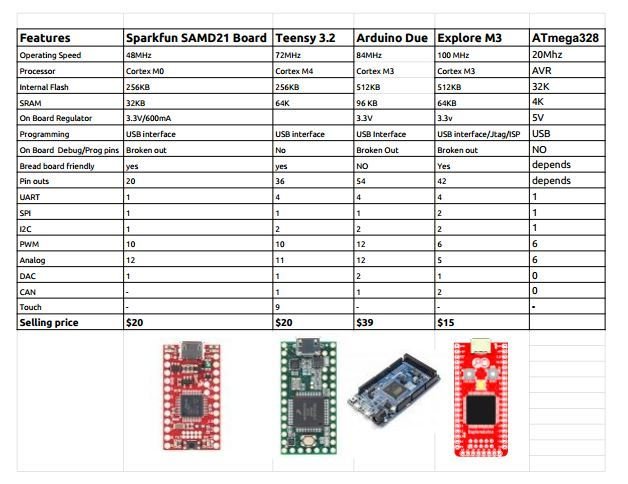
ARM Cortex M3 Vs AVR
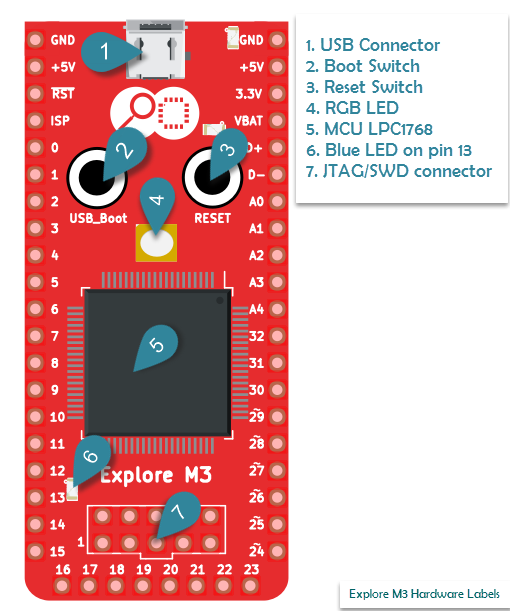
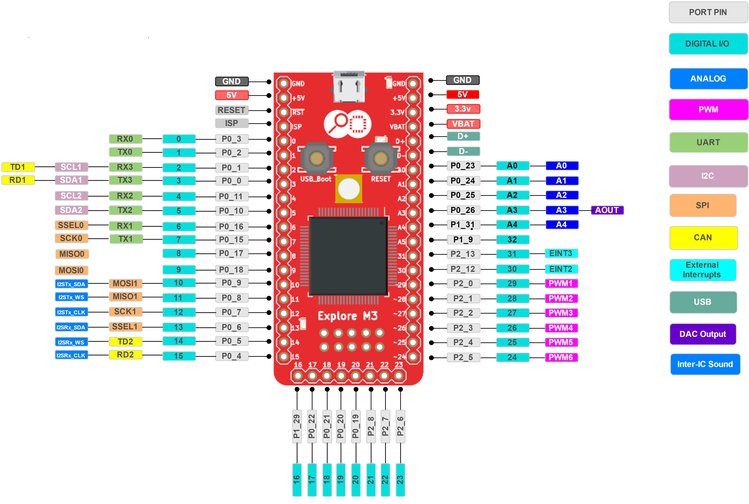
ARM Cortex M3 - architecture, peripherals
Explore M3
Programming with
ARM GCC

https://exploreembedded.com/wiki/Using_ARM_GCC_with_LPC_1768
Programming with Arduino
Blinky
/*
Blink
Turns on an LED on for one second, then off for one second, repeatedly.
This example code is in the public domain.
*/
int led = 13;
// the setup routine runs once when you press reset:
void setup() {
// initialize the digital pin as an output.
pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop routine runs over and over again forever:
void loop() {
digitalWrite(led, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(led, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}Blinky with Arduino
If Arduino programming is indeed C++, why don't I see any header files? Where did the setup() and loop() function come from?
What compiler does this thing use?
How is the program uploaded to the board?
Let's open the Can!
