Android Fundamentals (1)
Set up tools
build tools
sdk tools
java 8
Gradle 篇
Gradle is a build automation tool for multi-language software development. It controls the development process in the tasks of compilation and packaging to testing, deployment, and publishing.
Gradle wrapper
The Wrapper is a script that invokes a declared version of Gradle, downloading it beforehand if necessary. As a result, developers can get up and running with a Gradle project quickly without having to follow manual installation processes saving your company time and money.
.
├── build.gradle
├── settings.gradle
├── gradle
│ └── wrapper
│ ├── gradle-wrapper.jar
│ └── gradle-wrapper.properties
├── gradlew
└── gradlew.bat.our-app-android
├── build.gradle
├── settings.gradle
├── [our-app-name].gradle
├── [maven-publish].gradle
├── [gradle].properties
├── gradle
│ └── wrapper
│ ├── gradle-wrapper.jar
│ └── gradle-wrapper.properties
├── gradlew
└── gradlew.batExample
Our app
build tools
sdk tools
java 8
sdkmanager
The sdkmanager is a command line tool that allows you to view, install, update, and uninstall packages for the Android SDK.
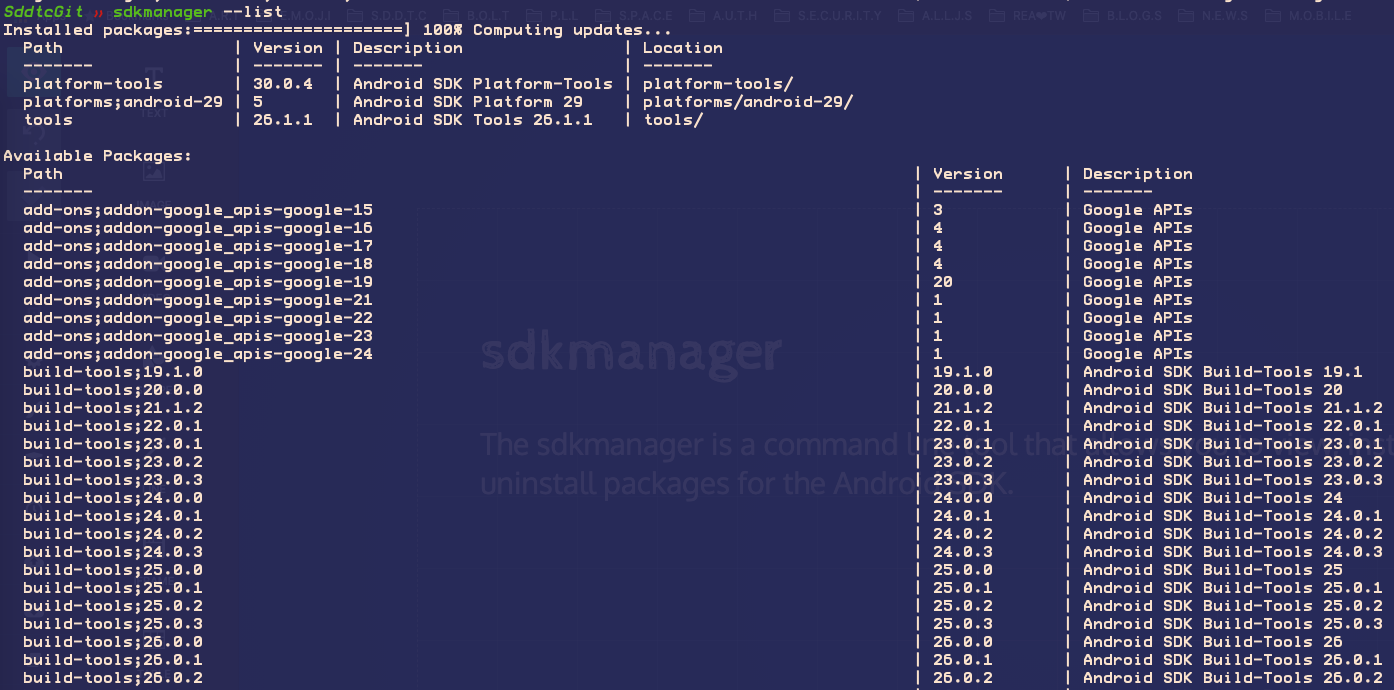
ADK manager in Idea

build tools
sdk tools
java 8 - jvm
Hello world
ceate a new project in IDEA
-
An Activity is a single, focused thing that the user can do. Every app must have at least one activity as its entry point.
