A Changelog for react
16.2 ~ 16.8
16.3
- createContext
- createRef
- forwadRef
- Lifecycle change
- <StictMode />
create Context
public render() {
return (
<PanelContext.Provider value={ this.state }>
<Panel />
</PanelContext.Provider>
)
}Parent:
Any Nested Children:
export class Panel extends React.Component {
public render() {
return (
<PanelContext.Consumer>
{ this.content }
</PanelContext.Consumer>
)
}
private content(context: IPanelContext) {
return (
<>
<div>
{ context.actived }
</div>
<button onClick={ context.changeType }>
change
</button>
</>
)
}
}
但凡在组件树中的某一个节点上挂载了 Context.Provider
那么这个节点的任意一个子孙节点都可以使用 Context.Consumer 来获得状态
(一种跨层级的状态传递)
- 可以一定程度缓解使用 Redux 时产生的层层传递状态的问题
- 解决 GTA 埋点需要各种破坏组件的 interface 问题
create Ref
export default class extends React.Component {
private ref = React.createRef<HTMLDivElement>()
private handleClick = () => {
console.log(this.ref.current, '当前节点')
}
public render() {
return (
<div ref={ this.ref } onClick={ this.handleClick }>
CREATE REF DEMO
</div>
)
}
}
CURRENT:
PREVIOUS:
export default class extends React.Component {
private ref: HTMLDivElement | null
private saveRef = (ref: HTMLDivElement | null) => {
this.ref = ref
}
render() {
return <div ref={ this.saveRef } />
}
}没什么好多说的,更好用呗
FORWARD Ref
import React from 'react'
import { Button } from '@teambition/clarity-design'
export HOCWrap class extends React.Component {
render() {
return React.forwardRef((props, ref) => <Button ref={ ref } { ...props } />)
}
}解决 HOC / Decorator 下 ref 穿透的问题
Lifecycle change
Add:
getDerivedStateFromProps
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
UNSAFE:
componentWillMount
componentWillReceiveProps
componentWillUpdate
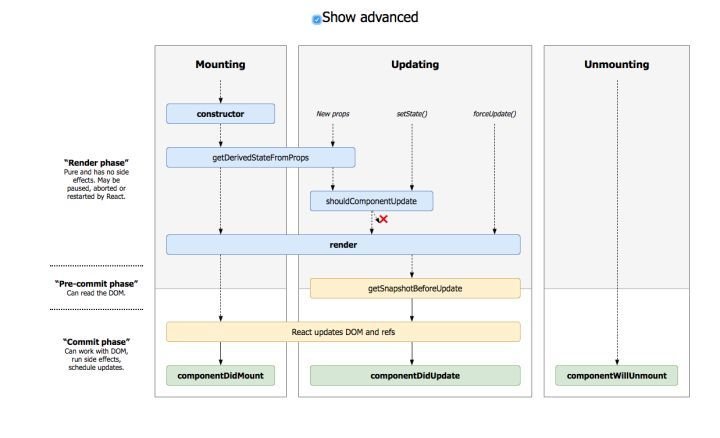
static getDerivedStateFromProps
- 用于取代 componentWillReceiveProps
- 原先 componentWillReceiveProps 是一个实例方法,而这个 API 是一个类的静态方法
- 如果改变 props 的同时,有副作用的产生,这时应该使用 componentDidUpdate
- 如果想要根据 props 计算属性,应该考虑将结果 memoization 化
- 如果想要根据 props 变化来重置某些状态,应该考虑使用受控组件
static getDerivedStateFromProps
UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps: TabsProps) {
if ('activeKey' in nextProps) {
this.setState({
activeKey: nextProps.activeKey!
})
} else if (!this.activeKeyIsValid(nextProps, this.state.activeKey)) {
this.setState({
activeKey: this.getDefaultActiveKey(nextProps),
})
}
}
abstract class A extends React.Component {
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props: TabsProps, state: TabsState) {
if ('activeKey' in props) {
return {
activeKey: nextProps.activeKey!
