java.util.concurrent

new Thread();
~ JDK 1.4
java.util.concurrent
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello Thread!");
}
}).start();
}Thread 관리
ServerSocket socket = new ServerSocket(80);
while (true) {
final Socket connection = socket.accept();
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
handleRequest(connection);
}
};
new Thread(runnable).start();
}무한 Thread ??
private static int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
++count;
System.out.println("count: " + count);
}
}).start();
}
}
count = ???경쟁 조건 (race condition)
private final Object left = new Object();
private final Object right = new Object();
private void leftRight() {
synchronized (left) {
synchronized (right) {
System.out.println("leftRight");
}
}
}
private void rightLeft() {
synchronized (right) {
synchronized (left) {
System.out.println("rightLeft");
}
}
}Deadlock!
volatile , synchronized, run(), stop(), interrupt(), yield(), sleep(), join(), wait(), notify(), notifyAll() .....

java.util.concurrent
JDK 1.5 ~
java.util.concurrent
java.util.concurrent
package java.util.concurrent;
...
/**
* Factory and utility methods for {@link Executor}, {@link
* ExecutorService}, {@link ScheduledExecutorService}, {@link
* ThreadFactory}, and {@link Callable} classes defined in this
* package. This class supports the following kinds of methods:
*
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
*/
public class Executors { .. }
java.util.concurrent
Executor Framework
JDK 1.5
Producer - Consumer
Pattern
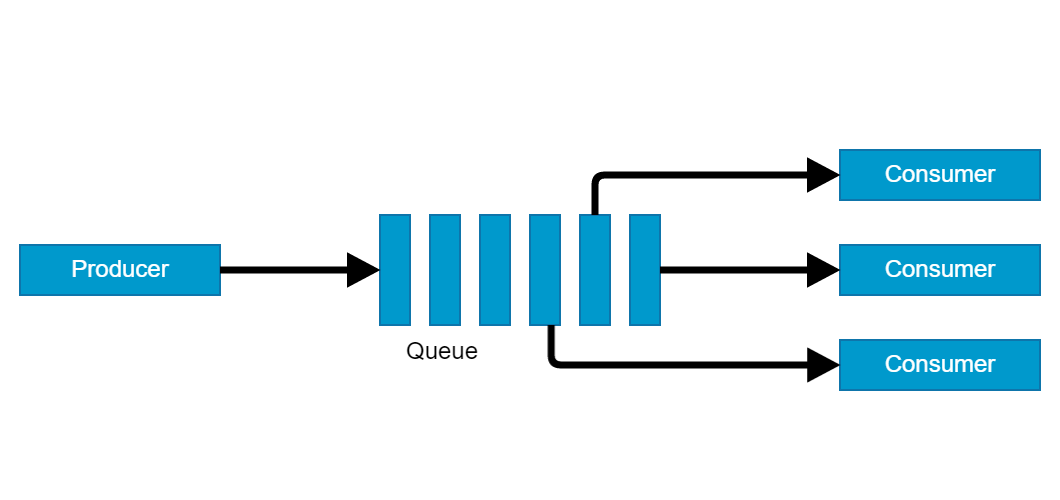
Executor
public interface Executor {
/**
* Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command
* may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, or in the calling
* thread, at the discretion of the {@code Executor} implementation.
*
* @param command the runnable task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if this task cannot be
* accepted for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if command is null
*/
void execute(Runnable command);
}ExecutorService <1>
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
// 작업을 종료합니다.
// 이미 주어진 작업은 실행하지만 새로운 작업은 받지 않습니다.
void shutdown();
// shutdown 되었는지 확인합니다.
boolean isShutdown();
// shutdown 이후 모든 작업이 완료되었는지 확인합니다.
boolean isTerminated();
// 현재 실행중인 작업을 중단하고 남은 작업을 반환합니다.
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
// shutdown()을 실행하고, 지정된 시간만큼 모든 작업이 종료될때까지 대기합니다.
// 지정된 시간내에 모든 작업이 완료되면 true를 반환합니다.
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
...
}ExecutorService <2>
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
// 주어진 작업을 추가합니다.
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
// 주어진 작업을 추가하고 정상적으로 완료되면 result를 반환합니다.
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
// 주어진 작업을 추가하고 결과를 반환합니다.
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
// 주어진 작업을 실행하고 결과를 반환합니다.
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks);
// 주어진 작업을 실행하고 정상적으로 실행된 결과를 반환합니다.
// 가장 먼저 정상적으로 완료된 결과를 반환하고 나머지는 무시합니다.
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks);
...
}Callable
public interface Callable<V> {
/**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}Future
public interface Future<V> {
// 작업을 취소합니다.
