C4: Session 8
Intro to JavaScript
JavaScript Foundations
What is JavaScript
JavaScript is a programming language used to control the behavior of web pages and make them interactive

JavaScript is too long...
can I call it Java?
No!
but you can abbreviate it as "JS"
JavaScript
JavaScript is a scripting language built specifically for developing HTML web pages.
Java
Java is an object-oriented programming language built for developing applications for devices and browsers.


class MyClass {
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello World!!"");
}
}<script>
alert(“Hello World!!”);
</script>What can JavaScript do?
Adding interactive behavior to web pages
Building web servers and applications
Create web and mobile apps and even games
Concept:
Ways to Run
JavaScript Foundations
Linking JavaScript to HTML
There are two ways to add JavaScript to your HTML page:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>Basic Javascript Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
This page just demonstrates including a basic
JavaScript file. The JavaScript file just tells an
alert box to pop up when the page loads.
</p>
</body>
</html>
JavaScript Foundations
Linking JavaScript to HTML
1. Internal script placed before the closing <body> tag
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>Basic Javascript Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
This page just demonstrates including a basic
JavaScript file. The JavaScript file just tells an
alert box to pop up when the page loads.
</p>
<script>
alert("This alert box was called on page load");
</script>
</body>
</html>
JavaScript Foundations
Linking JavaScript to HTML
2. External script file placed before the closing <body> tag
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>Basic Javascript Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
This page just demonstrates including a basic
JavaScript file. The JavaScript file just tells an
alert box to pop up when the page loads.
</p>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
// script.js
alert("This alert box was called on page load");
JavaScript Foundations
Running locally without a browser
Node is a runtime environment that allows you to run JavaScript outside of a web browser. In other words, it lets you run JavaScript code on your computer or server.
- JavaScript is traditionally used to create interactive web pages, but with Node.js, you can use it for a variety of tasks, such as building web servers, command-line tools, desktop applications, and more.
- Download the LTS Version: https://nodejs.org/en/download
JavaScript Foundations
Running locally without a browser
To run your script file:
$ node <path-to-your-file>
Concept:
Debugging JavaScript
Debugging JavaScript
Dev Console
Using the console is a very important part of learning JavaScript. If you don't know if something works or what the command is for something, go to the console and figure it out!
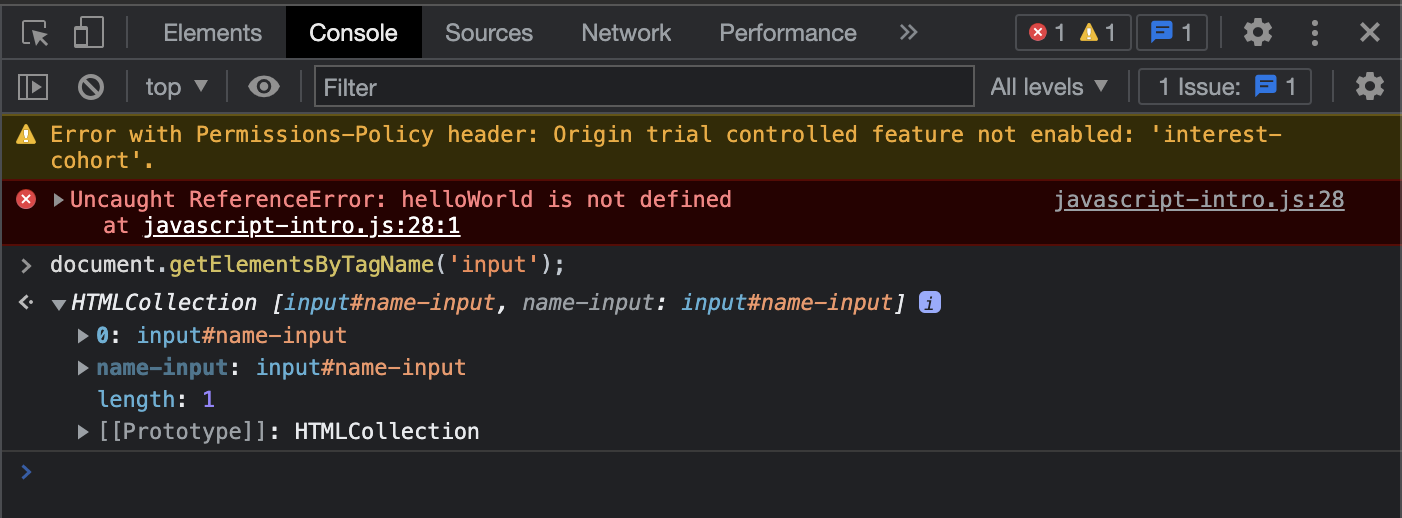
Debugging JavaScript
Example
Debugging JavaScript
Bug Found
How do we know what this error means?