Bare Metal Blinky


The GPIO Registers
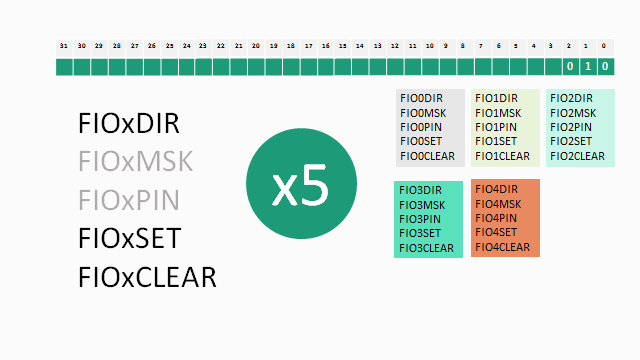
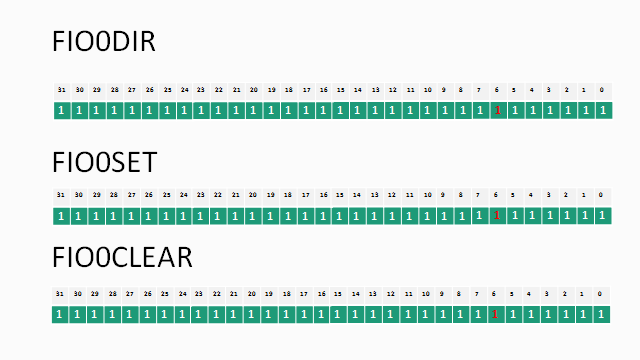
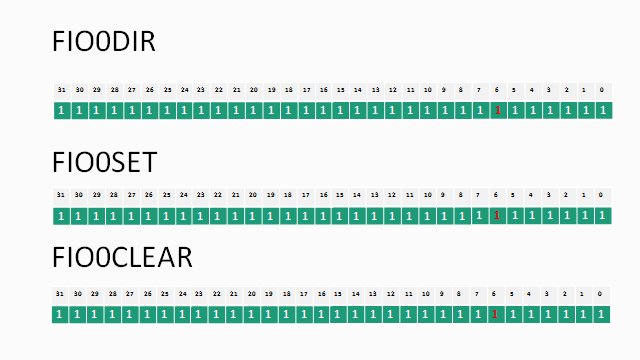
#include <lpc17xx.h>
/* start the main program */
int main()
{
SystemInit(); //Clock and PLL configuration
LPC_PINCON->PINSEL0 = 0x000000; //Configure the PORT2 Pins as GPIO;
LPC_GPIO0->FIODIR = 0xffffffff; //Configure the PORT2 pins as OUTPUT;
while(1)
{
LPC_GPIO0->FIOSET = 0xffffffff; // Make all the Port pins as high
delay(1000);
LPC_GPIO0->FIOCLR = 0xffffffff; // Make all the Port pins as low
delay(1000);
}
}Blinky with Registers
Let's look a little more deep.
Blinky with Address!
The Memory Map
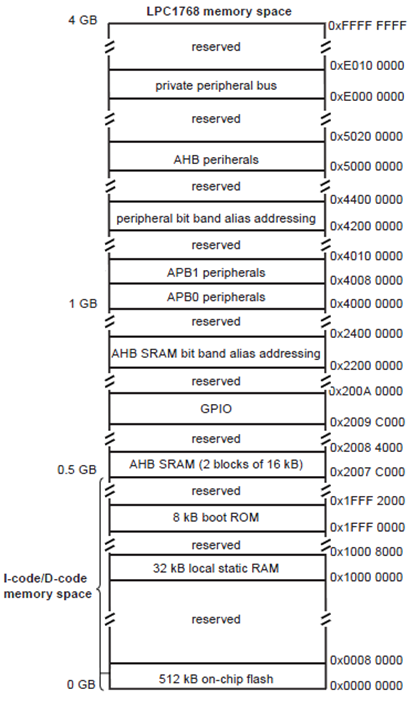
GPIO
The Code
//#include <lpc17xx.h>
/* start the main program */
int main()
{
SystemInit(); //Clock and PLL configuration
*(uint32_t *)0x4002C000 = 0x00000000; //pin select register
*( uint32_t *)0x2009C000 = 0xffffffff; // port direction
while(1)
{
*(uint32_t *)0x2009C018 = 0xffffffff; // Make all the Port pins as high
delay(500);
*(uint32_t *)0x2009C01C = 0xffffffff; // Make all the Port pins as low
delay(500);
}
}Things to think about?
-
How did I figure out the address?
-
Can I write code without affecting other bits?
