\(\LaTeX\) Tutorial
Sheng Long
Sep 2021
1. What
2. Why
3. How
What is \(\LaTeX\)?
- It is a tool used to create professional looking documents
- WYSIWYM
- What You See Is What You Mean
- Focus on content and let computer take care of the formatting
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
Why should I learn \(\LaTeX\)?
- Because this course
requiressuggests it- The homework is written in \(\LaTeX\)
- Because you can use it to create beautiful things
- Because \(\LaTeX\) separates content from style \(\implies\) change styling at ease once you have the contents ready
- Additional reading on why \(\LaTeX\) for the curious
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
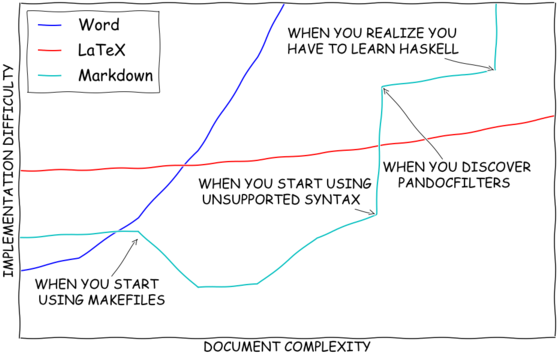
More motivation
https://villeklar.com/post/Scientifc_writing_with_Latex/learningcurve.png
How to write in \(\LaTeX\)?
Basic Syntax
- Bold, Italic, Underline
- Math
-
Tables andLists Pictures
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
Advanced Syntax
- Commands
- Environments
- Packages
Basic syntax
- Go to Overleaf.com, create an account
- New Project \(\to\) Blank Project \(\to\) "My First Project"
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
First document. This is a simple example, with no extra parameters or packages included.
\end{document}https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
\documentclass[12pt, letterpaper]{article}
\usepacakge[utf8]{inputenc}
\begin{document}
First document. This is a simple example, now with one package included.
\end{document}Adding title, author, date
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
\documentclass[12pt, letterpaper]{article}
\usepacakge[utf8]{inputenc}
\title{My First \LaTeX{} Project}
\author{Sheng Long}
\date{\today}
\begin{document}
\maketitle
First document. This is a simple example, now with one package included.
\end{document}Basic Font Formatting
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
\documentclass[12pt, letterpaper]{article}
\usepacakge[utf8]{inputenc}
\title{My First \LaTeX Project}
\author{Sheng Long}
\date{\today}
\begin{document}
\maketitle
\textbf{bold}
\textit{italicised}
\underline{underlined}
\end{document}Exercise (1)
- Produce something that looks like the following:
- This is some important text.
This is some \textbf{\underline{important}} text. Lists (ordered)
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
...
\begin{document}
An example of an ordered list:
\begin{enumerate}
\item Uno
\item Dos
\item Tres
\end{enumerate}
\end{document}Lists (un-ordered)
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
The above haiku was written by Matuso Basho.
...
\begin{document}
An example of an un-ordered list:
\begin{itemize}
\item The old pond
\item ... A frog leaps in
\item ... Sound of the water.
\end{itemize}
\end{document}Exercise (2)
Produce a nested list, as shown in the following:
- Shopping list:
- Eggs
- Milk
- Apples
\begin{itemize}
\item Shopping list:
\begin{enumerate}
\item Eggs
\item Milk
\item Apples
\end{enumerate}
\end{itemize}Math
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
-
Use $ ... $ (or \( ... \)) for inline math
- Use \(\texttt{\$\$}\) ... \(\texttt{\$\$}\) for displaying math
- To index equations, use the \(\texttt{equation}\) environment
- To write equations with multiple lines, use the \(\texttt{align}\) environment (requires the \(\tt amsmath\) package to work)
Exercise 3(a)
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
-
Produce the following inline equations:
-
\(y = kx + b\)
-
\(\frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{2} = 1\)
-
\(a_1^2 + a_2^2 = a_3^2\)
-
\(\sqrt{9} \leq 3\)
-
Hints:
-
-
use \\(\texttt{frac}\{n\}\{d\}\) to express fractions
-
use \(\texttt{\_}\) for subscripts and ^ for superscripts
-
$y= kx+b$
$\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2} = 1$
$a_1^2 + a_2^2 = a_3^2$
$\sqrt{9} \leq 3$Exercise 3(b)
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
-
Produce the following display-style equations:
-
Hints:
-
\begin{align*} ... \end{align*} - superscripts use ^
-
Math (special characters)
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
- Greek letters: \Pi \(\to \Pi\); \pi \(\to \pi\)
- Requires the package \(\texttt{amsmath}\) -- good to always include in the preamble
- \\(\texttt{mathbb}\): turns letters from \(R\) to \(\mathbb{R}\)
- "bb" stands for "blackboard bold"