}
} else if (!A.activeKeyIsValid(props, state.activeKey)) {
return {
activeKey: A.getDefaultActiveKey(props),
}
}
return null
}
static activeKeyIsValid(props: TabsProps, key: string) {
return true
}
static getDefaultActiveKey() {
return // balabala
}
abstract render()
}getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
// 使用 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 时必须和 componentDidUpdate 成对出现
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps: any, prevState: any) {
if (this.props.value !== this.state.str) {
return { needScroll: true }
}
return null
}
componentDidUpdate(_1, _2, snapshot) {
if (snapshot.needScroll) {
this.domRef.scrollTop = 0
}
}
<StrictMode />
- 识别被标志位不安全的生命周期函数
- 对弃用的 API 进行警告
- 探测某些产生副作用的方法
- 检测是否使用 findDOMNode
- 检测是否采用了老的 Context API
16.4
- Pointer Events
Pointer Events
指针事件是为指针设备触发的 DOM 事件。它们旨在创建单个 DOM 事件模型来处理指向输入设备,例如鼠标,笔 / 触控笔或触摸(例如一个或多个手指)。指针是一个与硬件无关的设备,可以定位一组特定的屏幕坐标。拥有指针的单个事件模型可以简化创建 Web 站点和应用程序,并提供良好的用户体验,无论用户的硬件如何。但是,对于需要特定于设备的处理的场景,指针事件定义了一个 pointerType 属性,用于检查产生事件的设备类型。
Ref
https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/05/23/react-v-16-4.html
16.5
- Profiler
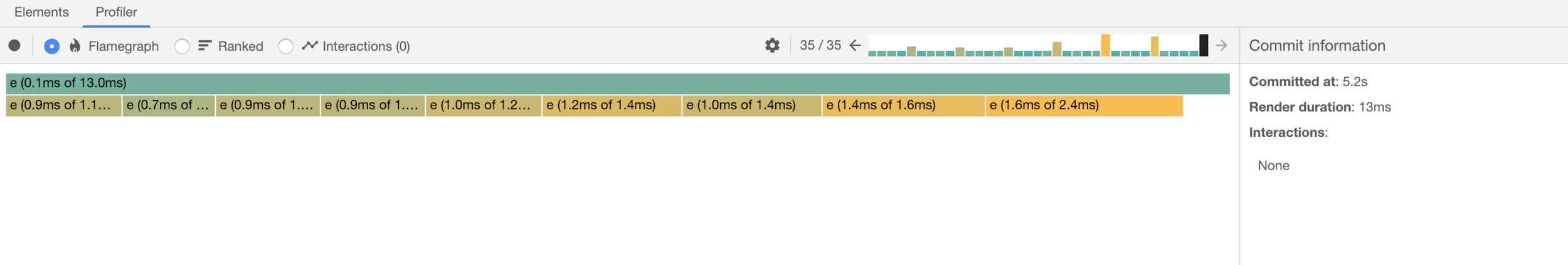
Profiler
React 16.5 添加了对新的 profiler DevTools 插件的支持。这个插件使用 React 的 Profiler 实验性 API 去收集所有 component 的渲染时间,目的是为了找出 React App 的性能瓶颈,它将会和 React 即将发布的 时间片 特性完全兼容。
P.S. 该模块支持 Production 模式下的 profile
Ref
https://juejin.im/post/5ba0f8e4f265da0ab915bcf2
import { unstable_Profiler as Profiler } from "react";
import { render } from "react-dom";
import { unstable_trace as trace } from "scheduler/tracing";
trace("initial render", performance.now(), () =>
render(
<Profiler id="Application" onRender={onRender}>
<Application />
</Profiler>,
domElement
)
);16.6
- Memo
- lazy / Suspense
- static contextType
- getDerivedStateFromError
memo
const MemoizedComponent = React.memo(props => {
// 类似等价于给 SFC 的 SCU
})lazy / Suspense