PWM
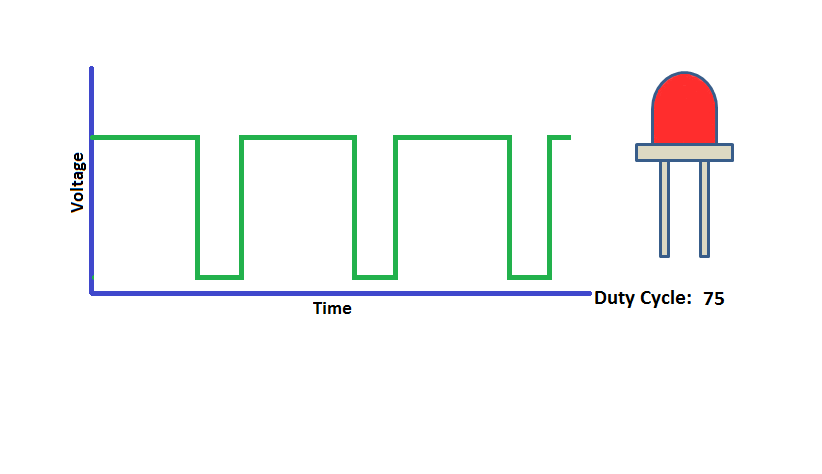
PWM with Arduino
#define mRightA 24
int cnt = 0;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(mRightA, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
for( cnt = 0; cnt< 255; cnt++){
analogWrite(mRightA, cnt);
delay(10);
}
for( cnt = 255; cnt > 0; cnt--){
analogWrite(mRightA, cnt);
delay(10);
}
}PWM on Bare Metal
#include "gpio.h"
#include "pwm.h"
#include "delay.h"
#define CYCLE_TIME 255
#define PWM_PIN 29
/* start the main program */
int main()
{
int dutyCycle;
SystemInit(); /* Clock and PLL configuration */
PWM_Init(CYCLE_TIME); /* Initialize the PWM module and the Cycle time(Ton+Toff) is set to 255(similar to arduino)*/
PWM_Start(PWM_PIN); /* Start PWM signal generation on Selected pin */
while(1)
{
for(dutyCycle=0;dutyCycle<CYCLE_TIME;dutyCycle++) /* Increase the Brightness of the LED */
{
PWM_SetDutyCycle(PWM_PIN,dutyCycle);
DELAY_ms(5);
}
for(dutyCycle=CYCLE_TIME;dutyCycle>0;dutyCycle--) /* Decrease the Brightness of the LED */
{
PWM_SetDutyCycle(PWM_PIN,dutyCycle);
DELAY_ms(5);
}
}
}More In-depth tutorial on PWM
https://exploreembedded.com/wiki/LPC1768:_PWM
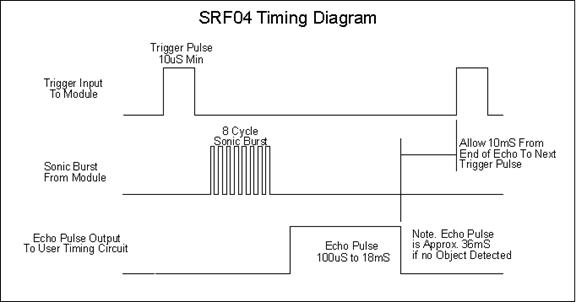
Digital input - ultrasonic sensor
Hook up
Trig
Echo
VCC
GND
8
7
GND
5V
Let's check the distance!
const int trigPin = 7;
const int echoPin = 8;
void setup() {
// initialize serial communication:
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT);
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
// establish variables for duration of the ping,
// and the distance result in inches and centimeters:
long duration, inches, cm;
// The PING))) is triggered by a HIGH pulse of 2 or more microseconds.
// Give a short LOW pulse beforehand to ensure a clean HIGH pulse:
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(5);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
// The same pin is used to read the signal from the PING))): a HIGH
// pulse whose duration is the time (in microseconds) from the sending
// of the ping to the reception of its echo off of an object.
duration = pulseDuration(echoPin, HIGH);
// convert the time into a distance
inches = microsecondsToInches(duration);
cm = microsecondsToCentimeters(duration);
Serial.print(inches);
Serial.print("in, ");
Serial.print(cm);
Serial.print("cm");
Serial.println();
delay(100);
}
long microsecondsToInches(long microseconds)
{
// According to Parallax's datasheet for the PING))), there are
// 73.746 microseconds per inch (i.e. sound travels at 1130 feet per
// second). This gives the distance travelled by the ping, outbound
// and return, so we divide by 2 to get the distance of the obstacle.
// See: http://www.parallax.com/dl/docs/prod/acc/28015-PING-v1.3.pdf
return microseconds / 74 / 2;
}
long microsecondsToCentimeters(long microseconds)
{
// The speed of sound is 340 m/s or 29 microseconds per centimeter.