-
Think of this entry-point activity as the main() function in other programs.
-
An activity typically has a layout associated with it that defines how user interface (UI) elements appear on a screen.
Open IDEA
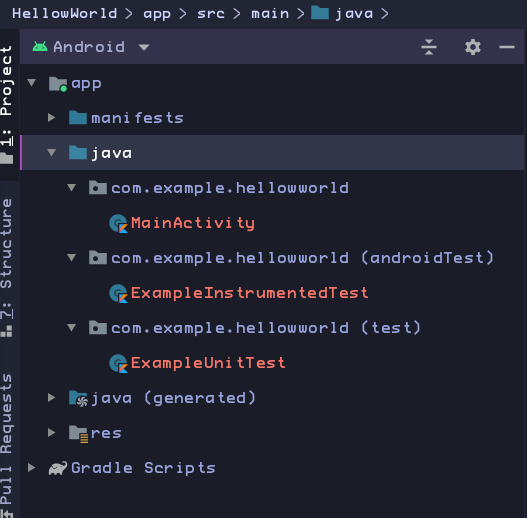
1. Explore the Project pane
Open IDEA
2. Explore the app folder
-
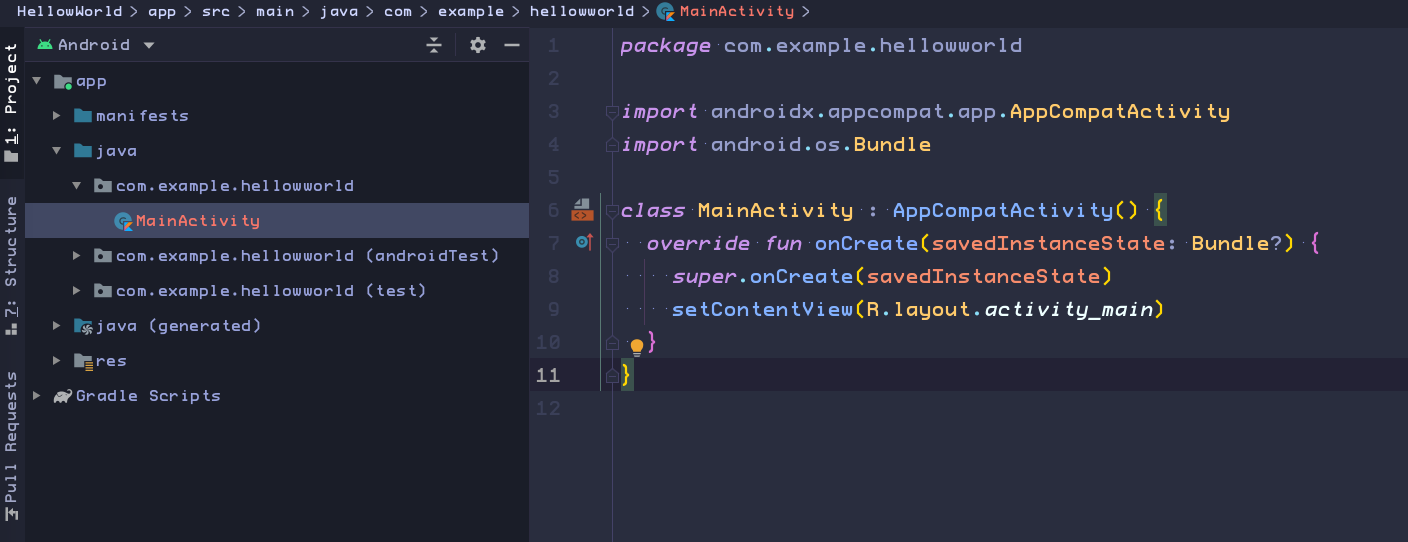
The java folder contains all the main Kotlin code for an Android app.
