TESTS
— by Youcef MADADI, FREELANCER & PROJECT MANAGER

Index for Testing




Introduction to Testing
Introduction to Software Testing
What is Software Testing?
-
Ensuring that software behaves as expected and meets specified requirements.
-
Detect bugs early.
-
Ensure functionality and reliability.
-
Improve code maintainability.
-
Build confidence for deployment.
Why Use Test?
Types of Software Testing
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Tests individual units of code in isolation. |
| Integration Testing | Tests interactions between different units or modules. |
| End-to-End (E2E) | Tests the entire application workflow from start to finish. |
| Performance Testing | Tests the system's performance under load. |
| Regression Testing | Ensures new code changes don't break existing functionality. |
| UI Testing | Focuses on the user interface and user experience. |
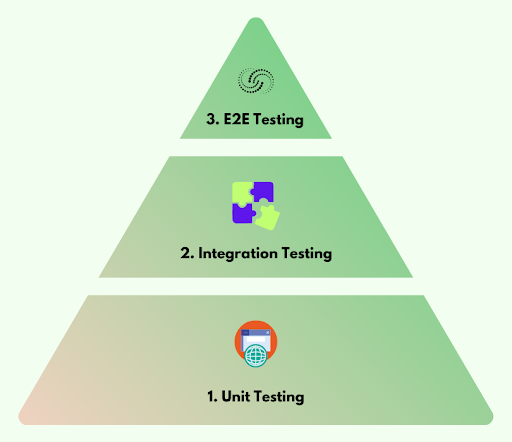
Testing Pyramid
-
Unit Tests (Foundation)
-
Most numerous and executed frequently.
-
Ensure individual components work as expected.
-
-
Integration Tests (Middle Layer)
-
Validate module interactions.
-
Fewer in number than unit tests.
-
-
End-to-End Tests (Top Layer)
-
Test complete workflows.
-
Few but critical for overall functionality.
-
-
Why Test in React?
- Ensure application reliability and functionality.
- Validate reusable components and services.
- Simplify debugging and refactoring.
-
React’s Common Testing Tools
Vitest / Jest → Test runner and assertion library.
React Testing Library (RTL) → Renders components and simulates user interactions.
Cypress / Playwright → For full end-to-end browser testing.
MSW (Mock Service Worker) → Mock APIs in integration and E2E tests.
Testing in
Angular
Types of Testing in Angular
| Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Tests isolated parts of the code (e.g., services, components). | Test if a CalculatorService returns the correct sum of two numbers. |
| Integration Testing | Tests how components or modules interact. | Test if a form component correctly validates user input. |
| End-to-End (E2E) | Tests the application workflow as a user would experience it. | Test if the login process works end-to-end. |
| Snapshot Testing | Compares the output of components or templates against a saved snapshot. | Test if a component's rendered HTML matches the expected structure. |
Unit Testing Overview
Focus:
- Test individual components, services, or pipes.
Tools in Angular:
-
Jasmine,Karma,TestBed.
Characteristics:
- Quick to execute.
- Works with mock dependencies.
- Verifies specific functionality.
it('should add two numbers correctly', () => {
const result = calculatorService.add(2, 3);
expect(result).toBe(5);
});Integration Testing Overview
Focus:
- Test how components or services work together.
Angular Example:
- Test interaction between a parent component and a child component.
it('should pass input to child component', () => {
const fixture = TestBed.createComponent(ParentComponent);
fixture.componentInstance.childInput = 'Test Input';
fixture.detectChanges();
const childElement = fixture.nativeElement.querySelector('app-child');
expect(childElement.textContent).toContain('Test Input');
});End-to-End (E2E) Testing Overview
- Test application workflows as a user would experience them.
Focus:
- Protractor (legacy) or Cypress.
Tool in Angular:
it('should login successfully', () => {
cy.visit('/login');
cy.get('#username').type('testuser');
cy.get('#password').type('password123');
cy.get('button[type="submit"]').click();
cy.url().should('include', '/dashboard');
});Summary of Testing in Angular
- Angular provides robust tools for writing and running tests.
- Balance testing efforts using the Testing Pyramid:
- Unit tests (majority).
- Integration tests (fewer).
- End-to-end tests (least).
- Focus on maintainable, readable, and reliable tests.
Unit Testin in Angular
Key Angular Testing Tools
-
Jasmine: Test framework for writing specs.
- Example:
describe,it,expect.
- Example:
- Karma: Test runner to execute tests in browsers.