// The ping travels out and back, so to find the distance of the
// object we take half of the distance travelled.
return microseconds / 29 / 2;
}
unsigned long pulseDuration(uint8_t pin, uint8_t state)
{
uint32_t startTime,currentTime;
while(digitalRead(pin)!=state); //Wait till the requested state is same as current state
startTime = micros(); // Capture the time once the state transition occurs
while(digitalRead(pin)==state) // Wait till the state change and keep track of timeout
{
currentTime = micros();
}
return (currentTime - startTime);
}Let's Build a 2WD Robot
Test the wheels!
#define mRightA 24
#define mRightB 25
#define mLeftA 26
#define mLeftB 27
int cmd;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(2000);
Serial.print("Turn the wheels! \n\r W-Forward \n\r S-Reverse \n\r A-Left \n\r D-Right");
pinMode(mRightA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(mRightB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(mLeftA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(mLeftB, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
cmd = Serial.read();
switch(cmd)
{
case 'w': roboForward(); break;
case 's': roboReverse(); break;
case 'a': roboLeft(); break;
case 'd': roboRight(); break;
//in case the caps lock is ON
case 'W': roboForward(); break;
case 'S': roboReverse(); break;
case 'A': roboLeft(); break;
case 'D': roboRight(); break;
default: roboStop(); break;
}
}
void roboForward(){
digitalWrite(mRightA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mRightB, HIGH);
digitalWrite(mLeftA, HIGH);
digitalWrite(mLeftB, LOW);
}
void roboReverse(){
digitalWrite(mRightA, HIGH);
digitalWrite(mRightB, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftB, HIGH);
}
void roboLeft(){
digitalWrite(mRightA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mRightB, HIGH);
digitalWrite(mLeftA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftB, LOW);
}
void roboRight(){
digitalWrite(mRightA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mRightB, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftA, HIGH);
digitalWrite(mLeftB, LOW);
}
void roboStop(){
digitalWrite(mRightA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mRightB, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftB, LOW);
}Demo
Let's Make it Autonomous with Ultrasonic Sensor
//motor Pins
#define mRightA 24
#define mRightB 25
#define mLeftA 26
#define mLeftB 27
//ultrasonic pins
const int trigPin = 7;
const int echoPin = 8;
int distance;
void setup() {
//Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(mRightA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(mRightB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(mLeftA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(mLeftB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT);
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
distance = getDistance();
//look for an obstacle, go back and take a random turn
if((distance>0) && (distance<15) )
{
// Serial.print("Obstacle in Range:");
// Serial.println(distance);
//Serial.println("Taking a Step back");
roboReverse();
delay(3000);
if(random(2))
{
//Serial.println("moving left");
roboLeft();
delay(500);
}
else
{
// Serial.println("moving Right");
roboLeft();
delay(500);
}
}
//march on!!
roboForward();
}
void roboForward(){
digitalWrite(mRightA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mRightB, HIGH);
digitalWrite(mLeftA, HIGH);
digitalWrite(mLeftB, LOW);
}
void roboReverse(){
digitalWrite(mRightA, HIGH);
digitalWrite(mRightB, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftB, HIGH);
}
void roboLeft(){
digitalWrite(mRightA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mRightB, HIGH);
digitalWrite(mLeftA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftB, LOW);
}
void roboRight(){
digitalWrite(mRightA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mRightB, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftA, HIGH);
digitalWrite(mLeftB, LOW);
}
void roboStop(){
digitalWrite(mRightA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mRightB, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftA, LOW);
digitalWrite(mLeftB, LOW);
}
unsigned long pulseDuration(uint8_t pin, uint8_t state)
{
uint32_t startTime,currentTime;
while(digitalRead(pin)!=state); //Wait till the requested state is same as current state
startTime = micros(); // Capture the time once the state transition occurs
while(digitalRead(pin)==state) // Wait till the state change and keep track of timeout
{
currentTime = micros();
}
return (currentTime - startTime);
}
long microsecondsToCentimeters(long microseconds)
{
// The speed of sound is 340 m/s or 29 microseconds per centimeter.
// The ping travels out and back, so to find the distance of the
// object we take half of the distance travelled.
return microseconds / 29 / 2;
}
long microsecondsToInches(long microseconds)
{
// According to Parallax's datasheet for the PING))), there are
// 73.746 microseconds per inch (i.e. sound travels at 1130 feet per
// second). This gives the distance travelled by the ping, outbound
// and return, so we divide by 2 to get the distance of the obstacle.
// See: http://www.parallax.com/dl/docs/prod/acc/28015-PING-v1.3.pdf
return microseconds / 74 / 2;
}
int getDistance(){
long duration;
//send the trigger
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(5);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
return microsecondsToCentimeters(pulseDuration(echoPin, HIGH));
}