- \\(\texttt{mathcal}\): turns letter from \(G\) to \(\mathcal{G}\)
- Refer to Overleaf for more details
- I also find cheat-sheets to be helpful

Advanced Syntax
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Environments
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Commands
- Commands
- Environments
- Packages
Commands
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Commands
- Usually start with a backslash \
- For example, \(\texttt{\textbackslash textbf}\) and \(\texttt{\textbackslash pi} \)
- May take in required parameters or optional parameters
- For example,
\(\texttt{\textbackslash documentclass [12pt] \{article\}}\)
optional
required
Define new command
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Commands
- Define new command with \(\texttt{\textbackslash newcommand\{...\}\{...\} } \)
- For example,
\(\implies\) this will allow you to type \(\texttt{\textbackslash R}\) instead of the full \(\texttt{\textbackslash mathbb\{R\}}\)
- See the Overleaf tutorial page for more detailed examples on what else you can do with commands
- Also checkout the preamble in homework
\newcommand{\R}{\mathbb{R}}Environments
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Environments
https://ctan.math.illinois.edu/macros/latex/contrib/enumitem/enumitem.pdf
- Environments format blocks of text
- Environments are delimited by an open tag \(\texttt{\textbackslash begin}\) and a close tag \(\texttt{\textbackslash end}\)
- For example,
\begin{itemize}[nosep]
\item Apples
\item Bananas
\end{itemize}\(\texttt{nosep}\) is an optional parameter that one can use when using the \(\texttt{enumitem}\) package
Define new environment
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Environments
https://www.dickimaw-books.com/latex/novices/html/newenv.html
- Environment \(\approx\) command "sandwich"
- Define two new commands for a "new" environment
- Can also use the \\(\texttt{newenvironment}\) command
\newenvironment{exercise}
{\textbf{Exercise}\begin{itshape}}
{\end{itshape}}Theorems and Proofs
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Theorems_and_proofs
- Use command \\(\texttt{newtheorem}\) to define new environments for math theorems, lemmas, corollaries
- For example,
- Use the \(\texttt{amsthm}\) package to use the \(\texttt{proof}\) environment
\\(\texttt{newtheorem}\)\(\texttt{\{thm\}}\)\(\texttt{\{Theorem\}}\)
name of new environment
printed text
Packages
- \\(\texttt{documentclass}\) tells the compiler the basic formatting of the document
- Common document classes include \(\texttt{article}\), \(\texttt{beamer}\), and \(\texttt{book}\)
- Example of \(\texttt{beamer}\):
Useful Packages
- \(\texttt{amsmath}\) -- for math formatting
-
\(\texttt{TikZ}\) -- for creating graphical elements
- \(\texttt{pgfplots}\) -- for creating scientific plots
- \(\texttt{booktabs}\) -- creates beautiful tables
- \(\texttt{enumitem}\) -- allows advanced list formatting
- Refer to the Comprehensive \(\TeX\) Archive Network (CTAN) for more information on packages and classes
For the bold
- So far, we've covered how to write in \(\LaTeX\) online
- But what if you don't have access to the internet?
- Tufte-latex
- NotesTeX
Last but not least
Adding images (in Overleaf)
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
\documentclass[12pt, letterpaper]{article}
\usepacakge{graphicx}
\graphicspath{...}
\begin{document}
The following is a picture of my cat, Tora.
\includegraphics{Tora.jpg}
\end{document}Captions, labels, refs
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
\documentclass[12pt, letterpaper]{article}
\usepacakge{graphicx}
\graphicspath{...}
\begin{document}
The following is a picture of my cat, Tora.
\begin{figure}[h]
\centering
\includegraphics{Tora}
\caption{Tora -- the sweetest cat in the world}
\label{fig:tora-1}
\end{figure}
\end{document}Math
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
For example, try
-- the double backslash means new line
-- \(\&\) aligns the equations together
-- to avoid line indexing, use the \(\texttt{align*}\) environment instead
\begin{align}
(a+b)^2 &= a(a+b)+ b(a+b) \\
&= a^2 + 2ab + b^2
\end{align}
\usepackage{amsmath}Math
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
- Fractions use \\(\texttt{frac}\): \(\frac{1}{2}\) is \\(\texttt{frac\{1\}\{2\}}\)
- Superscripts use ^: \(\texttt{a\^ 2} \implies a^2\)
- Subscripts use _: \(\texttt{a\_1} \implies a_1\)
- Checkout the math section on Overleaf!
