React JS
context and routing
Context in React
What is React Context API?
Context provides a way to pass data through the component tree without having to pass props down manually at every level.
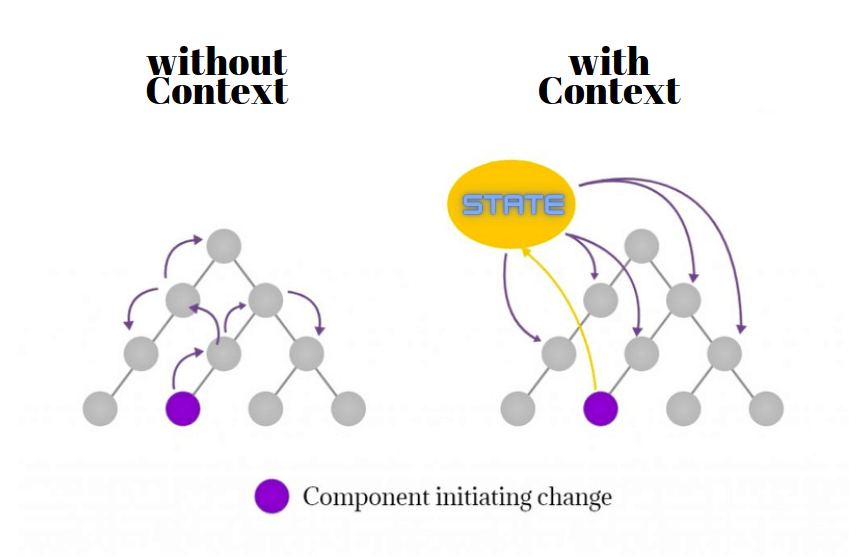
Role of Providers in Context API
- Context allows you to share values like themes, user preferences, or any global data.
- Useful for components that need specific data regardless of their position in the component tree.
Benefits of Using Context API
- Eliminates prop drilling
- Centralizes state management
- Improves code readability
How to declare a Context
const ThemeContext = createContext();How to create its Provider
const ThemeProvider = ({ children }) => {
const [theme, setTheme] = useState('light');
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={{ theme, setTheme }}>
{children}
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
};How to use context
const { theme, setTheme } = useContext(ThemeContext);return (
<div>
<p>Current Theme: {theme}</p>
<button onClick={() => setTheme(theme === 'light' ? 'dark' : 'light')}>
Toggle Theme
</button>
</div>
);
Example of Using Context API
Demonstration of creating a sidebar switcher using useContext and providers to manage the theme state.

Example of Using Context API
Demonstration of creating an AuthContext to manage authentication state
Best Practices for Using Context API
- Separate concerns with multiple contexts
- Avoid unnecessary re-renders
- Optimize performance with memoization
Conclusion
Recap of the benefits of using useContext and providers in React to efficiently manage state across components.
React Router DOM
What is React Router DOM?
- React Router DOM is a library used to handle routing in React applications.
- It enables navigation between different components or views within a single-page application (SPA) without refreshing the entire page.
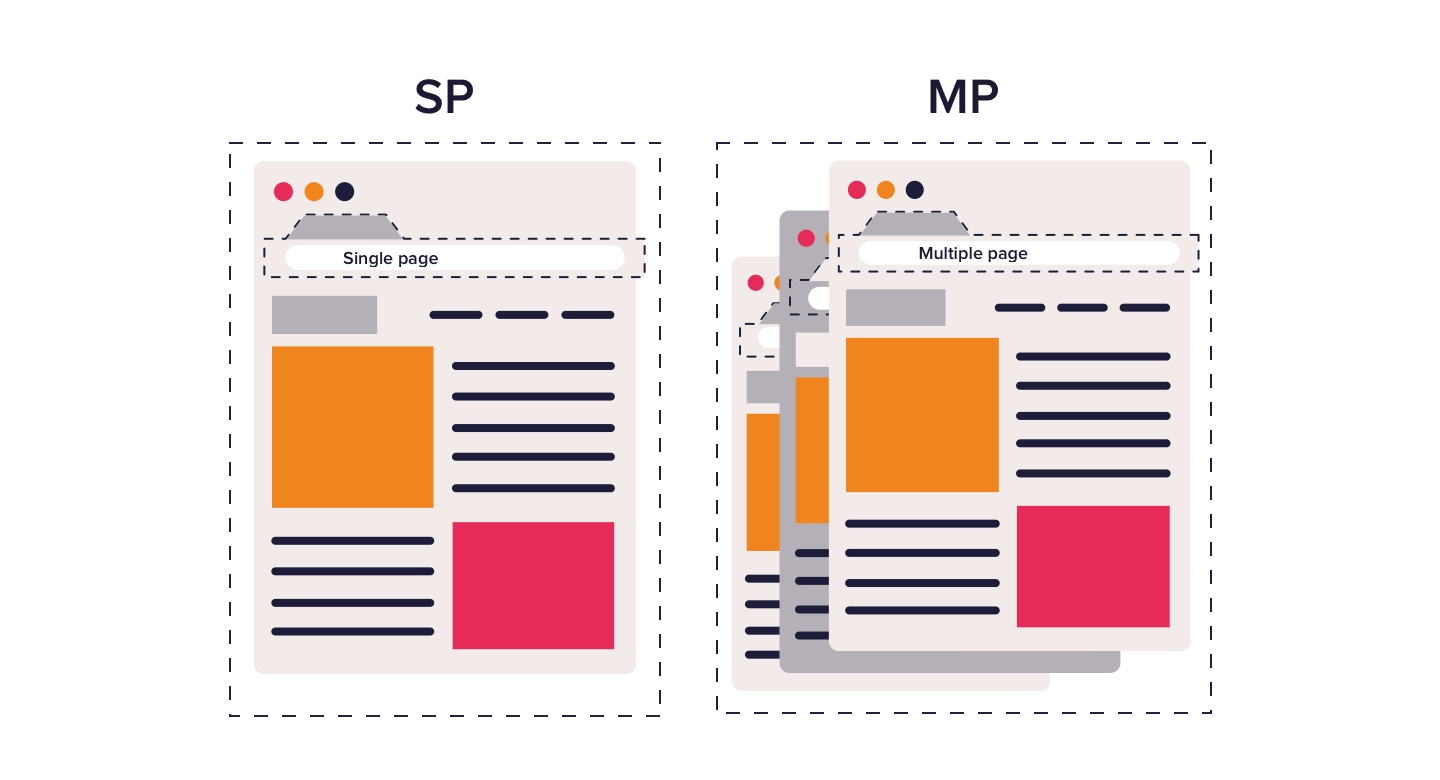
Why Use React Router DOM?
- SPA Navigation: Allows for dynamic navigation in SPAs, enhancing user experience by avoiding full page reloads.
- URL Management: Keeps the UI in sync with the URL, enabling deep linking and browser navigation controls (back/forward).
- Declarative Routing: Defines routes declaratively in your component tree, making your routing logic easy to read and maintain.
BrowserRouter
