

Sefa Said Deniz
Frontend Engineer @ FrontValue

Frontend development
What is frontend?
Frontend refers to a website or application that the user interacts with. This can include elements such as buttons, menus, forms, and many more.
Frontend development involves languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create the visual and interactive elements of a website or application.



HTML
CSS
JavaScript
So what is backend?
The backend refers to the part of a website or application that runs behind the scenes and is not visible to the user. This includes the server, database, and application logic that handles tasks such as processing user input, storing data, and retrieving data. Also backend development can be done in Javascript these days

JavaScript


PHP
Java
HTML

What is HTML?
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the standard language used for creating web pages. It is used to structure content and define the layout and appearance of a web page. HTML uses tags to define elements such as headings, paragraphs, links, and images.
To display the world's most famous "Hello World" on webpage using HTML, you can use the following code:
Basic markup
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
</body>
</html>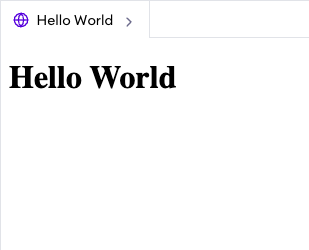
<DOCTYPE html>: It's information to the browser about what document to expect.
Break it down
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
</body>
</html>Note*: In older documents (HTML 4 or XHTML), the declaration is more complicated because it must refer to a DTD (Document Type Definition).
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html>: The HTML tag represents the root of a document and is the container for all other HTML elements
Break it down
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
</body>
</html><head>: The head tag is a container for metadata (data about data) and is placed between the<html>tag and the<body>tag.
It's content is not displayed
Break it down
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
</body>
</html><body>: The body tag contains all the contents of the HTML document.
Break it down
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
</body>
</html>Note*: There can be only one <body> element in an HTML document
HTML - Elements

What are Elements?
HTML Elements are defined by tags. It begins with a start tag, some content in between, and an end tag. This content can be anything from regular text to other elements.
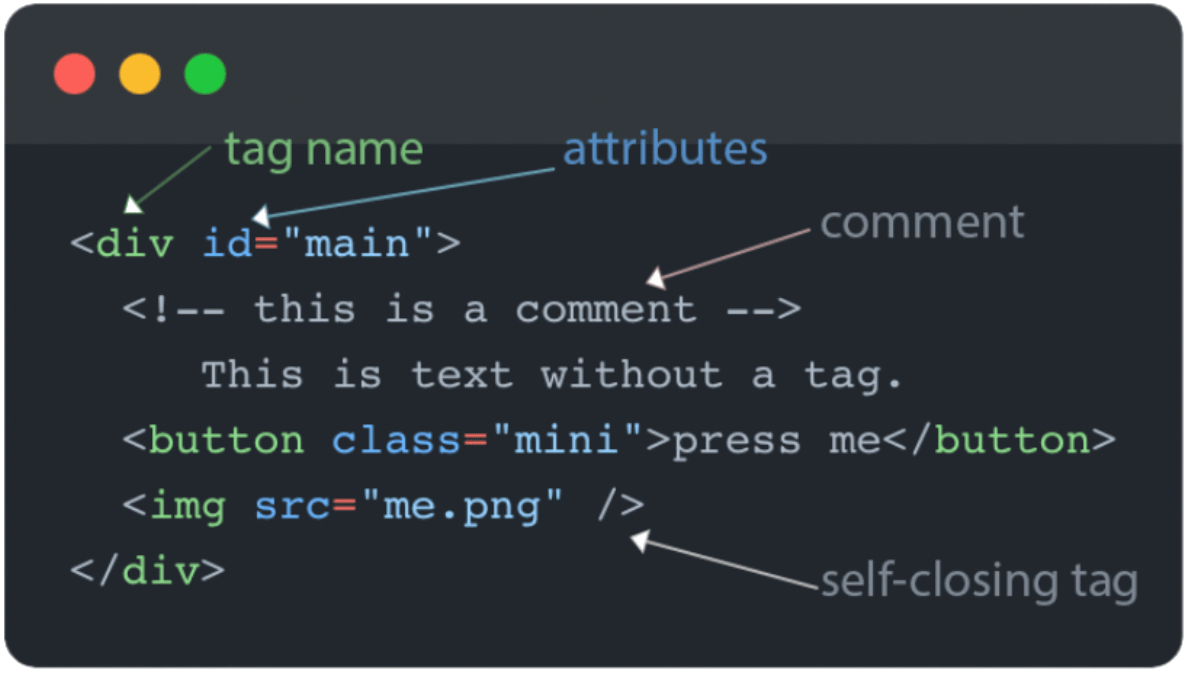
HTML Elements
Paragraph
<p>: represents a paragraph. Paragraphs are usually represented in visual media as blocks of text separated from adjacent blocks by blank lines
<p>
Some paragraph
</p>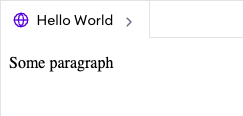
HTML Elements
Headings
<h1-6>: h elements represent six levels of section headings.
<h1>is the highest section level and<h6>is the lowest.
<h1>This is a headline.</h1>
<h2>This is a headline.</h2>
<h3>This is a headline.</h3>
<h4>This is a headline.</h4>
<h5>This is a headline.</h5>
<h6>This is a headline.</h6>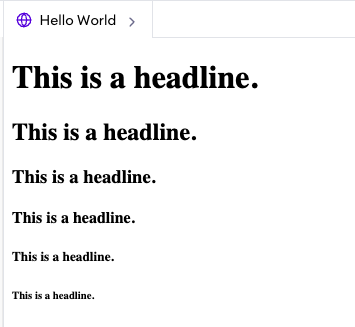
HTML Elements
Span
<span>: the span element is a generic inline container for phrasing content, which does not inherently represent anything. It can be used to group elements for styling purposes.
<p>This is a <span>span</span> element.</p>
HTML Elements
Div
<div>: a special element that lets you group similar sets of content together on a web page. You can use it as a generic container for associating similar content.
<div>
<p>This is some text.</p>
<p>This is some more text.</p>
</div>
HTML Elements
Image
<img>: The image tag is used to embed an image in an HTML page, using the src attribute to specify the URL of the image
<img src="image.jpg" />
HTML Elements
Button
<button>: The button tag is used to define a clickable button element. It's able to submit / reset forms or behave as button and mostly Javascript will handle the click.
<button type="button">Click Me!</button>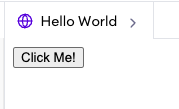
HTML Elements
Ordered List
<ol>: The
<ol>tag defines an ordered list. An ordered list can be numerical or alphabetical. It always is used together with the <li> tag to create ordered lists.
<ol>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Milk</li>
<li>Tea</li>
</ol>
HTML Elements
Unordered List
<ul>: The
<ul>tag defines an unordered (bulleted) list. It always is used together with the <li> tag to create unordered lists.
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>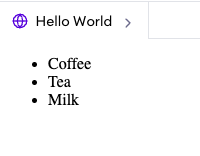
HTML Elements
The anchor tag
<a>:The tag defines a hyperlink, which is used to link from one page to another.
<a href="google.com">Google</a>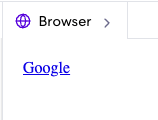
Many more
HTML Elements
Assignment
Assignment 1
HTML Elements
HTML - Styling


