PBDS
12528賴柏宇<-即將燒雞的傢伙
{Index}
{什麼是PBDS}
> 講師在看到題目之前根本沒看過這東西
> 不是STL但是是C++內建的資料結構「們」
> 其實STL都有內建類似功能//除了trie 那個我真的沒找到
>> 為什麼要用PBDS?
>> 有更多功能
>> 據說比STL更快
{使用PBDS}
#include<ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include<ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>//用tree
#include<ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>//用hash table
#include<ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>//用trie
#include<ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>//用priority_queue
using namespace __gnu_pbds;#include<bits/extc++.h>
using namespace __gnu_pbds;或者你也可以但注意用#include<bits/extc++.h>時Dev-C++和Codeblocks會跳錯(似乎是因為文件缺失?)
{使用PBDS}
如果你在這步就遇到問題(特別是Windows使用者)Step 1: 到你的MinGW安裝的地方
Step 2: 接著到\lib\gcc\mingw32\8.2.0\include\c++\ext\pb_ds\detail\resize_policy
Step 3:
將檔案“hash_standard_resize_policy_imp.hpp0000644” 重新命名為 “hash_standard_resize_policy_imp.hpp”
{Tree-平衡樹}
> 自平衡二元搜尋樹
>> 從二元搜尋樹講起
{自平衡二元搜尋樹}
> 二元樹 : 一個節點有兩個子節點
> 二元搜尋樹 : 利用二分搜在節點上搜尋的二元樹
>> 左子節點值小於節點值,右子節點值大於節點值
{自平衡二元搜尋樹}
> 最壞情況退化為偏斜樹,搜尋時間O(n)
> 平衡樹 : 自行平衡形狀的樹,如RBT(紅黑樹)
{Tree-平衡樹}
> 所以?
> 可以拿來記錄元素是否存在,還會順便sort


{Tree-平衡樹}
>簡單來講就是std的set/map但是不只紅黑樹的實作方法
>最後那個比較複雜,建議直接去看文件
>>>蛤?
>>>反正會多order_of_key(), find_by_order()等功能就對了
#include<bits/extc++.h>
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
using namespace std;
tree<int, null_type, less<int>, rb_tree_tag, tree_order_statistics_node_update> t;
/*
int:樹的key值型態
nulltype:對應的資料 不用對應就是用int
less<int>:比較函數
rb_tree_tag:樹的類型 可以用splay
tree_order_statistics_node_update:
*/{Tree-平衡樹}
>支援的操作如下 *split文件是寫O(log n) 實際似乎是O(n) 修改/優化方式
>多了join,也可以自定義節點更新
#include<ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include<ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include<iostream>
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
tree<int, null_type, std::less<int>, rb_tree_tag, tree_order_statistics_node_update> t, a;
int main(){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
t.insert(i);//插入0~9
a.insert(i+10);
}
t.erase(1);//刪除1
std::cout << t.order_of_key(2) << std::endl;//輸出2是樹中第幾小的元素(0-base) 輸出1
std::cout << *t.lower_bound(0) << std::endl;//同std::set 回傳>=1的元素的迭代器 輸出0
std::cout << *t.upper_bound(0) << std::endl;//同std::set 回傳>1的最小元素的迭代器 輸出2
t.join(a);//將a併入t, 前提是key值範圍不相交
for(auto&i:t) std::cout << i << ' '; //輸出0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
return 0;
/*
其他的小函式: get_l_child(), get_r_child()-獲取左/右節點的迭代器
node_begin()樹根的迭代器
node_end()最後的葉節點的後面一個迭代器
begin()同std::set
end()同std::set
get_metadata()-獲得結構維護的數據
自定義節點更新:
template<class Node_CItr,class Node_Itr,class Cmp_Fn,class _Alloc>
struct my_node_update{
typedef my_type metadata_type;
void operator()(Node_Itr it, Node_CItr end_it)
{
...
}
};
*/
}
{Tree-平衡樹}
介紹網站裡提到關於部分因資料類型造成優化上的差距:
"It should be noted that an std::set can only solve these types of problems with linear complexity."
