Broadcast Field Study
Basic Camera Concepts I
CMS 3510 "Sports" / CMS 3511 "Performing Arts" - Spring 2019




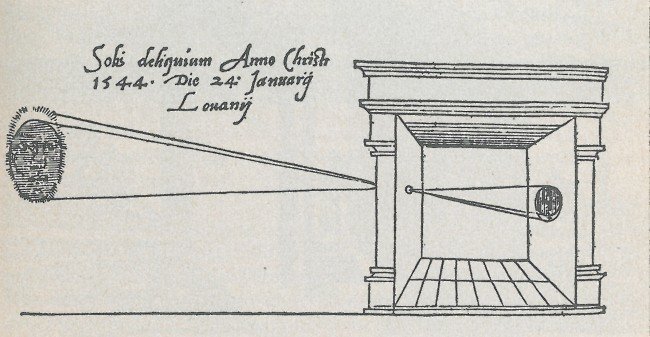
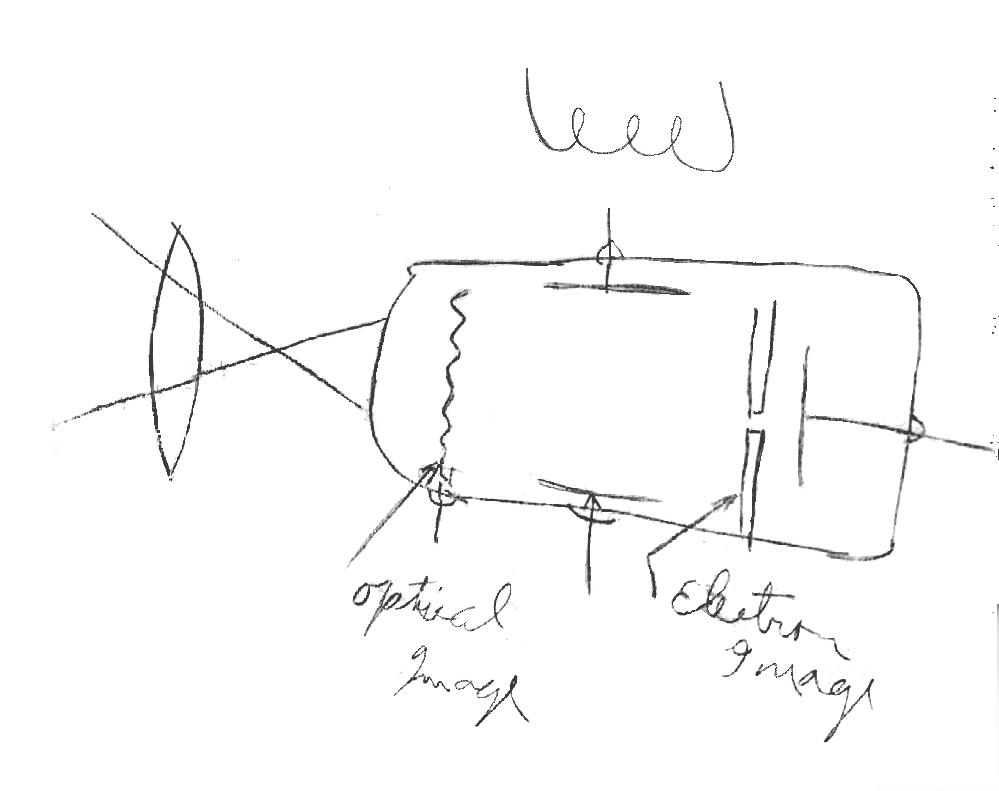
Camera Obscura
"Dark Room"
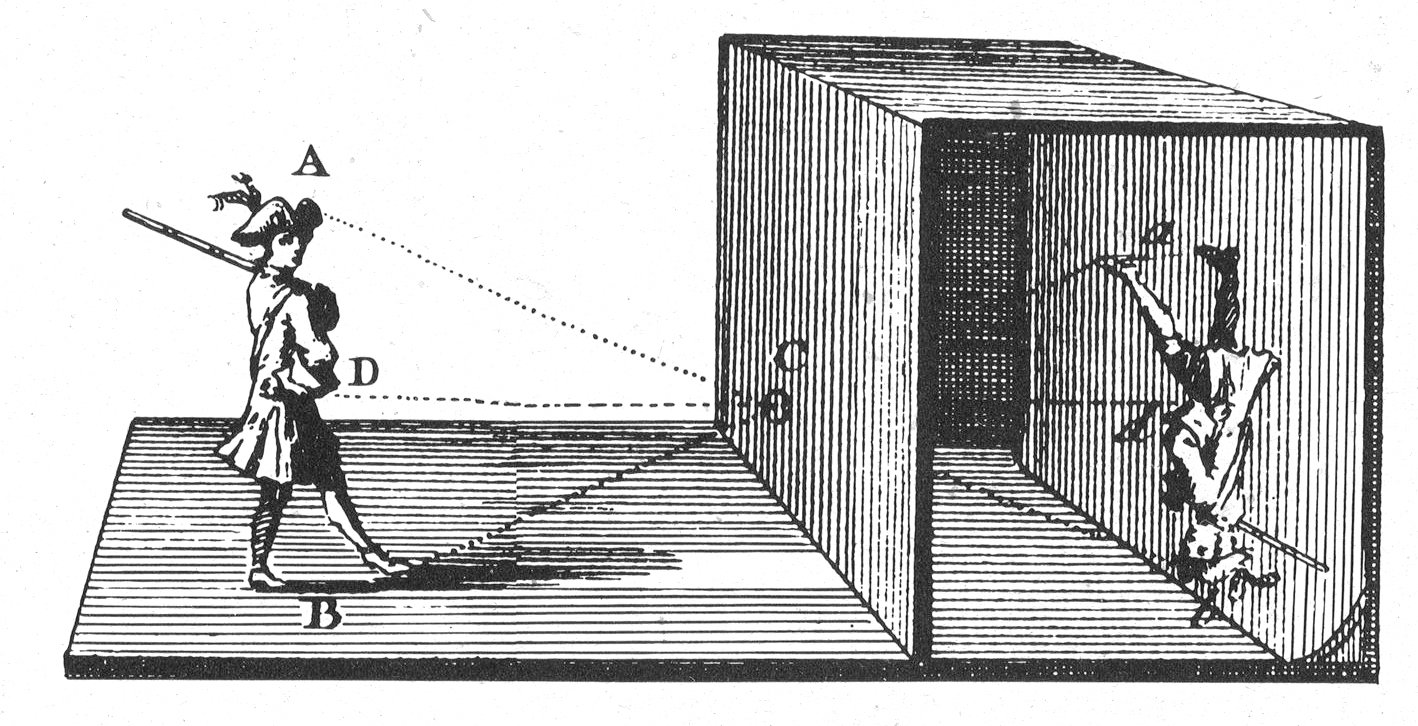
Not to scale!
In order to produce a reasonably clear projected image, the aperture has to be about 1/100th the distance to the screen
Hole in the tile floor in Prague Castle:

Camera Obscura in SF:

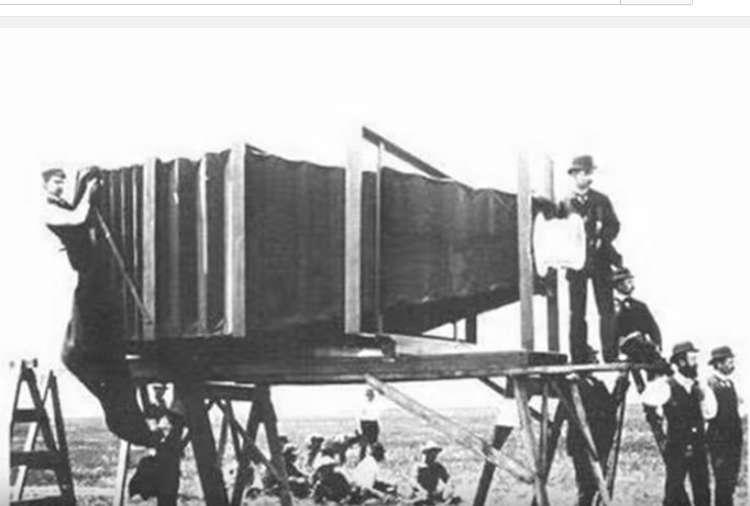
Early camera (1900)
Photography cameras
(1911 +)


Camcorder 1967
with live transmission

Camcorders
Photographic Cameras


Television Still Photography
Video Cassette Tape Film
Tape
Film


Cinema cameras

A modern (-ish) camcorder
Sony Handycam

A DSLR
Canon 70D
DSLR = "Digital Single Lens Reflex"

Converging back to video...
Reconvergence...