-
Angular Testing Utilities:
-
TestBed: Configure and initialize the testing environment. -
fakeAsyncandtick: Test asynchronous operations. -
ComponentFixture: Access and manipulate components.
-
Angular Testing Utilities - Overview
| Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| TestBed | Sets up the test environment for components, services, and modules. |
| ComponentFixture | Allows testing and querying of component instances and DOM elements. |
fakeAsync/tick
|
Simulates asynchronous behavior for observables, promises, or timeouts. |
| async | Wraps async code for execution in Angular's zone. |
Steps to Create a Unit Test
-
Setup the Test Environment:
- Use
TestBedto configure the testing module. - Import necessary dependencies.
- Use
-
Write the Test:
- Use
describeto group tests. - Use
itto define individual test cases. - Use
expectto define assertions.
- Use
-
Execute and Debug Tests:
- Run tests with
ng test. - Check outputs and coverage.
- Run tests with
Service Testing Example
export class MathService {
add(a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b;
}
}describe('MathService', () => {
let service: MathService;
beforeEach(() => {
service = new MathService();
});
it('should return the sum of two numbers', () => {
const result = service.add(2, 3);
expect(result).toBe(5);
});
});Scenario: Test a service that adds two numbers.
Component Testing Example
@Component({
selector: 'app-message',
template: `<p>{{ message }}</p>`,
})
export class MessageComponent {
message = 'Hello, World!';
}Scenario: Test a component that displays a message.
describe('MessageComponent', () => {
let component: MessageComponent;
let fixture: ComponentFixture<MessageComponent>;
beforeEach(async () => {
await TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [MessageComponent],
}).compileComponents();
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(MessageComponent);
component = fixture.componentInstance;
fixture.detectChanges();
});
it('should display the correct message', () => {
const compiled = fixture.nativeElement;
expect(compiled.querySelector('p').textContent).toBe('Hello, World!');
});
});Directive Testing Example
@Directive({
selector: '[appHighlight]',
})
export class HighlightDirective {
@HostBinding('style.color') color = 'blue';
}Scenario: Test a directive that changes text color.
describe('HighlightDirective', () => {
let fixture: ComponentFixture<TestComponent>;
@Component({
template: `<p appHighlight>Test Text</p>`,
})
class TestComponent {}
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [TestComponent, HighlightDirective],
});
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(TestComponent);
fixture.detectChanges();
});
it('should highlight the text with blue color', () => {
const p: HTMLElement = fixture.nativeElement.querySelector('p');
expect(p.style.color).toBe('blue');
});
});import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'reverseCapitalize',
})
export class ReverseCapitalizePipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: string): string {
if (!value) return '';
const reversed = value.split('').reverse().join('');
return reversed.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + reversed.slice(1);
}
}import { ReverseCapitalizePipe } from './reverse-capitalize.pipe';
describe('ReverseCapitalizePipe', () => {
let pipe: ReverseCapitalizePipe;
beforeEach(() => {
pipe = new ReverseCapitalizePipe();
});
it('should reverse a string and capitalize the first letter', () => {
const result = pipe.transform('angular');
expect(result).toBe('Ralugna');
});
it('should handle empty strings', () => {
const result = pipe.transform('');
expect(result).toBe('');
});
});import { ReverseCapitalizePipe } from './reverse-capitalize.pipe';
describe('ReverseCapitalizePipe', () => {
let pipe: ReverseCapitalizePipe;
beforeEach(() => {
pipe = new ReverseCapitalizePipe();
});
it('should handle undefined input gracefully', () => {
const result = pipe.transform(undefined as any);
expect(result).toBe('');
});
it('should not alter single-character strings other than capitalizing them', () => {
const result = pipe.transform('a');
expect(result).toBe('A');
});
it('should reverse and capitalize strings with spaces correctly', () => {
const result = pipe.transform('hello world');
expect(result).toBe('Dlrow olleh');
});
});Pipe Testing Example
Scenario: Test a pipe that changes text to reverse capitalized text
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class DataService {
constructor(private http: HttpClient) {}
fetchData(): Observable<any> {
return this.http.get('https://api.example.com/data');
}
}import { TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { HttpClientTestingModule, HttpTestingController } from '@angular/common/http/testing';
import { DataService } from './data.service';
describe('DataService', () => {
let service: DataService;
let httpTestingController: HttpTestingController;
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [HttpClientTestingModule],
providers: [DataService],
});
service = TestBed.inject(DataService);
httpTestingController = TestBed.inject(HttpTestingController);
});
afterEach(() => {
httpTestingController.verify(); // Ensures no pending HTTP requests are left.