What is CSS?
CSS is the acronym of “Cascading Style Sheets”. CSS is a computer language for laying out and structuring web pages (HTML or XML).

What is inline styling?
Inline CSS is used to apply a unique style to a single HTML element. The
styleproperty contains specific style information for this element.
HTML Inline styling
<p style="color: red;">
This text is red.
</p>
<p style="font-family: Arial; font-size: 20px; font-weight: bold;">
This text is bold and in Arial font with 20px size.
</p>
<p style="background-color: yellow;">
This text has a yellow background.
</p>HTML Internal styling
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: blue;
}
h1 {
color: red;
padding: 60px;
}
</style>
</head>Css selecting
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<style>
h1 {
color: red;
padding: 60px;
}
.title {
color: red;
padding: 60px;
}
#header {
color: red;
padding: 60px;
}
</style>
</head><body>
<h1>
Title
</h1>
<h2 class="title">
Css class selection
</h2>
<h3 id="header">
Css id selection
</h3>
</body>Css Basic styling
color: red;width:50px;
height:50px;background-color: green;/* width, type, color */
border: 1px solid red;



Assignment
Assignment 2
HTML - Tables


What are Tables?
A table in HTML consists of table cells inside rows and columns.
Table Elements
<table>:element represents tabular data—that is, information presented in a two-dimensional table comprised of rows and columns of cells containing data.
<table>
</table>Table Elements
<tr>:HTML element defines a row of cells in a table
<table>
<tr>
<!-- row content -->
</tr>
<tr>
<!-- row content -->
</tr>
</table>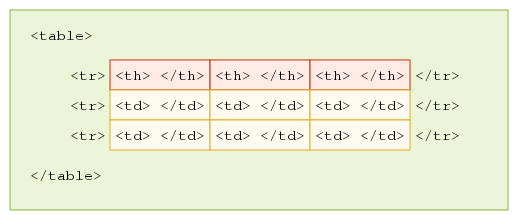
Table Elements
<th>:tag stands for table heading. It is used to define a single data cell in the HTML table.
<table>
<tr>
<th>
Table Header
</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<!-- row content -->
</tr>
</table>
Table Elements
<td>:stands for table data.
<table>
<tr>
<th>
Table Header
</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Table Data
</td>
</tr>
</table>
Assignment
Assignment 3