Concept:
Variables
Variables
Variables
We use variables to store and work with data.
let mutableVariable;
const immutableVariable;Variables
Variables
We use variables to store and work with data.
let mutableVariable = 12345;
const immutableVariable;Variables
Variables
We use variables to store and work with data.
let mutableVariable = 12345;
const immutableVariable = "hello world";Variables
Why shouldn't we use var anymore?
There are multiple reasons but one of the biggest reasons is the var keyword allows you to overwrite the data.
var budget = 500;
var budget = 3000;
console.log(budget);
Concept:
Data Types
Data Types
String
A series of characters, words, or phrases. They begin and end with a quotation mark (single, double, or backticks).
// Single quotes
let str1 = 'Hello, my name is Sharynne';
// Double quotes
let str2 = "Hello, my name is Sharynne";
// Backticks
let str3 = `Hello, my name is Sharynne`;Data Types
String
Using apostrophes or adding quotes to the text:
// If you need to use an apostrophe, use double quotes to surrond the string
let str1 = "Hello, my name is Sharynne. I'm from Kansas City.";
// If you need to quote a text, use single quotes to surround the string
let str2 = 'She typed "Hello World" into the console.';
// Or you can escape the quote using a slash before using it
let str3 = 'Hello, my name is Sharynne. I\'m from Kansas City.';
let str4 = "She typed \"Hello World\" into the console.";
Data Types
String
Concatenating (joining) strings:
let guestName = 'Sharynne';
let greeting = 'Hello, my name is ' + guestName + '. I\'m from Kansas City.';Data Types
String
Concatenating (joining) strings:
let guestName = 'Sharynne';
let greeting = 'Hello, my name is ' + guestName + '. I\'m from Kansas City.';
// backticks method
let greeting = `Hello, my name is ${guestName}. I'm from Kansas City.`;
Data Types
String
Finding the length of a string:
let myName = 'Sharynne';
console.log(myName.length);Data Types
Number
Any negative or positive integers or floating point numbers.
// Positive integer
let num1 = 12345;
// Negative integer
let num2 = -12345;
// Float (aka decimals)
let num3 = 3.14159;
Data Types
Number
Number operations:
let addResult = 5 + 10;
let substractResult = 1000 - 99;
let multiplyResult = 10 * 10;
let divideResult = 16 / 2;Data Types
Number
The ++ and -- operators:
let num = 0;
// increments by one, short for num = num + 1;
num++;
// decrements by one, short for num = num - 1;
num--;Data Types
Number
Augmented operations:
let num = 0;
// same as num = num + 5;
num += 5;
// same as num = num - 10;
num -= 10;
// same as num = num * 4;
num *= 4;
// same as num = num / 2;
num /= 2;
Data Types
Boolean
Have only two values: true or false. Usually used to determine if a condition is true or false.
console.log(4 + 5 < 1);
// returns false
let age = 30;
console.log(age >= 21);
// returns true
let name = "John";
console.log(name === 'Sharynne');
// returns falseData Types
null and undefined
null: empty data
undefined: unset or non-existing data
Concept Practice: Data Types
Practice Data Types
Next Session
Conditional Logic
Loops
Functions