「注意到這個問題在std::set裡只能用線性時間解決。」
>很嗆 不過我喜歡
{Tree-平衡樹}
>tree tag有三種
>>rb_tree_tag
>>splay_tree_tag
>>ov_tree_tag
>rb_tree_tag就是紅黑樹,原理等等講,用的時候只需要知道這鬼東西超級快而且超難刻就好
>splay_tree_tag就是splay,用途比較特殊,一樣等等講
>ov_tree_tag是ordered vector tree,通常不太會用(吧
{Tree-平衡樹}
>樹旋轉
>>剛剛提到平衡樹要改變樹的結構,但平衡樹還是不能改變資料資料順序
>>樹旋轉不改變中序遍歷(左節點->父節點->右節點)的順序
>>使用樹旋轉減低樹高
>一次最多動到五個節點
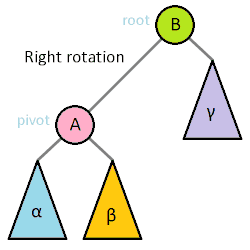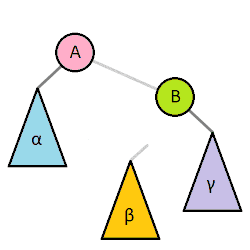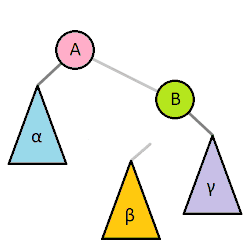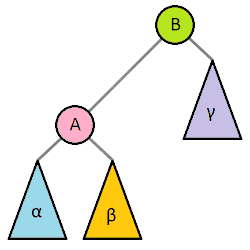
{Tree-平衡樹}
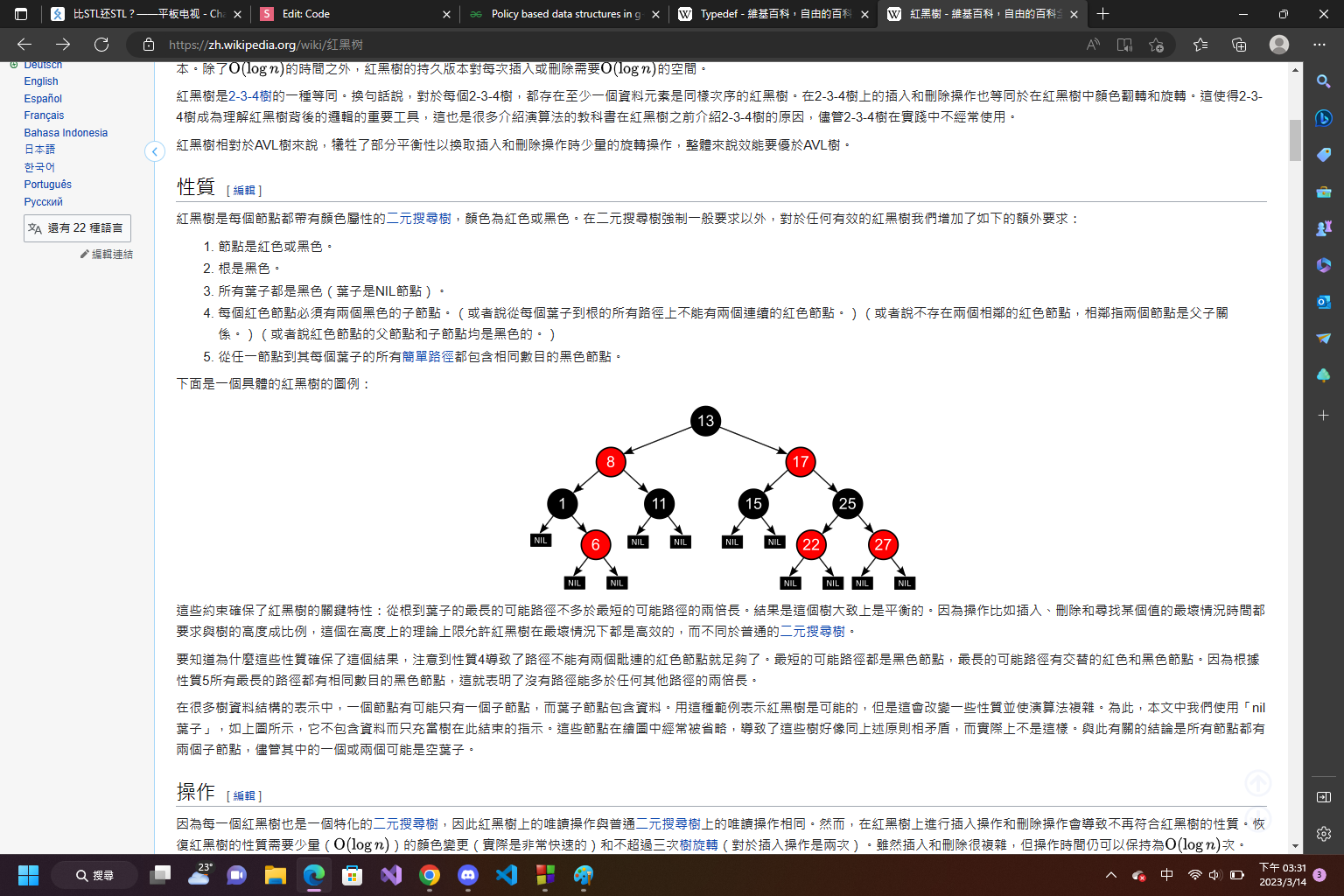
>紅黑樹:在節點裡記錄節點的紅/黑
並遵守以下規則:
1.節點只有紅色/黑色
2.葉子(NIL)和根是黑色//葉子通常不記錄資訊
3.紅節點不能有紅的子節點
4.每個從根到葉節點有相同數量的黑節點->最長分支不超過最短分支的2倍
>如果違反規則,就透過樹旋轉和改節點顏色恢復
>插入不超過2次樹旋轉,刪除不超過3次樹旋轉
{Tree-平衡樹}
>每次查詢都要O(log n)有點麻煩?
