PHP OOP master class




PHP OOP master class
- What is a coding paradigm and why use one?
- What is OOP and what it provides us with?
- Properties and methods and access modifiers
- The this keyword
- Typed properties
- Self and static keyword
Coding paradigms
> A coding paradigm is a way of classifying languages based on their features.
Procedural
Functional
OOP
Reactive
Parallel
Object-oriented programming (OOP)
> OOP is a paradigm that gathers related state (data) and their modifiers to be exposed as a whole entity
<?php
$user = [
'username' => 'ahmedosama-st',
'first_name' => 'ahmed',
'last_name' => 'osama',
'email' => 'ahmedosama@sectheater.io',
'updateUsername' => function ($newUsername) use (&$user) {
$user['username'] = $newUsername;
return $user;
},
'posts' => []
];
$user['updateUsername']('khaled');
var_dump($user);
Props and methods
> Props represent the members of the class which later are referred to as the state of each class instance (object).
> Methods represent the modifiers of the state, they're (usually) unified for all class instances (objects).
<?php
$user = [
'username' => 'ahmedosama-st',
'updateUsername' => function ($newUsername) use (&$user) {
$user['username'] = $newUsername;
return $user;
},
];
$user['updateUsername']('khaled');
var_dump($user);
$this pseudo variable
> The "this" keyword refers to the context of the class it's bound to
> $this can be thought of as passing a self-reference to where the function is defined to the function itself
<?php
$user = [
'username' => 'ahmedosama-st',
'updateUsername' => function ($newUsername) use (&$user) {
$user['username'] = $newUsername;
return $user;
},
];
$user['updateUsername']('khaled');
var_dump($user);
class User
{
public function whoami()
{
return $this;
}
}
$u = new User();
var_dump($u->whoami());> $this can be thought of as passing a self-reference to where the function is defined to the function itself
Note: Do not think of $this as a self-reference to the class!!
It's only a contextual bound
Self and static keyword
> The "self" keyword refers to the class itself
Unlike "this", this one is actually a self-reference yup.
> The "static" keyword can be used to define CLASS level members
PHP OOP master class
- OOP 4 pillars
- Inheritance
- Parent keyword
- Overriding
- Final keyword
- Abstraction
- Interfaces and abstract classes
- Polymorphism
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
Inheritance
> The mechanism of deriving a class from another class that share a set of attributes and methods (Sharing functionality)
Model
Post
Comment
Overriding
> Mutating the behaviour of the parent's class method to add/change its implementation
<?php
class Parser
{
public function parse(string $data)
{
return (array) $data;
}
}
class JSONParser extends Parser
{
public function parse(string $data)
{
return json_encode(parent::parse($data));
}
}Abstraction
> Only publish what others absolutely need to know.
Process
abstraction
Data
abstraction
> More abstraction means less coupling
Higher level of abstraction types
Functional
Programmatic
Logic
Quality of service
Technology
Polymorphism
> The mechanism by which a class or one of its members may be displayed in many forms.
<?php
interface DatabaseManager {}
interface SQLDatabaseManager extends DatabaseManager {}
interface NonSQLDatabaseManager extends DatabaseManager {}
class MySQLManager implements SQLDatabaseManager {}
class PostgreSQLManager implements SQLDatabaseManager {}
class SQLiteManager implements SQLDatabaseManager {}
class MongodbManager implements NonSQLDatabaseManager {}
Encapsulation
> The mechanism of bundling data and their modifiers in a single entity (unit)
<?php
class Validator
{
protected array $rules = [];
protected array $aliases = [];
public function setRules(array $rules)
{
$this->rules = $rules;
}
public function setAliases(array $aliases)
{
$this->aliases = $aliases;
}
}
PHP OOP master class
- Object creation
- Constructor
- Destructor
- Dependency Injection
- Property overloading
- __set
- __get
- Method overloading
- __call
- __callStatic
PHP OOP master class
- Object serialization
- __serialize, __unserialize
- __sleep, __wakeup
- Object cloning
- __clone
- Object transformations
- __toString
- __invoke
PHP OOP master class
Object creation
> Constructor is used for building your objects and loading dependency which helps you to compose your object of other objects.