-
There are historical reasons why your Kotlin code appears in the java folder.
That convention allows Kotlin to interoperate seamlessly with code written in the Java programming language, even in the same project and app.
-
In particular, the MainActivity class is the main entry point for your app.
-
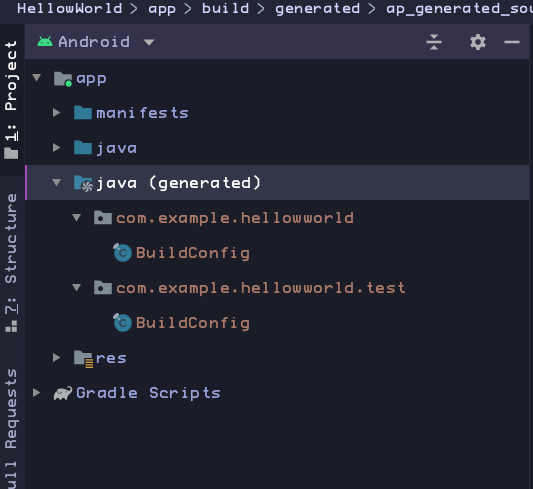
Note the Java(generated) folder.
-
Contains files that Android Studio generates when it builds the app.
-
Don't edit anything in this folder
-
It's useful to know about this folder when you need to look at these files during debugging.
Open IDEA
3. Explore the res folder
-
Resources in Android are static content used in your apps.
-
Resources include images, text strings, screen layouts, styles, and values such as hexadecimal colors or standard dimensions.
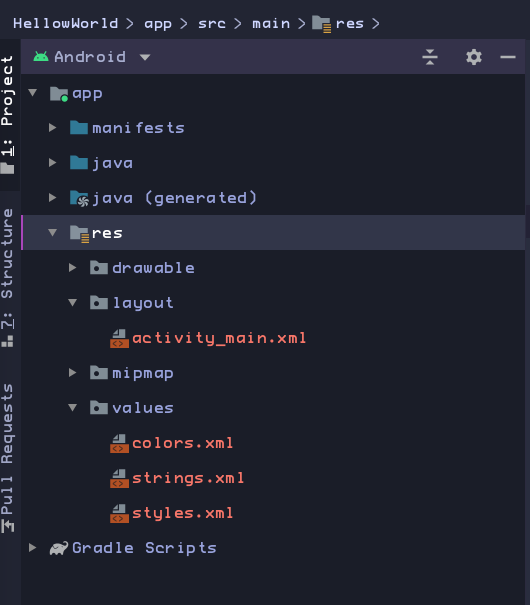
Android apps separate Kotlin code and resources as much as possible
-
That makes it much easier to find all the strings or icons that are used in the app's UI.
-
Also, when you change one of these resource files, the change takes effect everywhere that the file is used in the app.
-
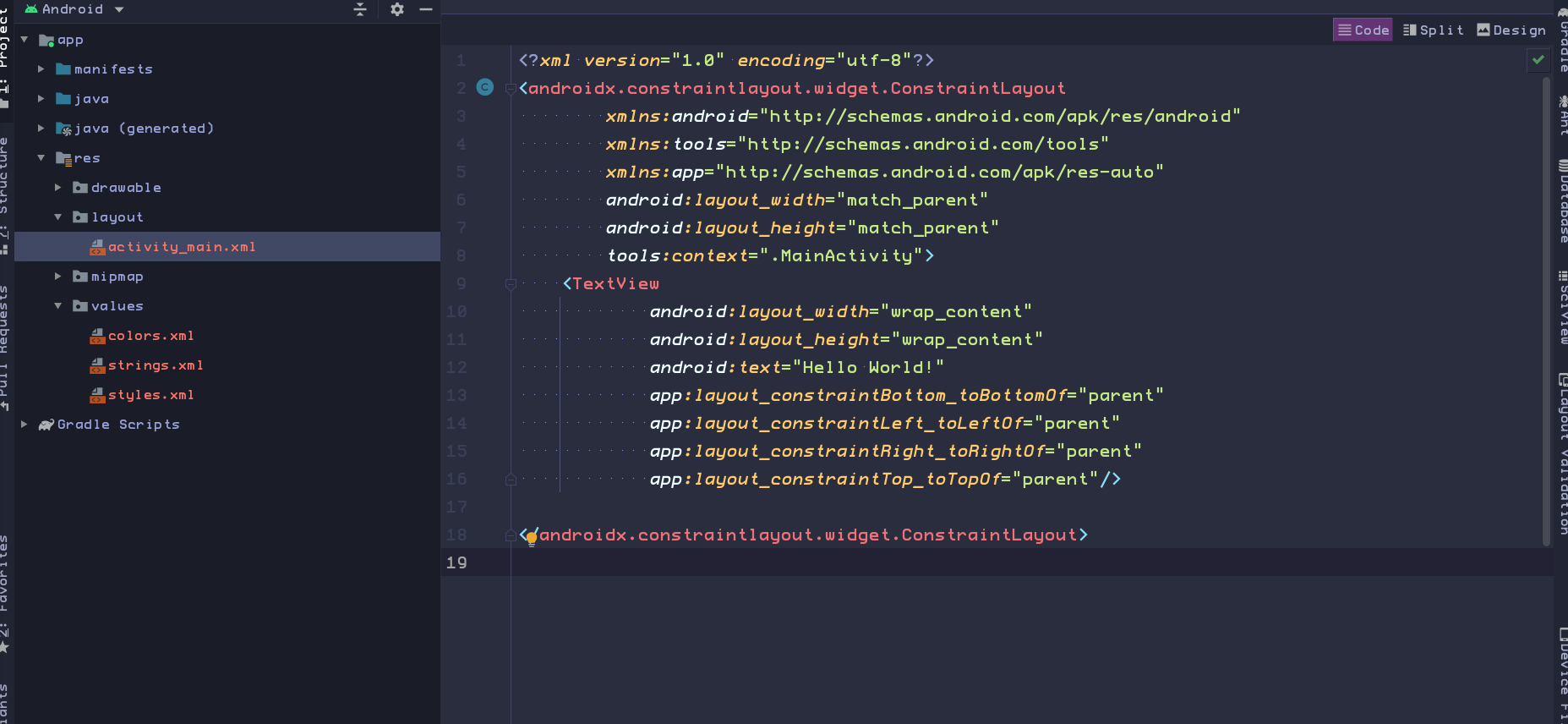
Your Activity is usually associated with a UI layout file
-
Defined as an XML file in the res/layout directory.
-
That layout file is usually named after its activity:
-
In our case, the activity name is MainActivity, so the associated layout is activity_main.
-
Open IDEA
4. Explore the manifests folder
The manifests folder contains files that provide essential information about your app to the Android system.
-
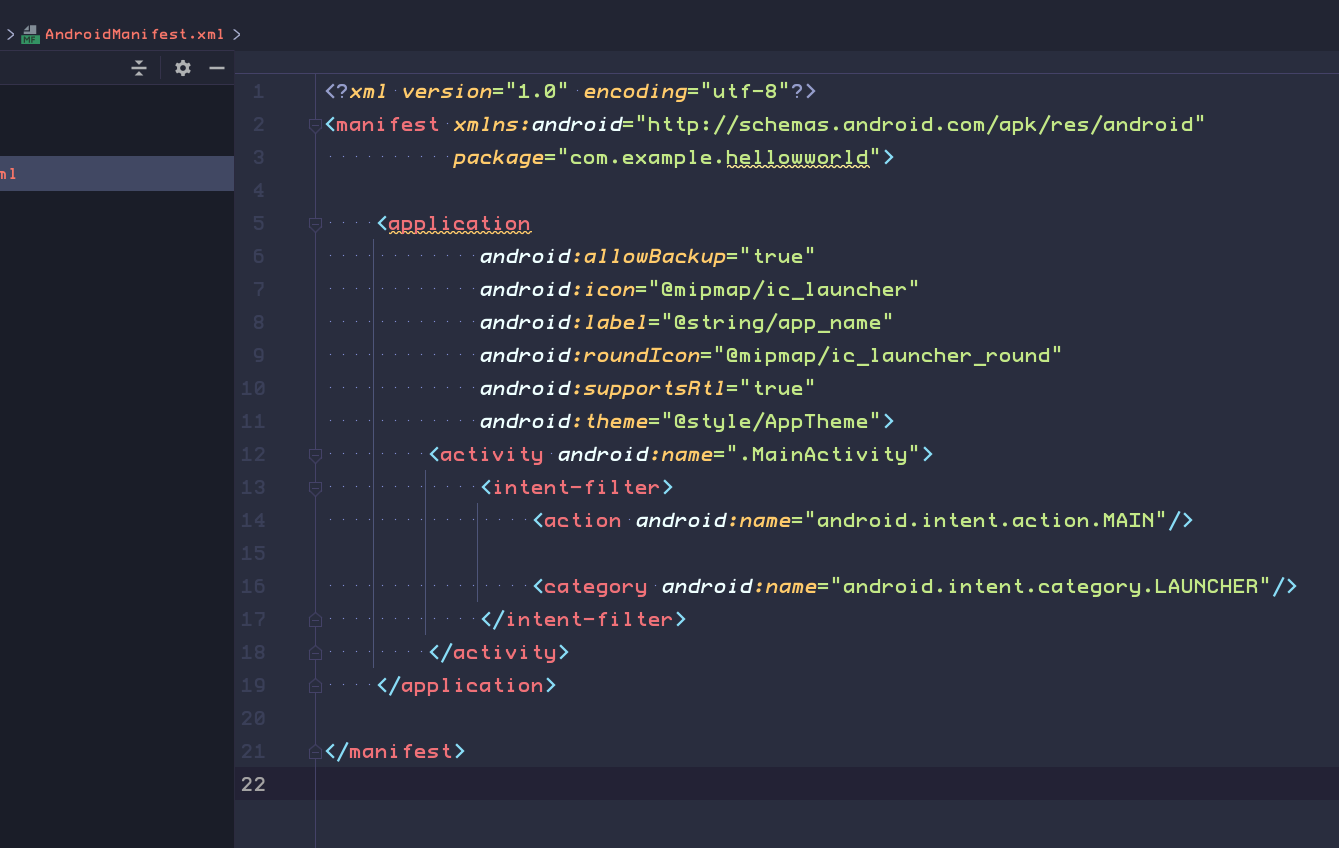
The AndroidManifest.xml file includes details that the Android system needs in order to run your app, including what activities are part of the app
-
MainActivity is referenced in the <activity> element. Any Activity in your app must be declared in the manifest.
-
The <intent-filter> element inside <activity>. The <action> and <category> elements in this intent filter tell Android where to start the app when the user clicks the launcher icon.

-
The AndroidManifest.xml file is also the place where you would define any permissions that your app needed.
-
Permissions include the ability for your app to read phone contacts, send data over the internet, or access hardware such as the device's camera.
-

Explore the manifests folder and AndroidManifest.xml
The manifests folder contains files that provide essential information about your app to the Android system.
-
Expand the manifests folder and double-click AndroidManifest.xml to open it. The AndroidManifest.xml file includes details that the Android system needs in order to run your app, including what activities are part of the app -
MainActivity is referenced in the <activity> element. Any Activity in your app must be declared in the manifest.
-
The <intent-filter> element inside <activity>. The <action> and <category> elements in this intent filter tell Android where to start the app when the user clicks the launcher icon.
-
The AndroidManifest.xml file is also the place where you would define any permissions that your app needed. Permissions include the ability for your app to read phone contacts, send data over the internet, or access hardware such as the device's camera.
Explore the manifests folder and AndroidManifest.xml
The manifests folder contains files that provide essential information about your app to the Android system.
-
Expand the manifests folder and double-click AndroidManifest.xml to open it. The AndroidManifest.xml file includes details that the Android system needs in order to run your app, including what activities are part of the app -
MainActivity is referenced in the <activity> element. Any Activity in your app must be declared in the manifest.
-
The <intent-filter> element inside <activity>. The <action> and <category> elements in this intent filter tell Android where to start the app when the user clicks the launcher icon.