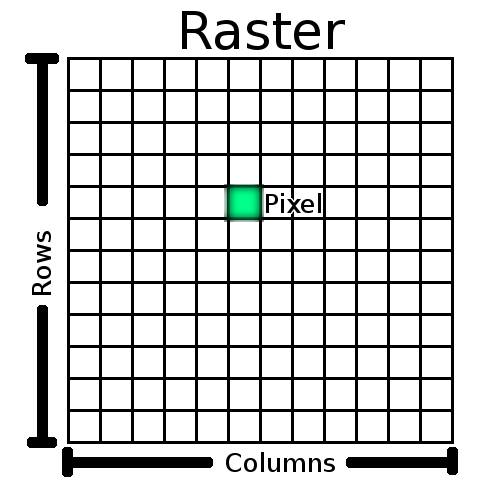
Pixels
- "Picture elements"
- RGB = red green blue
Pixels
(Retina display)
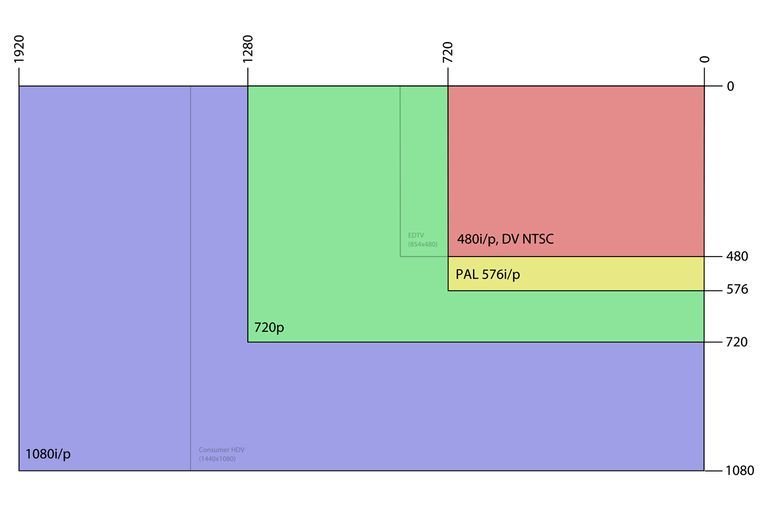
Format
- Rows of pixels
- Format = how many rows?
- 1080 x 1920 (HD)
- 3840 x 2160 (UltraHD) "4k"

a potato field...

Philo T. Farnsworth
(1906 - 1971)

Philo T. Farnsworth
"Green Street Lab"

202 Green Street, San Francisco
Raster
"Mosaic" - but how to make images move? (video)
Scan lines

Scan lines are the rows of pixels being 'fired up' by the image scanning beam, starting at the top and working its way down. There are two ways to do this:
Progressive vs. Interlaced
(in HD video, 1080p vs 1080i)
Frames per second
Progressive = 30 fps
Interlaced = 60 fields per second, but it's 1 field of the odd scan lines followed by 1 field of the even scan lines...