>每次查詢就把剛剛查詢的節點轉到根!
>但結構不穩定,而且還是可能退化成偏斜二元樹
{hash table}
>嗯。就是哈希表,STL的unordered_set也是同樣原理實作的,不過函數本身值域很大所以通常不會用
>支援[ ]和find()
#include<ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include<ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
using namespace std;
gp_hash_table<string, int> h;//string:key值類型, int:資料類型 gp:實現方法,有gp, cc兩種,不過gp據說通常比較快
int main(){
string key;
cin >> key;
h[key]=1;
cout << h[key];
return 0;
}{hash table}
>底層: 陣列
>>陣列可以O(1)取值!
>>如何利用?
>透過函數把key轉成陣列的索引值
>>假設我有幾個string "apple" "orange" "banana" 要對應到int
>>透過a=0, b=1.....的方式將每個字母*(27^位置)加起來除以一個數字?
>>不用想也知道會有多對一的情況發生(碰撞)
>碰撞如何解決?
{hash table}
>陣列開更大?
>>要多大?
>>好問題,我也不知道,看你的函數和資料量囉
>如果同時有兩個資料想佔同一個位置,那晚來的就去搶隔壁的位置(。∀。)
>>陣列紀錄原始資料之類的......或是經過其他處理的資料
>>搜尋時如果該格不是想找的資料就繼續往右找
>>如果搜到空格就回傳沒找到
>最壞搜尋複雜度O(n) 說到底就是雜湊函數要做好最重要
{priority queue}
>今天我想要一個資料結構,可以透過優先值大小來取值,最好還是O(1)
>支援插入、刪除等
>priority queue!
{priority queue}
>底層用堆(Heap)實現
>>堆: 完全二元樹,子節點比父節點小(最小堆 Min Heap)
>>高[log n]+1 插入和刪除都是O(log n) 取top O(1)
>插入:放到最後,如果比父節點小就交換
>刪除堆頂:將最後的元素替換到堆頂
選較小的那邊不斷向下交換
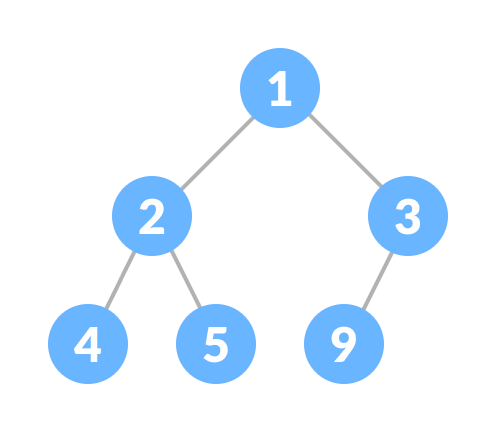
{priority queue}
#include<ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include<ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
using namespace std;
bool greater_than_ten(int v){
return v>=10;
}
int main(){
typedef __gnu_pbds::priority_queue<int, greater<int>, pairing_heap_tag> pq;//注意greater是最小堆 less是最大堆 並且最好加上__gnu_pbds::因為std裡也有priority queue
pq Q, other;
/*
int:優先權值
greater<int>:見上
pairing_heap_tag:實作方式
有
pairing_heap_tag
thin_heap_tag
binomial_heap_tag
rc_binomial_heap_tag
binary_heap_tag
這幾種
其中pairing_help_tag最快 另外根據資料binary_heap_tag似乎有bug
*/
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
Q.push(i);
other.push(i+10);
}
cout << Q.top() << endl;//0
cout << Q.size() << endl;//10
cout << Q.empty() << endl;//0
Q.pop();
cout << Q.top() << endl;//1
Q.join(other);
cout << other.empty() << endl;//1
Q.split(greater_than_ten, other);
cout << other.top() << endl;//10
auto a=Q.push(100);
Q.modify(a, -1);
cout << Q.top() << endl;//-1
/*
push() 推入元素 會返回一个迭代器
top() 堆頂 最大優先權的元素
size() 堆的大小
empty() 是否為空
clear() 清空堆
pop() 刪除堆頂
join(other) 合併兩個堆,other會被清空
split(Pred prd, priority_queue &other) 將一個堆拆分成兩個堆,其中prd(v)如果返回true則v被分到other裡,other須與Q同類型
modify(point_iterator it, const key) 修改一個節點的值
*/
return 0;
}>多了join這個函式
{priority queue}
>pairing_heap_tag 根據文件有均攤O(1)的join和push
>?????
