Sickle Cell Anaemia
By: Ashleigh Robertson, Shannah del Rosario and Sharon Qiao (Xiaoxi)
LSB555: Principles and Practice of Clinical Haematology

Case Study
- A young 6 year old girl presented to ED with fever, tiredness, pallor and acute episodes of pain
- Clinical examination:
- Icteric sclera
- Splenomegaly
- hand-foot syndrome (pain and swelling of fingers and toes)
- Family immigrated from Nigeria 3 years ago


Empirical Dx: Sickle Cell Anaemia
Tests Requested: FBE and other relevant tests
What is Sickle Cell Anaemia?
- Sickle cell anaemia is a haemoglobinopathy affecting normal haemoglobin production
- Forms distinct sickle red blood cells

Genetics of Sickle Cell Disease
- Sickle cell disease is autosomal recessive
- 25% chance of producing offspring with homozygous sickle cell disease - symptomatic phenotype
- 50% chance of passing down sickle cell trait genotype [1]

Source: CDC Website [2]


What mutation causes Sickle Cell Disease?


HbA (normal Hb)
HbS
(Sickle cell Hb)
Source: BBC Website [3]
How does sickling occur?
• Glutamic acid has a net charge of -1 (polar)
• Polar glutamic acid would normally bind water molecules – soluble in cytosol
• Valine has a net charge of 0 (non-polar)
• Non-polar valine is hydrophobic [1]

Source: American Society of Hematology [4]
How does sickling occur?
• Valine searches for hydrophobic niche to bind
• Oxygenated HbS has no hydrophobic niche – freely soluble
• Deoxygenated HbS creates hydrophobic pocket for valine from adjacent Hb to bind [1]
Source: New England Journal of Medicine [5]

How does sickling occur?
• HbS molecules polymerise when deoxygenated
• Forming long, rigid fibres
• Sickling reversible by oxygenation of HbS molecules
• Extensive membrane damage can cause irreversible sickle cell formation [2]
Source: New England Journal of Medicine [5]

Sickling manifestations
- Chronic Haemolytic Anaemia
- Microvascular occlusion
- Tissue damage
Chronic Haemolytic Anaemia
• Sickle cells are fragile and more prone to haemolysis – shortened RBC lifespan
• Haemolysis of RBCs cause anaemia and hyperbilirubinaemia [6]

Empirical Dx:
Jaundice in sclera - hyperbilirubinaemia
Fatigue and pallor - haemolytic anaemia

Microvascular occlusion
• Occurs due to blockage of small vasculature by sickle cells
• Hypoxic injury to these vessels cause pain crisis
• Commonly occurs in the bones of the hands and feet
• Adhesion of sickle cells to endothelium promotes occlusion [6]

Empirical Dx:
Hand-Foot Syndrome - vaso-occlusive crises
Recurring episodes of acute pain - occlusion of microvasculature
Tissue damage
• Sickle cells commonly get trapped in the spleen
• Can lead to splenic infarction, fibrosis, and progressive shrinkage – decreasing the functionality of the spleen
• Sickle cells can also cause infarctions in other tissues – causing organ failure [6]
Empirical Dx:
Splenomegaly - continuous screening and removal of sickle cells (Autosplenectomy)


Prevalence of Sickle Cell Anaemia
• Sickle Cell Anaemia is frequently found in West and Central Africa, as well as the Middle East and India [7]

Source: Encylopaedia Britannica Inc. [7]

Occurrence of sickle cell anaemia parallels the incidence of endemic malaria – suggests protective adaptation with resistance against malaria parasite [7]
Source: Encylopaedia Britannica Inc. [7]

Diagnosis of Sickle Cell Anaemia

Morphology on Peripheral Blood Smear


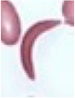
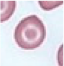



Peripheral Blood Smear [8]
Howell Jolly Bodies [10]
Sickle cell [8]
Target Cell [8]
Hypochromic Cell [9]
Polychromatic Cell [8]
Red Cell Fragment (Schistocyte) [11]
Full Blood Examination

Patient Dx:
-
Hb - Decreased -
RCC - Decreased -
Hct - Decreased -
MCV - Normal -
MCH - Normal -
MCHC - Normal -
RDW - Increased -
WCC - Increased -
PLT - Increased
Source: [12],[13],[14]
Haemoglobin Electrophoresis

Source: American Society of Hematology [15]
Haemoglobin Electrophoresis

Source: Helena Laboratories [16]
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)

Source: Universite Libre de Bruxelles [17]
Isoelectric Focusing (IEF)

Source: Universite Libre de Bruxelles [17]
Sickle Solubility Test - Sickledex

Source: Streck [18]
Negative
Positive
Treatment of Sickle Cell Anaemia

Treatment
- Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Hydroxyurea
- Treatment of complications

Blood and Bone Marrow Stem Cell Transplantation
- Sickle cell anaemia has no universal cure yet
- A small number of people are cured by blood and bone marrow transplants [19]
- Transplant aims to replace defective stem cells with normally functioning ones
- Normal function? Reject reaction?