> Destructor is used for deleting any hanging references from your object and cannot be reached by the GC to prevent any possible memory leaks
PHP OOP master class
Dependency injection
> Dependency injection is technically when one of your classes uses another class as a property of its own i.e. DI is the technique by which you can compose objects.
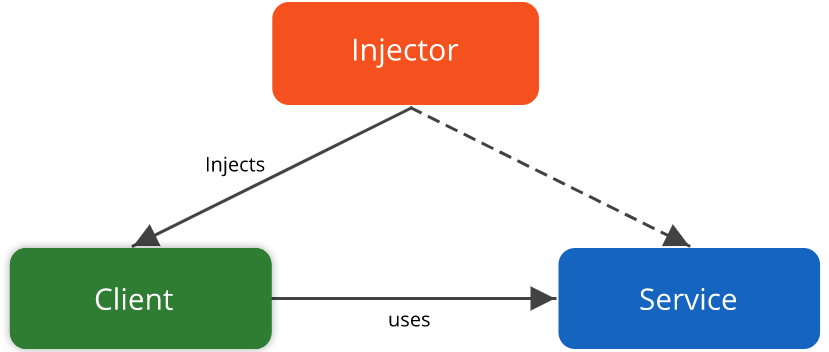
Credits to company.ona
PHP OOP master class
Dependency injection
class Database // Dependency for your models
{
public function query(string $query)
{
/*
$instance is meant to be your database manager
i.e. the PDO instance that talks to the database
driver you are working with.
*/
$this->instance->execute($query);
}
}
class User
{
protected Database $db;
public function __construct(Database $db)
{
$this->db = $db;
}
public function register()
{
// Some validation logic
$this->db->create(/* Validated credentails */);
}
}
Dependency
Client
Uses through an injector
PHP OOP master class
Property/method overloading
> Property overloading is dynamically using "creating/accessing" variables and methods in case they do not exist (not defined within the class) or they're not accessible (have protected/private modifier)
class Collection
{
protected array $items = [];
public function __construct(array $items = [])
{
$this->items = $items;
}
public function __set($key, $value)
{
if (!$this->__isset($this->$key)) {
$this->items[$key] = $value;
}
}
}
$c = new Collection();
$c->first_name = 'Ahmed';
var_dump($c);
class Collection
{
// ...
public function __isset($key)
{
return array_key_exists($key, $this->items);
}
public function __get($key)
{
return ($this->__isset($key)) ? $this->items[$key] : null;
}
public function __unset($key)
{
if ($this->__isset($key)) {
unset($this->items[$key]);
}
}
}
class Collection
{
// ...
public function __call($name, $args)
{
if (method_exists($this, $name)) {
$this->$name(...$args);
// call_user_func_array([$this, $name], $args);
}
}
}PHP OOP master class
Object transformation
> Serialization is simply transforming your objects into a storable representation into files or your database and preserving the state of your object so that you can unserialize it without losing your properties.
PHP OOP master class
Serialization
> Serializing your objects can be used for persisting them against your database or a log file, therefore it can be used for persisting your sessions into your database or queuing jobs.
PHP OOP master class
Object cloning
> Objects in PHP are thought to be passed by reference which is not true according to the PHP documentation
> Instead, they're passed by their identifier which varies between objects, therefore it may look like you're making a reference to the variable.
You can read more about objects and references here
<?php
class User
{
public $name;
}
$u1 = new User;
$u2 = new User;
var_dump(spl_object_id($u1) === spl_object_id($u2)); // falsePHP OOP master class
Object cloning
> You can create a copy of an object using the clone keyword in PHP which creates a shallow copy rather than a deep copy
Deep copying is when your object's dependencies are copied
Deep copy
Shallow copy
Shallow copying is when your object is copied one level deep only
I recommend you read this article
PHP OOP master class
- Object binding
- Compile-time binding
- Runtime-time binding
- SPL classes
- Iterator
- ArrayAccess
- IteratorAggregate
- Errors and exceptions
- Generators