});
// tests here
});
it('should fetch data from the API', () => {
const mockData = { id: 1, name: 'John Doe' };
service.fetchData().subscribe((data) => {
expect(data).toEqual(mockData);
});
const req = httpTestingController.expectOne('https://api.example.com/data');
expect(req.request.method).toBe('GET');
// Simulate a successful HTTP response with mock data.
req.flush(mockData);
});
it('should handle HTTP errors gracefully', () => {
const mockError = { status: 404, statusText: 'Not Found' };
service.fetchData().subscribe({
next: () => fail('Expected an error, not data'),
error: (error) => {
expect(error.status).toBe(404);
expect(error.statusText).toBe('Not Found');
},
});
const req = httpTestingController.expectOne('https://api.example.com/data');
expect(req.request.method).toBe('GET');
// Simulate an HTTP error response.
req.flush(null, mockError);
});Obsevable data fetching Example
Scenario: Test an http request with httpClient observables.
import { Component, signal } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-signal-example',
template: `<p>{{ count() }}</p>`,
})
export class SignalExampleComponent {
count = signal(0);
increment() {
this.count.set(this.count() + 1);
}
decrement() {
this.count.set(this.count() - 1);
}
}import { ComponentFixture, TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { SignalExampleComponent } from './signal-example.component';
describe('SignalExampleComponent', () => {
let component: SignalExampleComponent;
let fixture: ComponentFixture<SignalExampleComponent>;
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [SignalExampleComponent],
}).compileComponents();
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(SignalExampleComponent);
component = fixture.componentInstance;
});
it('should initialize count signal to 0', () => {
expect(component.count()).toBe(0);
});
// more tests
});
it('should increment count signal', () => {
component.increment();
expect(component.count()).toBe(1);
});
it('should decrement count signal', () => {
component.increment();
component.increment();
component.decrement();
expect(component.count()).toBe(1);
});Signal state Example
Scenario: Test a counter state that is registered with signal.
import { Component, signal, computed } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-computed-example',
template: `<p>{{ doubleCount() }}</p>`,
})
export class ComputedExampleComponent {
count = signal(5);
doubleCount = computed(() => this.count() * 2);
increment() {
this.count.set(this.count() + 1);
}
}import { ComponentFixture, TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { ComputedExampleComponent } from './computed-example.component';
describe('ComputedExampleComponent', () => {
let component: ComputedExampleComponent;
let fixture: ComponentFixture<ComputedExampleComponent>;
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [ComputedExampleComponent],
}).compileComponents();
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(ComputedExampleComponent);
component = fixture.componentInstance;
});
// tests
});
it('should initialize doubleCount computed signal correctly', () => {
expect(component.doubleCount()).toBe(10);
});
it('should update doubleCount when count changes', () => {
component.increment();
expect(component.doubleCount()).toBe(12);
});Computed state Example
Scenario: Test a counter state that double is registered with computed.
import { Component, signal, effect } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-effect-example',
template: `<p>Log Count: {{ count() }}</p>`,
})
export class EffectExampleComponent {
count = signal(0);
constructor() {
effect(() => {
console.log(`Count has changed: ${this.count()}`);
});
}
increment() {
this.count.set(this.count() + 1);
}
}import { ComponentFixture, TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { EffectExampleComponent } from './effect-example.component';
describe('EffectExampleComponent', () => {
let component: EffectExampleComponent;
let fixture: ComponentFixture<EffectExampleComponent>;
let consoleSpy: jasmine.Spy;
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [EffectExampleComponent],
}).compileComponents();
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(EffectExampleComponent);
component = fixture.componentInstance;
consoleSpy = spyOn(console, 'log');
});
// tests
});it('should log message when count changes', () => {
component.increment();
expect(consoleSpy).toHaveBeenCalledWith('Count has changed: 1');
});
it('should log the correct message after multiple increments', () => {
component.increment();
component.increment();
component.increment();
expect(consoleSpy.calls.mostRecent().args[0]).toBe('Count has changed: 3');
});Signal change with effect Example
Scenario: Test a counter state that call effect on change of state with effect.
Integration Testing in Angular
Key Angular Testing Tools
- Jasmine: BDD (Behavior-Driven Development) testing framework.
- Karma: Test runner for executing tests in different environments.