Before and after procedure:
-
HLA tissue typing -
Chemotherapy -
Side effect:-
Infection -
Graft-vs-Host Disease -
Graft Failure
-
What's Next?
- Slow recovery [19]
- Takes 6-12 months to recover normal RBC levels and immune function
- Monitor risk of infection
- Some patients may need regular blood transfusion

Patient Rx:
-
Routine health care every 6 months -
Eye check up -
Ultrasound scan of brain -
Penicillin and Folate acid -
Parental education: learn to manage symptoms -
Genetic counselling
Hydroxyurea
- For severe sickle cell anaemia [19]
- Increases production of Foetal Haemoglobin (HbF)
- Prevents RBC from sickling
- Improve anaemia
- Reduces painful sensation from sickle cell crises
- Reduces chances of blocking small vessels
- Reduces visits to hospital


Hydroxyurea will manage patient's: Fatigue and Pallor Recurrent pain crises Hand-Foot Syndrome
Management of complications

Source: National Institute of Health [19]
Any Questions?
References
[1] Keohane EM, Smith LJ, Walenga JM. Rodak’s Hematology: Clinical Principles and Application. 5th Edition. Elsevier Inc: 2012. Chapter 27, Hemoglobinopathies (Structural Defects in Hemoglobin); p. 431-6.
[2] CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sickle cell trait [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2015 Apr 24]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/sicklecell/traits.html
[3] BBC. Gene mutations [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2015 Apr 24]. Available from: http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/higher/biology/genetics_adaptation/mutations/revision/1/
[4] Schechter A. Hemoglobin research and origins of molecular medicine [Internet]. American Society of Hematology. 2008 [cited 2015 Apr 24]. Available from: http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/112/10/3927?sso-checked=true
[5] Bunn FH. Pathogenesis and Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine, Vol 337. 1997 [cited 2015 Apr 24].
[6] Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N, Aster JC. Robbins and Cotran: Pathologic Basis of Disease. 8th edition. Elsevier Inc: 2010. Chapter 14, Anemias.
[7] Encyclopaedia Britannica Online. “Malaria and sickle cell anemia, distribution of” Map [Internet]. [cited 2015 Apr 24]. Available from: http://www.britannica.com/Ebchecked/topic/556001/South-Asia/images-videos/160694/malaria-and-sickle-cell-anemia-distribution-of
[8] Chambers K. Blood smears from patients with sickle cell disease – part 3 [internet] Leicester, UK: De Montfort University; August 23, 2011 [cited 2015, April 26] available from: http://www.sicklecellanaemia.org/OER/article.php?id=68
[9] Maslak P. Hypochromic erythrocytes – 1 [internet] Washinton DC, USA: American Society of Hematology (ASH) ; March 04, 2009 [cited 2015, April 27] available from: http://imagebank.hematology.org/AssetDetail.aspx?AssetID=3901
[10] Maslak P. Howell-Jolly bodies– 1 [internet] Washinton DC, USA: American Society of Hematology (ASH) ; January 10, 2008 [cited 2015, April 27] available from: http://imagebank.hematology.org/AssetDetail.aspx?AssetID=3677
[11] Maslak P. Schistocytes – 1 [internet] Washinton DC, USA: American Society of Hematology (ASH) ; January 10, 2008 [cited 2015, April 27] available from http://imagebank.hematology.org/AssetDetail.aspx?AssetID=3718&AssetType=Asset
[12] Valavi E, Ansari, M-J A, Zandian K, How to Reach Rapid Diagnosis in Sickle cell Disease? [internet] Iran J Pediatr, vol 20 (no 1) 69-74, March 2010 [cited 2015, April 28] available from www.bioline.org.br/pdf?pe10009
[13] Thame M, Grandison Y, Mason K, Thompson M, Higgs D, Morris J, Serjeant B, Serjeant G. The Red Cell Distribution Width in Sickle Cell Disease – is it of Clinical Value? [internet] Clinical and Laboratory Hematology volume 13 [p 229-237] September 1991 [cited 2015, April 26] available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2257.1991.tb00277.x/abstract
[14] Lichtin AE, Sickle Cell Disease [internet] Merck Manual, October 2013 [cited 2015, April 26] available from: www.merckmanuals.com/professional/hematology-and-oncology/anemias-caused-by-hemolysis/sickle-cell-disease
[15] Kuo K. Case Study: A 12-Year-Old Boy With Normocytic Anemia and Bone Pain [internet] American Society of Hematology (ASH) ©2015 [cited 2015, April 27] available from: http://www.hematology.org/Fellows/Case-Studies/725.aspx
[16] Helena Laboratories: Haemoglobin Electrophoresis Procedure [internet] Beaumont, Texas: Helena Laboratories [date unknown] [cited 2015, April 20] available from: http://www.helena.com/Procedures/Pro015%20Rev6.pdf
[17] Diagnosis, last updated 2001, August 16. [cited 2015, April 25] available from: http://erasmeinfo.ulb.ac.be/globule/English/sickle_diag.htm
[18] Streck, Sickledex [internet] Omaha, USA [date unknown] [cited 2015, April 27] available from: http://www.indianablood.org/lab-services/DonorTestingLab/Documents/Package%20Inserts-Donor%20Testing/Donor%20Tesing_Uploaded_8-22-2013/SICKLEDEX%20for%20Hgb-S.pdf
[19] National Institutes of Health, D.o.H.a.H.S., How Is Sickle Cell Anemia Treated. September 28, 2012.