>超級扯。而且一樣做了一堆優化,自己刻搞不好還比較慢
>不過pop的最壞時間複雜度比較差,實際實做可以自行替換tag
{Trie字典樹}
>*****STL沒實作注意*****
>利用字元當作鍵值,存在邊裡面
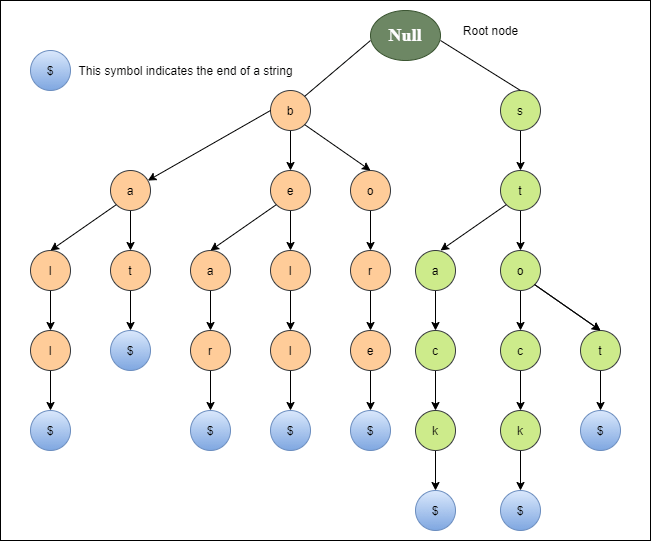
{Trie字典樹}
>一般的實作使用struct node封裝一個node*陣列和節點值
>其實很吃空間?
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int value=-2147483648;//節點資料
bool is_leaf=true;//是否為葉節點,如果要支援刪除請開int,也更吃空間
node* child[26]={nullptr};//這東西很燒空間 而且這只是支援a~z的trie
};
struct trie{
node* root=new node;
};
//其實可以實作在trie裡 但我覺得用指標對我來講比較清楚(?
void Insert(string& key, int value, node* cur, int depth){
if(depth==signed(key.size())-1){
cur->value=value;
return;
}
else if(cur->child[key[depth]-'a']==nullptr) cur->child[key[depth]-'a']=new node;
cur->is_leaf=false;
Insert(key, value, cur->child[key[depth]-'a'], depth+1);
return;
}
int Search(string& key, node* cur, int depth){
if(depth==signed(key.size()-1)) return cur->value;
if(cur->is_leaf) return -2147483647;
return Search(key, cur->child[key[depth]-'a'], depth+1);
}
int main(){
trie T;
string apple="apple", app="app";
Insert(apple, 100, T.root, 0);
cout << Search(app, T.root, 0) << endl;//-2147483648
cout << Search(apple, T.root, 0) << endl;//100
Insert(app, 48763, T.root, 0);
cout << Search(app, T.root, 0) << endl;//48763
cout << Search(apple, T.root, 0) << endl;//100
return 0;
}{Trie字典樹}
>bruh 看起來就有一大堆可以優化的地方吧
>我甚至還沒實作remove 再做下去代碼量和可以優化的量可想而知
>通常是直接背模板code......如果真的不想背就靠這個了
>不過實際上因為trie用到的地方比較少,需要的時候手刻一個也不是不行
>實際運行速度可能比手刻的慢
{Trie字典樹}
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include<ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
using namespace std;
int main(){
typedef trie<string, null_type, trie_string_access_traits<>, pat_trie_tag, trie_prefix_search_node_update> tr;
/*
string:key
null_type:對應值,用不到就用null_type
trie_string_access_traits<>:特徵,似乎可自定義,見說明https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/libstdc++/ext/pb_ds/trie_based_containers.html
pat_trie_tag:類似前面的 應該不用我多講
trie_prefix_search_node_update: 更新方式
*/
tr T;
string apple="apple", app="app";
T.insert(apple);//以apple當key插入trie
cout << *T.find(apple) << endl;//apple
T.erase(apple);//刪除apple
tr A;
A.insert(app);
T.join(A);//把A和T合併
cout << *T.find(app) << endl;//app
T.insert(apple);
pair<tr::iterator,tr::iterator> area=T.prefix_range(app);//auto是個好東西 這裡area是一個pair,提供前綴為app範圍的begin iterator和end itereator
for(tr::iterator it=area.first;it!=area.second;it++) cout<<*it<<' '<<endl;//輸出app apple
return 0;
}>嘛對trie不熟的人(像我)來說還挺有用的其實
謝謝大家
cf.網路上看到的小技巧
打競程時如果OJ不支援pbds那可以直接參(照)考(抄) pbds的源代碼ouo