- A wrapper that uses the HTML5 history API to keep the UI in sync with the URL.
- Typically used to wrap your entire application.
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
function App(){
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<App/>
</BrowserRouter>
)
}useRoutes
A hook that returns an element that renders the first matching child route.
const Routes = () => {
const routes = useRoutes([
{ path: '/', element: <Home /> },
{ path: '/about', element: <About /> },
{ path: '/contact', element: <Contact /> },
{ path: '/user/:username', element: <UserProfile /> },
]);
return routes;
};Link
A component used to create navigational links. Uses the to prop to specify the target URL.
<Link to="/register" />
<Link to="/login" replace/>useNavigate
A hook that provides a function to programmatically navigate between routes.
const navigate= useNavigate();
const onSubmit=()=>{
navigate("/profile")
}useLocation
A hook that returns the current location object, which represents where the app is now, where it was before, and how it got there.
function LocationDisplay() {
const location = useLocation();
return (
<div>
<h2>Current Location</h2>
<pre>{JSON.stringify(location, null, 2)}</pre>
</div>
);
}useParams
A hook that returns an object of key-value pairs of the URL parameters.
function UserProfile() {
const { username } = useParams();
return (
<div>
<h2>User Profile</h2>
<p>Username: {username}</p>
</div>
);
}Routing:
/users/:username
Example:
/users/youcefM
useParams
This hook allows you to read and manipulate the query string in the URL. It's useful for scenarios where you need to read or update URL query parameters.
function UserProfile() {
const { username } = useParams();
const [searchParams, setSearchParams] = useSearchParams();
const age = searchParams.get('age');
const handleAgeChange = (e) => {
setSearchParams({ age: e.target.value });
};
// rest
}
Routing:
/users/:username?age=
Example:
/users/youcefM?age=26
useParams - part 2
This hook allows you to read and manipulate the query string in the URL. It's useful for scenarios where you need to read or update URL query parameters.
return (
<div>
<h2>User Profile: {username}</h2>
<p>Age: {age}</p>
<input
type="number"
value={age || ''}
onChange={handleAgeChange}
placeholder="Set age"
/>
</div>
);Routing:
/users/:username?age=
Example:
/users/youcefM?age=26