-
The AndroidManifest.xml file is also the place where you would define any permissions that your app needed. Permissions include the ability for your app to read phone contacts, send data over the internet, or access hardware such as the device's camera.
Open IDEA
5. Explore the Gradle Scripts folder
-
This file contains the configuration options that are common to all the modules that
-
It's a single, top-level file. This file defines the Gradle repositories and dependencies that are common to all modules in the project.
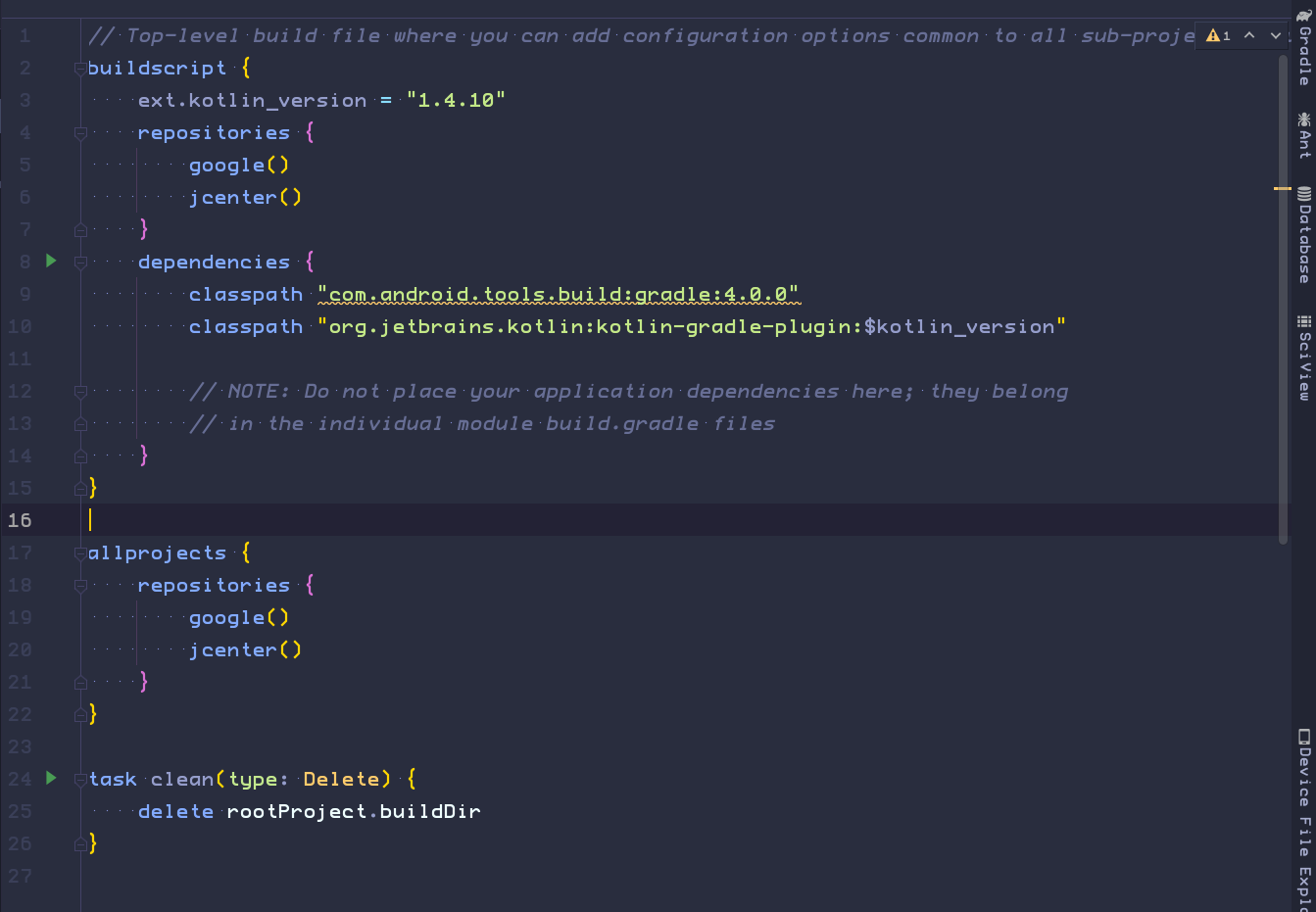
build.gradle(Project: HelloWorld) file.