React.lazy() 提供了动态 import 组件的能力,实现代码分割。
Suspense 作用是在等待组件时 suspend(暂停)渲染,并显示加载标识。
目前 React v16.6 中 Suspense 只支持一个场景,即使用 React.lazy() 和 实现的动态加载组件。
另外,在将来,Suspense 将会与 react-cache (WIP) 助力开发者面对简单缓存场景下的开发体验
import React, { lazy, Suspense } from 'react'
const OtherComponent = lazy(() => import('./OtherComponent'))
function MyComponent() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<OtherComponent />
</Suspense>
)
}static contextType
主要就是因为之前基于 render callback pattern 的 context 使用体验过于糟糕,因此在 16.6 做了改进
https://reactjs.org/docs/context.html#classcontexttype
const MyContext = React.createContext()
class MyClass extends React.Component {
static contextType = MyContext
componentDidMount() {
const value = this.context
}
componentDidUpdate() {
const value = this.context
}
componentWillUnmount() {
const value = this.context
}
render() {
const value = this.context
}
}getDerivedStateFromError
与 componentDidCatch 不同的是,该生命周期会更早的触发,允许开发者在 render 完成之前渲染 Fallback UI,也因此,我们可以在 getDerivedStateFromError 中更新状态,在 componentDidCatch 中上报错误信息。
16.7
- Bugfix
16.8
- Hooks
Hooks
export function useResizer() {
const [ value, setValue ] = useState([window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight])
useEffect(() => {
const subscription = resizer$.subscribe(setValue)
return () => subscription.unsubscribe()
}, []) // 第二个参数很重要
return value
}
-
状态逻辑复用
-
让函数式组件得以拥有 “状态”
-
降维异步数据
disadvantage
-
HOOK 虽然是一个 FUNCTION,但最好别当它是一个 JAVASCRIPT FUNCTION,更倾向于是一个 REACT FUNCTION,它的本质相对于 JAVASCRIPT 是不自然的
-
HOOK 和函数式组件相依相随,是严格的伴生关系
-
尽量不要试图去抽象 HOOK
-
在严格需要测试的场景中,测试的方案仍然不够明朗
Ref
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/49408348
https://www.zhihu.com/question/300049718
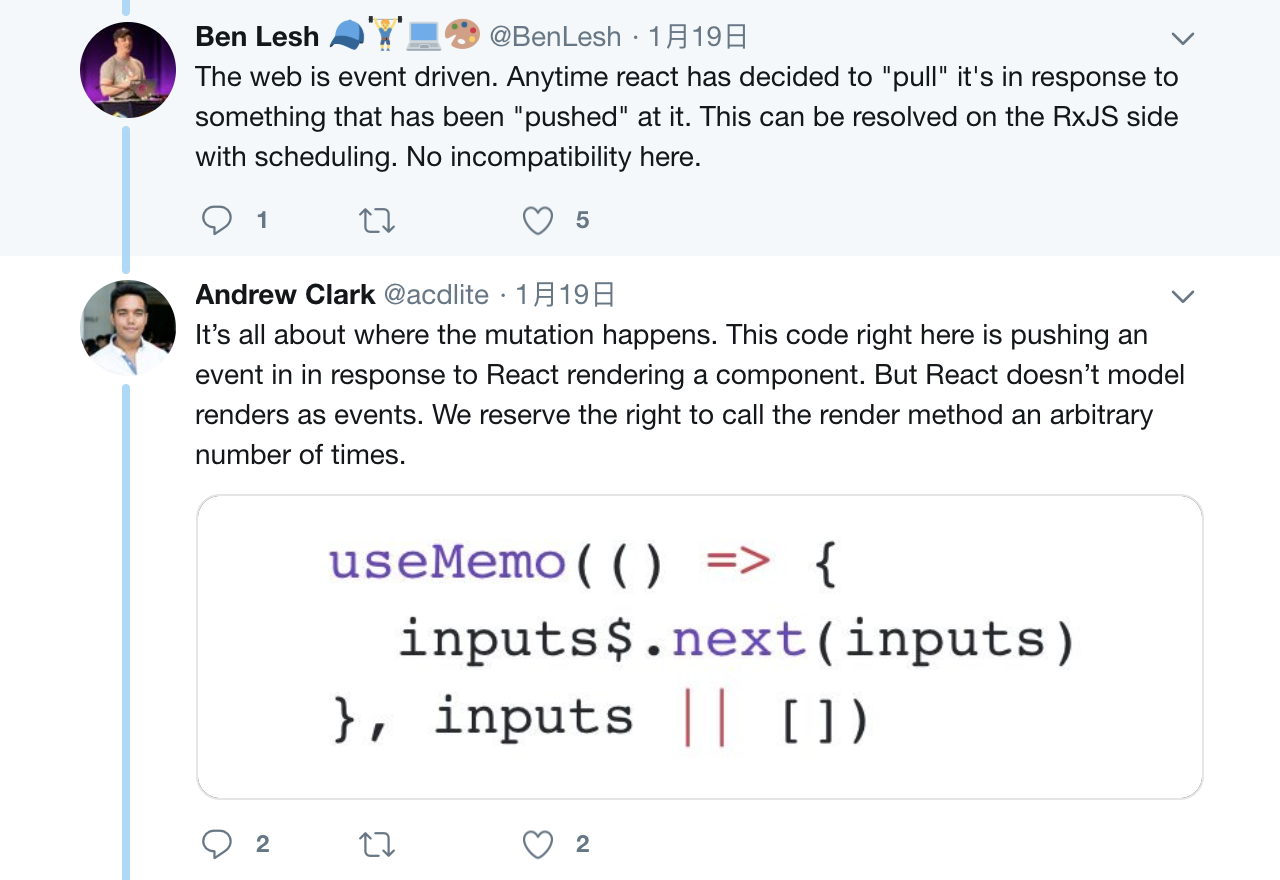
Event driven programming is not _inherently_ incompatible with React but if you start treating React’s render cycle as if it’s push based, then yeah, things are going to break.