Unity 3D Training Camp
Coding with C# part-2
Coding with C# Part-2
1- Programming Paradigms
2- Object-oriented programming
3- Parametric Polymorphism
4- Inheritance
5- Access Modifier
Coding with C# Part-2
Assembly programming
Functional programming
Object-oriented programming
Procedural programming
1- Programming Paradigms
1- Programming Paradigms
Assembly programming
Assembly programming is any low-level programming language in which there is a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions
1- Programming Paradigms
Functional programming
functional programming is a style of building the structure and elements of computer programs—that treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions and avoids changing-state and mutable data.


1- Programming Paradigms
Procedural programming
Procedural programming is a programming paradigm, derived from structured programming, based on the concept of the procedure call. Procedures, also known as routines, subroutines, or functions, simply contain a series of computational steps to be carried out. Any given procedure might be called at any point during a program's execution, including by other procedures or itself.

1- Programming Paradigms
Object-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which can contain data, in the form of fields (often known as attributes or properties), and code, in the form of procedures (often known as methods). A feature of objects is an object's procedures that can access and often modify the data fields of the object with which they are associated.
Coding with C# Part-2
Objects
classes
Methods
Attributes
2- Object-oriented programming
Constructor & new
2- Object-oriented programming
Objects
What is an object ?
- a material thing that can be seen and touched.
- a person or thing to which a specified action or feeling is directed.
Example :

2- Object-oriented programming
Classes
What is a class ?
a set or category of things having some property or attribute in common and differentiated from others by kind, type, or quality.
What is a class in OOP?
is a blueprint for creating objects (a particular data structure), providing initial values for state (member variables or attributes), and implementations of behavior (member functions or methods). The user-defined objects are created using the
class MyClassName{
//our Code
}How to use the class key word.
2- Object-oriented programming

class Bottle
{
double bottomRadius = 2.5,
height = 12,
capRaduis = 1,
neckRaduis = 1.5,
capacity = 1.5, //Liter
filledPercentage = 0;
}Attributes
2- Object-oriented programming
Methods
class Bottle {
float bottomRadius = 2.5f;
int height = 12;
int capRaduis = 1;
float neckRaduis = 1.5f;
float capacity = 1.5f; //Liter
float filledPercentage = 0f;
//methods
void fillBottle(amount) {
this.filledPercentage += ((amount * 100) / capacity) % 100;
}
void waterSpill(amount) {
this.filledPercentage -= ((amount * 100) / capacity) % 100;
}
}
2- Object-oriented programming
Constructor & new
What is a constructor ?

Not this one
A constructor is a special method that is used to initialize a newly created object and is called just after the memory is allocated for the object. It can be used to initialize the objects to desired values or default values at the time of object creation.
class Bottle {
public double bottomRadius,
height,
capRaduis,
neckRaduis,
capacity,
filledPercentage;
//constructor
public Bottle() {
bottomRadius = 2.5f;
height = 12;
capRaduis = 1;
neckRaduis = 1.5f;
capacity = 1.5f;
filledPercentage = 0f;
}
//the rest of the methods
}Important !!!
the constructor can only be declared using the class Name.
2- Object-oriented programming
Constructor & new
how to use the Constructor ?
ClassName varName = new ClassName();The word new is the one who calls the Constructor to create the object or what we Call an Instance.
Bottle bottle = new Bottle();
Example
2- Object-oriented programming
this
this is used to let the computer knows the variable name you are using belongs to the class of this object.
class Bottle
{
double bottomRadius = 2.5,
height = 12,
capRaduis = 1,
neckRaduis = 1.5,
capacity = 1.5,
filledPercentage = 0;
//methods
void fillBottle(double capacity)
{
filledPercentage += (capacity * 100 / this.capacity) % 100;
}
}We can see that we have capacity as a parameters and as an attribute. so to make the difference we use the word this to show the program which one belongs to the object.
Coding with C# Part-2
Polymorphism & methods
Polymorphism & constructors
constructors calling another
3- Parametric Polymorphism
What is Polymorphism ?
3- Parametric Polymorphism
What is Polymorphism ?
Poly : means many
morph: means forms
Polymorphism is the ability of an object to take on many forms.

3- Parametric Polymorphism
Polymorphism & methods
the use of Polymorphism in methods is to let you create a method with the ability to change it's work depending on it's parameters .
class Math
{
double max(double x, double y)
{
if (x > y) return x;
else return y;
}
int max(int x, int y)
{
if (x > y) return x;
else return y;
}
}3- Parametric Polymorphism
Polymorphism & constructors
the use of Polymorphism in constructors is pretty much the same as it with methods.
it's used for the cases that your object can have a default attributes or changeable attributes.
class Bottle
{
double height;
Bottle()
{
height= 12;
}
Bottle(double height)
{
this.height = height;
}
}3- Parametric Polymorphism
constructors calling another
we can call another constructor using the form bellow .most of the time we use it if there is commune instruction between them to reduce repetition.
class Bottle
{
double bottomRadius,
height;
Bottle()
{
this.bottomRadius = 2.5;
this.height = 0;
}
Bottle(int height) : this()
{
this.height = height;
}
}ClassName(prms1) : this(prms2) {
//code
}Coding with C# Part-2
what is Inheritance ?
how to use inheritance ?
Virtual Method
4- Inheritance
4- Inheritance
what is Inheritance ?
In object-oriented programming, inheritance is the mechanism of basing an object or class upon another object or class, retaining similar implementation. Also defined as deriving new classes from existing ones and forming them into a hierarchy of classes
The definition of inherit is to receive something, such as money, an asset, or a problem or characteristic from someone else. An example of inherit is when you born you take the characteristics of your parents.
4- Inheritance
how to use inheritance ?
class parent{
//code
}
class child : parent{
//code
}the ":" means that the child have the parent's attributes and methods now. without writing them again.
4- Inheritance
Virtual Method
class parent
{
void talk()
{
Debug.Log("wise speach");
}
}
class child : parent
{
void talk()
{
Debug.Log("stupid speach");
}
}We can override the method in the parent class by creating it again in the child.
Coding with C# Part-2
What is an Access modifier ?
public word
internal word
private word
5- Access modifier
protected word
5- Access modifier
What is an Access modifier ?
Access modifiers (or access specifiers) are keywords in object-oriented languages that set the accessibility of classes, methods, and other members.
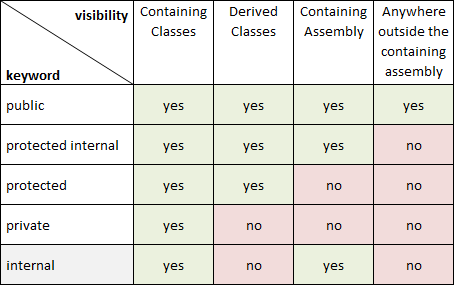
5- Access modifier
public word
The type or member can be accessed by any other code in the same assembly or another assembly that references it.
5- Access modifier
internal word
The type or member can be accessed by any code in the same assembly, but not from another assembly.
5- Access modifier
protected word
The type or member can be accessed only by code in the same class, or in a class that is derived from that class (inheritance).
5- Access modifier
private word
The type or member can be accessed only by code in the same class or struct.