// 작업이 이미 실행 중인 경우 mayInterruptIfRunning가 true인 경우 취소합니다.
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
// 작업이 완료되기 전에 취소된 경우 true를 반환합니다.
boolean isCancelled();
// 작업이 정상적으로 완료된 경우 true를 반환합니다.
boolean isDone();
// 작업이 완료될 때까지 대기하고, 완료되면 결과를 반환합니다.
V get();
// 주어진 시간만큼 대기하고 그 시간 내에 완료되면 결과를 반환합니다.
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
}Executors
public class Executors {
// 지정한 개수만큼 스레드를 가질수 있는 스레드 풀을 생성합니다.
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads);
// 하나의 스레드만 사용하는 스레드 풀을 생성합니다.
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 필요한 만큼의 스레드를 생성하여 사용하는 스레드 풀을 생성합니다.
// 작업보다 스레드가 적으면 더 생성하고, 작업보다 많으면 종료합니다.
// 스레드 생성에 제한을 두지 않습니다.
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool();
...
}Fork/Join Framework
JDK 1.7
Fork/Join
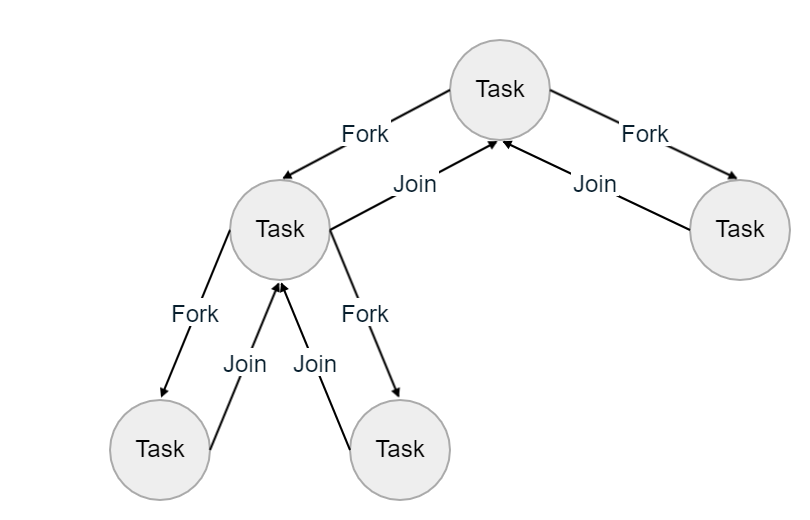
ForkJoinTask <1>
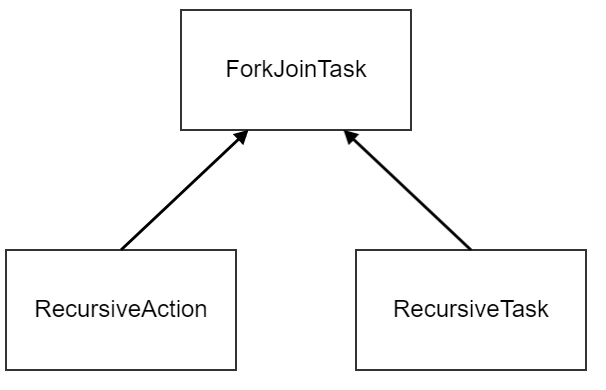
public abstract class RecursiveTask<V> extends ForkJoinTask<V> {
V result;
protected abstract V compute();
public final V getRawResult();
protected final void setRawResult();
protected final boolean exec();
}
public abstract class RecursiveAction extends ForkJoinTask<Void> {
protected abstract void compute();
public final Void getRawResult();
protected final void setRawResult();
protected final boolean exec();
}ForkJoinTask <2>
compute(task) {
if (task.size < threshold) {
return doWork(task)
} else {
fork {
leftResult = compute(left(task))
rightResult = = compute(right(task))
}
return join(leftResult, rightResult)
}
}ForkJoinPool
/**
* An {@link ExecutorService} for running {@link ForkJoinTask}s.
* A {@code ForkJoinPool} provides the entry point for submissions
* from non-{@code ForkJoinTask} clients, as well as management and
* monitoring operations.
*
* @since 1.7
* @author Doug Lea
*/
@sun.misc.Contended
public class ForkJoinPool extends AbstractExecutorService {
...