Interlaced not so good with fast motion!
Media Journals
Template in Google Docs - Shared with Instructor
1. Keep a log of some media you consume
2. Write about it
- "what?"
- "so what?"
- "now what?"
3. Read the chapter assignment and reflect
on the reading.
Check due dates in syllabus, usually 1 or 2 weeks after assigned.
Hand held vs.
Examples - unpredictable situations, protests, unplanned interviews "man on the street", special field level shots at sporting events, worm's eye view, battle documentation, cinema for rough, unstable, or realistic look, unusual environments like underwater. Horror movie running through the woods. Cinéma vérité, literally "true movie" -- Jean Rouch popularized it as a documentary technique of real life. 'Anti-cinematic.'
Examples - studios, anywhere with production lights, planned interviews, press conferences, lectures/speaking events, standard sports coverage shots, nature shots, timelapses. Cinematic, sweeping, smooth.
Decide how to shoot:
Hand-held










Tripod











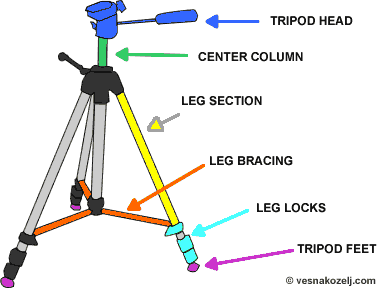
Other ways of shooting....









SET UP
cameras + tripod
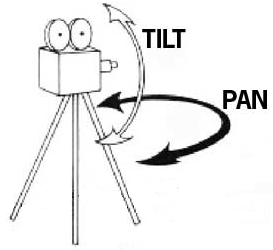
Tripod Movements
Turning left and right is known as "panning" or pan left or right. Looking up or down is known as "tilting" or tilt up or down.
ZOOM
focus
iris
IRIS
ZOOM
FOCUS
Narrow or widen the frame of the shot without moving the camera. Operated by the pressure sensitive Zoom rocker, smaller automatic zoom rocker on top, and the manual zoom ring.
Closing or opening the aperture to allow more or less light to enter the camera lens. A wider, open iris is needed in dark situations to let in more light and get as much detail as possible. A contracted, smaller opening is needed in harsh light situations when you want to get good detail, you are limiting the excessive light so you don't overwhelm the camera (ie blown out). Auto iris vs. manual iris.
iris function
Focus
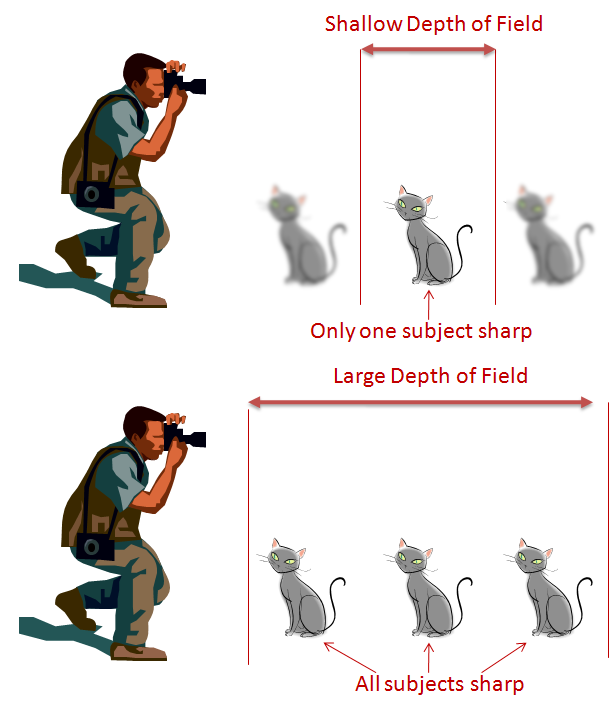
Controlling how far away the field of focus is. Focus is sharpening the image so that objects aren't blurry. Objects that are different distances away will each have different focus settings -- "focal length." You can also control "depth of field", which is how deep your field of focus is. In a "Wide Depth of Field" everything looks like it is in focus. In a "Shallow Depth of Field" only one object is in focus. To "Rack Focus" means to change the shallow depth of field from one object to another. Auto focus vs. manual focus.
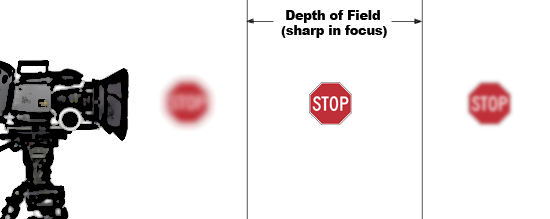
Shallow vs Wide (or large) Depth of Field