SQL Graph in SQL Server 2017
Stéphane Fréchette
Cloud Solution Architect - Data Platform @ Microsoft
twitter: @sfrechette | blog: stephanefrechette.com


(Graphs-(Are)->Everywhere)
SQL Graph
Graph Processing with SQL Server 2017
SQL Server offers graph database capabilities to model many-to-many relationships. The graph relationships are integrated into Transact-SQL and receive the benefits of using SQL Server as the foundational database management system.
SQL Graph
What is a graph database?
A graph database is a collection of nodes (or vertices) and edges (or relationships). A node represents an entity (for example, a person or an organization) and an edge represents a relationship between the two nodes that it connects (for example, likes or friends). Both nodes and edges may have properties associated with them.
SQL Graph

Property Graph
The property graph model is an extension of the graphs from mathematics. Property graphs provide finer-granularity on the meaning of nodes and edges (it’s the equivalent of an ERD – Entity Relationship Diagram but for Graphs)
SQL Graph
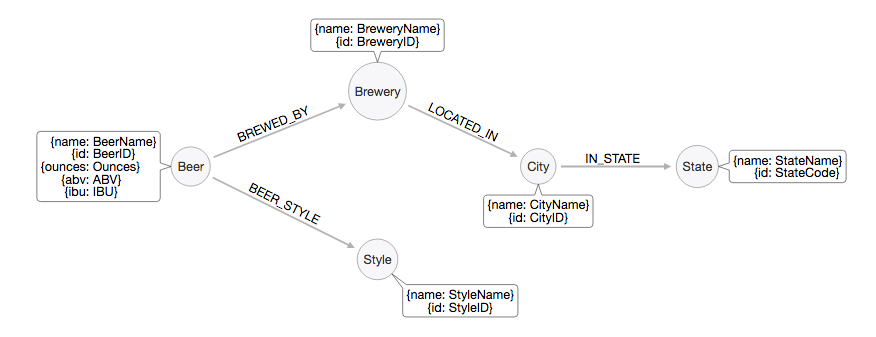
When to use a graph database?
- Your application has hierarchical data. The HierarchyID datatype can be used to implement hierarchies, but it has some limitations. For example, it does not allow you to store multiple parents for a node
- Your application has complex many-to-many relationships; as application evolves, new relationships are added
- You need to analyze interconnected data and relationships
SQL Graph
SQL Graph Database
- Can create one graph per database
- Node or edge tables can be created under any schema in the database, but they all belong to one logical graph
- Most of the operations supported on regular tables are supported on node or edge tables
SQL Graph

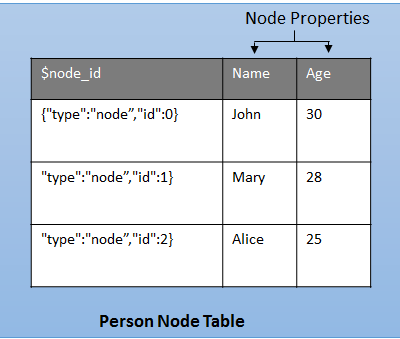
Node Table
A node table represents an entity in a graph schema. Every time a node table is created, along with the user defined columns, an implicit $node_id column is created, which uniquely identifies a given node in the database
SQL Graph
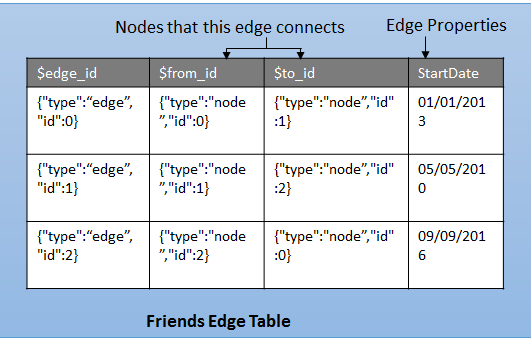
Edge Table
An edge table represents a relationship in a graph. Edges are always directed and connect two nodes. An edge table enables users to model many-to-many relationships in the graph. Every time an edge table is created, along with the user defined attributes, three implicit columns are created in the edge table: $edge_id, $from_id, and $to_id
SQL Graph
CREATE TABLE (SQL Graph)
SQL Graph
--Create a NODE table
CREATE TABLE Person (
ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
email VARCHAR(100)
) AS NODE;
--Create an EDGE table
CREATE TABLE friends (
id integer PRIMARY KEY,
start_date date
) AS EDGE;MATCH (SQL Graph)
Text
SQL Graph
-- Find a friend
SELECT Person2.name AS FriendName
FROM Person Person1, friend, Person Person2
WHERE MATCH(Person1-(friend)->Person2);
-- The pattern can also be expressed as below
SELECT Person2.name AS FriendName
FROM Person Person1, friend, Person Person2
WHERE MATCH(Person2<-(friend)-Person1);
-- Find 2 people who are both friends with same person
SELECT Person1.name AS Friend1, Person2.name AS Friend2
FROM Person Person1, friend friend1, Person Person2,
friend friend2, Person Person0
WHERE MATCH(Person1-(friend1)->Person0<-(friend2)-Person2);
-- this pattern can also be expressed as below
SELECT Person1.name AS Friend1, Person2.name AS Friend2
FROM Person Person1, friend friend1, Person Person2,
friend friend2, Person Person0
WHERE MATCH(Person1-(friend1)->Person0 AND Person2-(friend2)->Person0);Demo
SQL Graph
Limitations and know issues
There are certain limitations on node and edge tables in this release:
- Local or global temporary tables cannot be node or edge tables.
- Table types and table variables cannot be declared as a node or edge table.
- Node and edge tables cannot be created as system-versioned temporal tables.
- Node and edge tables cannot be memory optimized tables.
- Users cannot update the $from_id and $to_id columns of an edge using UPDATE statement. To update the nodes that an edge connects, users will have to insert the new edge pointing to new nodes and delete the previous one.
- Cross database queries on graph objects are not supported.
SQL Graph
Summary
Graph extensions are fully integrated in SQL Server engine. We use the same storage engine, metadata, query processor, etc. to store and query graph data. This enables users to query across their graph and relational data in a single query. Users can also benefit from combining graph capabilities with other SQL Server technologies like columnstore, HA, R services, etc. SQL graph database also supports all the security and compliance features available with SQL Server.
SQL Graph
Resources
SQL Graph