- TestBed: Angular's utility to configure and initialize test environments.
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class MyService {
fetchData(): Observable<string[]> {
// Simulating a data fetch
return of(['Item1', 'Item2']);
}
}Service integration test
Scenario: Test a fetching service integration with a component
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { MyService } from './my.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-my-component',
template: `
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let item of items">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
`,
})
export class MyComponent implements OnInit {
items: string[] = [];
constructor(private myService: MyService) {}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.myService.fetchData().subscribe((data) => {
this.items = data;
});
}
}import { ComponentFixture, TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { By } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { MyComponent } from './my.component';
import { MyService } from './my.service';
describe('MyComponent Integration Test', () => {
let component: MyComponent;
let fixture: ComponentFixture<MyComponent>;
beforeEach(async () => {
await TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [MyComponent],
providers: [{ provide: MyService, useClass: MockMyService }],
}).compileComponents();
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(MyComponent);
component = fixture.componentInstance;
fixture.detectChanges();
});
// tests
});
Service integration test
Scenario: Test a fetching service integration with a component
it('should create the component', () => {
expect(component).toBeTruthy();
});
it('should fetch data and display it in the template', () => {
// Verify the items are set correctly
expect(component.items).toEqual(['MockItem1', 'MockItem2']);
// Verify the template renders the items
const items = fixture.debugElement.queryAll(By.css('li'));
expect(items.length).toBe(2);
expect(items[0].nativeElement.textContent).toContain('MockItem1');
expect(items[1].nativeElement.textContent).toContain('MockItem2');
});End-to-End (E2E) Testing in Angular
E2E tests in angular uses Cypress
Why Cypress for Angular?
- Simple setup and configuration.
- Real-time reloading for test development.
- Powerful debugging with snapshots and browser-based tools.
What is Cypress?
- A next-generation frontend testing tool.
- Provides fast, reliable, and easy-to-write tests.
- Ideal for End-to-End (E2E) testing in Angular projects.
Installing Cypress
Open Cypress
npx cypress openFolder Structure:
-
cypress/fixtures/: Sample data for tests. -
cypress/integration/: Your test files. -
cypress/support/: Utility files for shared code.
npm install cypress --save-devAdd Cypress to Your Angular Project
Writing Your First Test
Test the Homepage
touch cypress/integration/homepage.spec.jsCreate a file in cypress/integration/:
describe('Homepage Tests', () => {
it('should load the homepage', () => {
cy.visit('/');
cy.contains('Welcome to My App').should('be.visible');
});
});Write the test:
Writing Form test
Testing Form Interactions
touch cypress/integration/form-page.spec.jsCreate a file in cypress/integration/:
describe('Form Tests', () => {
it('should fill and submit the form', () => {
cy.visit('/form-page');
cy.get('#name').type('John Doe');
cy.get('#email').type('john.doe@example.com');
cy.get('button[type="submit"]').click();
cy.contains('Form submitted successfully!').should('be.visible');
});
});Write the test:
Testing Navigation
Navigate Between Pages
touch cypress/integration/navigation-page.spec.jsCreate a file in cypress/integration/:
describe('Navigation Tests', () => {
it('should navigate to About page', () => {
cy.visit('/');
cy.get('a[href="/about"]').click();
cy.url().should('include', '/about');
cy.contains('About Us').should('be.visible');
});
});Write the test:
API Mocking with Cypress
Mock HTTP Requests
touch cypress/integration/api.spec.jsCreate a file in cypress/integration/:
describe('API Tests', () => {
it('should display mocked data', () => {
cy.intercept('GET', '/api/items', {
statusCode: 200,
body: [{ id: 1, name: 'Mock Item' }],
}).as('getItems');
cy.visit('/items');
cy.wait('@getItems');
cy.contains('Mock Item').should('be.visible');
});
});Write the test:
Advanced Features
Testing Responsiveness
touch cypress/integration/responsive.spec.jsCreate a file in cypress/integration/:
describe('Responsive Design Tests', () => {
it('should work on mobile', () => {
cy.viewport('iphone-6');
cy.visit('/');
cy.contains('Mobile View').should('be.visible');
});
});Write the test:
Custom Commands
Login
touch cypress/support/commands.jsCreate a file in cypress/integration/:
Cypress.Commands.add('login', (username, password) => {
cy.get('#username').type(username);
cy.get('#password').type(password);
cy.get('button[type="submit"]').click();
});Write the command:
cy.login('user1', 'password123');using it in specs

Let's practice