-
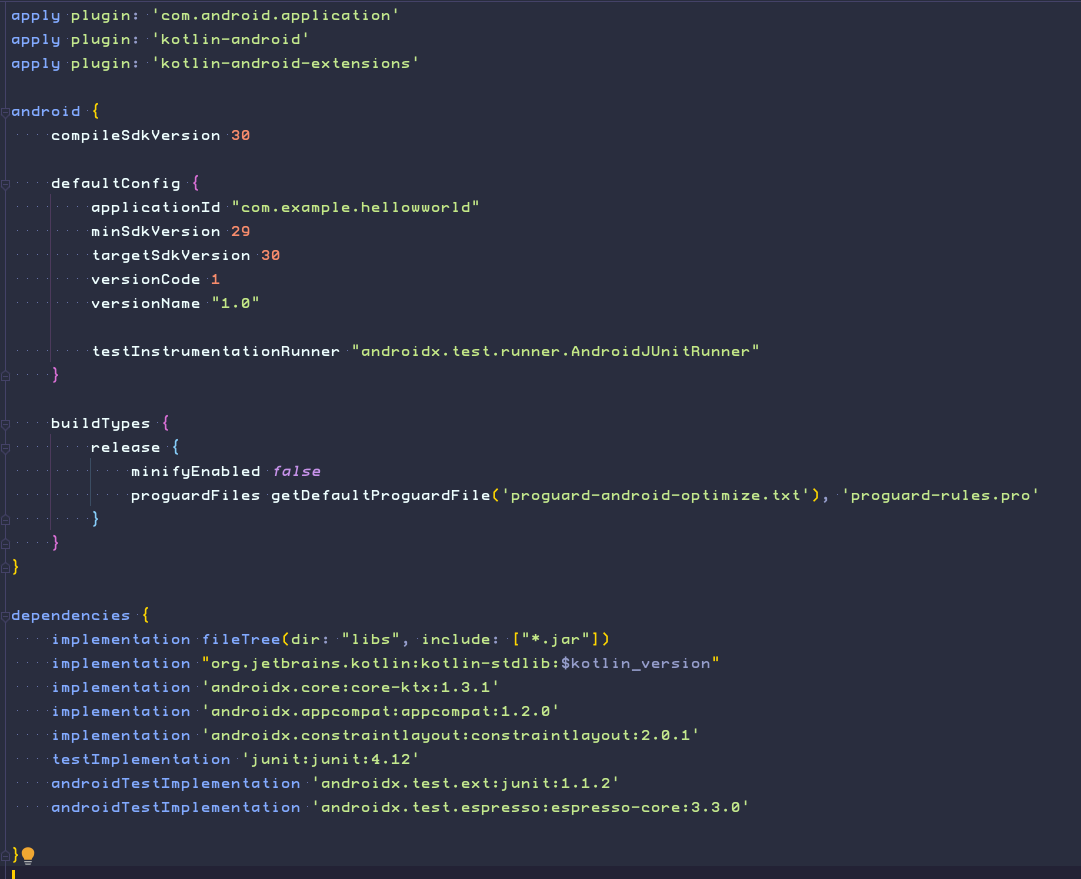
Allows you to configure build settings for each module.
-
It is the one you most often edit when changing app-level build configurations.
For example, change the SDK level that your app supports, or when you declare new dependencies in the dependencies section.
build.gradle(Module:app) file.
Run it
quize
Question1:
-
MainActivity.java -
AndroidManifest.xml -
activity_main.xml -
build.gradle
What is the name of the layout file for the main activity?
Question2:
-
app_name
-
xmlns:app
-
android:name
-
applicationId
What is the name of the string resource that specifies the app's name?
Question3:
-
Android Device Monitor
-
AVD Manager
-
SDK Manager
-
Theme Editor
Which tool do you use to create a new emulator?