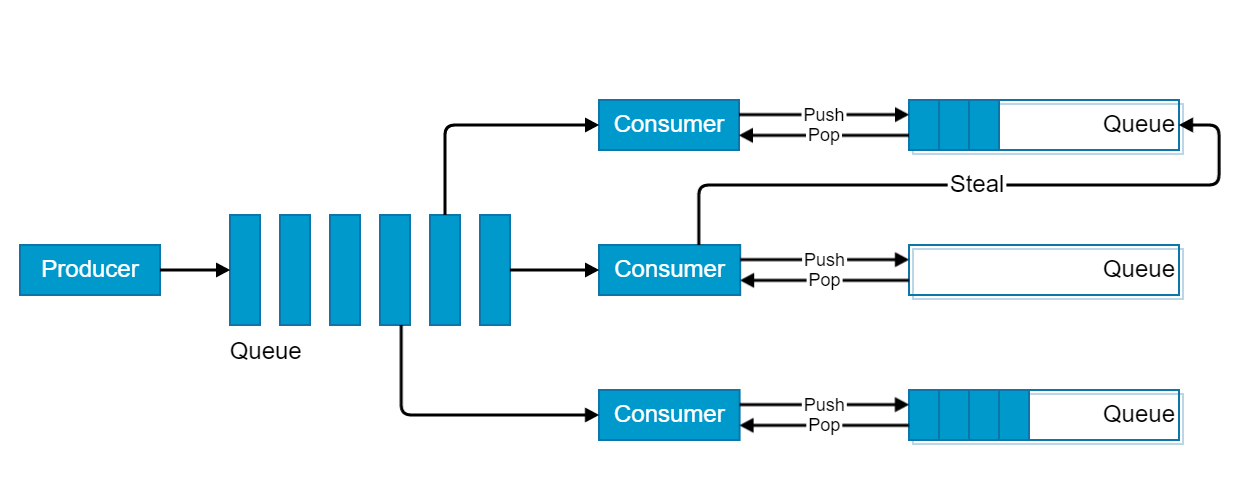
}Work-stealing <1>
Work-stealing <2>
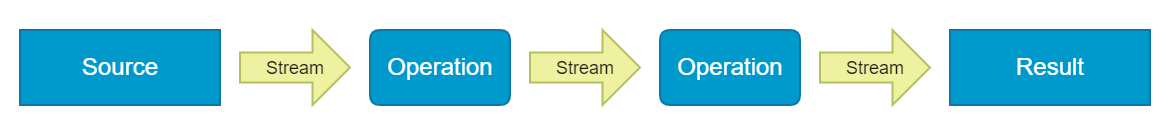
Parallel Streams
JDK 1.8
Stream
Parallel() <1>
long reduce = LongStream
.range(0, 1000000000)
.parallel()
.reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y);
실행 시간: 565ms
실행 시간: 205ms <= parallelParallel() <2>
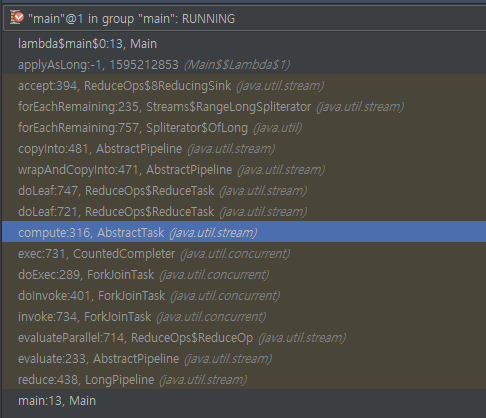
Parallel() <3>
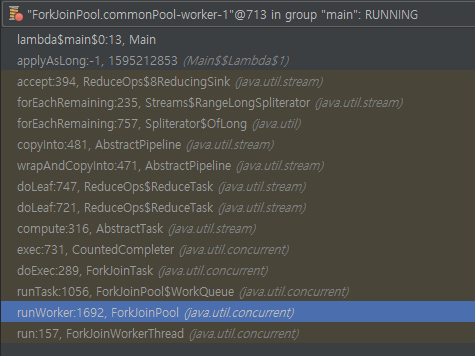
commonPool <1>
public static ForkJoinPool commonPool()
Returns the common pool instance.
This pool is statically constructed; its run state is unaffected by attempts to shutdown() or shutdownNow().
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
commonPool <2>
System.setProperty(
"java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism", 16);commonPool <3>
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(16);
long reduce = pool.submit(() ->
LongStream.range(0, 10000000)
.parallel()
.reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y)).get();병렬 처리시 주의할 점
-
대부분 작업은 병렬 처리가 필요없다.
-
반드시 실행해서 속도를 확인해야 한다.
-
Fork/Join Framework가 무조건 빠른건 아니다.
-
불필요한 Boxing / Unboxing은 없애자.
-
전체 길이를 알수 없는 자료구조(LinkedList)는 fork 하기 어렵다.
-
상태 공유는 알 수 없는 버그(Heisenbug)의 온상.
