React Reconciliation
- Overview of React Fiber
- React Reconciliation
- Elements of same type
- Elements of different type
- Iteration on Children
React Fiber Overview
Async
Prioritization
Reusability
React Reconciliation
It's the diffing that decides what to update in the DOM.
React uses Graph Edit Distance that has a complexity of O(n^3).
What if a list has 1000 elements.
1000^3 = 1,000,000,000
THAT'S A BILLION.
React Reconciliation
React uses some assumptions to enhance the performance of the algorithm which reduces the complexity to O(n).
Where n is the number of elements.
1. Two elements of different types will produce different trees.
2. Developers to dictate which elements will stay the same across different renders. This is achieved by "key" prop.
Elements of Same Type
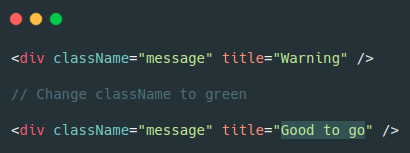
React know that it only has to update the title property on the element.
Elements of Different Type
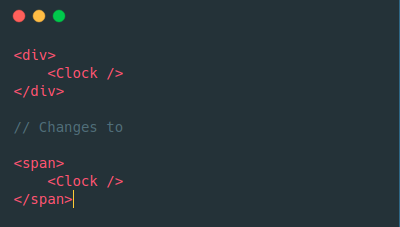
Here the whole tree is destroyed. componentWillUnmount is called on the component instance.
Iteration on Children
In the BAD example, React recreates all the DOM nodes again.
In the GOOD example, React assumes that the nodes with keys 1 & 2 just moved and 3 is added. So it only adds the 3rd element.
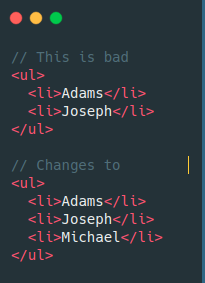
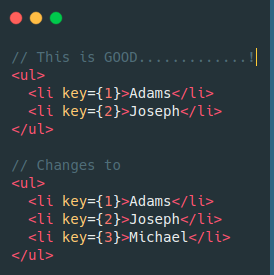
BUT....
React by default used the iterator index as the key if no key is provided.
BUT, if you pass index as a key, React assumes that you know about the Anti-Pattern.
What Anti-Pattern?
If we use index as a key and then add to the list, React will add the new item to the list, but it will not update what's not updated w.r.t the keys.