SCIST S5
演算法推廣課程
2024/09/15
講者:士育(4Yu)課前準備
-
開啟 Google 登入 Discord 帳號
並加入 SCIST 伺服器:https://discord.gg/g6qfD4Wk9j -
領取課程頻道 輸入代碼:S5_pro_Algo
-
登入或註冊好 ZeroJudge 帳號
並參加課程,代碼:5a4zWF -
開啟 OnlineGDB 等等寫程式用
-
開啟今天的 即時匿名提問平台 Slido

自我介紹
ShiYu{4Yu}
- SCIST 南臺灣學生資訊社群 S5 演算法總召
- 南大附中資訊研究社第一屆 NFIRC 1st 創辦人|社長
- 南 9 校資訊社 x SCIST x 成大資工 2024 聯合寒訓 副召
- APCS 觀念 4 級/實作 4 級
- CPE 大學程式能力檢定 專業級 前 7 %
- 112 學年度學科能力競賽南區複賽 資訊科 佳作
- 第 11 屆高一生程式設計排名賽 實體組 第 8 名
- 台大資訊之芽南區算法班學員
- 一日資訊體驗營 總召 兼 台南 & 台中場 講師
- 南四校聯合社課 副召 兼 人工智慧課程 講師
- APCS Simulation x APCS Guide Camp 行政團隊
- 2024 FUN AI WINTER CAMP 個人特優
- AIS3 Junior 2024 最佳專題獎
個人網站:https://4yu.dev/

課程目的
-
推廣程式設計與演算法
-
提供免費入門課程
-
培訓課程的試辦場
-
帶你踏入資訊領域
今日課程
9:00~9:30
SCIST 介紹
14:00~17:00
基礎資料結構與演算法
9:30~12:00
C++ 程式語法
12:30~14:00
午餐時間
17:00~17:30
大合照、QA
學員程度
初學者
-
跟隨著課程內容學習
-
有問題舉手提出或匿名問答
已有基礎
-
可利用簡報預習、自學
-
先試著自行練習題單
程式電神
-
應該不需要聽這堂課 -
可以協助身邊的學員

南臺灣學生資訊社群
Students' Community of Information in Southern Taiwan
由嘉義、台南、高雄、屏東等四地高中生組成的學生自治資訊教育社群。
長期透過舉辦課程與活動推廣資訊領域,減少南北資訊領域的資源落差。
爲南部提供一個良好的學習環境,提升南部學生整體的資訊能力。
SCIST 總覽
行政招募
7 月
推廣課程
9 月
培訓課程
每年 10 月 ~ 隔年 6 月
多元主題工作坊(暫)
暑假
聯合營隊
寒假
資訊社團合作、社課支援
長期
南部多校聯合寒訓
-
課程
-
演算法
-
資訊安全
-
-
闖關活動
-
晚會表演
-
科技公司講座
-
經驗分享講座

副召籌辦心得文
(我拖到現在還沒寫完
但有一堆照片可以看)
培訓課程
-
免費課程
-
演算法
-
資訊安全
-




C++ 基礎語法
-
基本架構
-
輸入輸出
-
變數
-
運算子
-
條件判斷式
-
迴圈(for、while)
-
陣列
-
實作與進階應用
C++ 基本架構
要運行 C++ 最基本必須寫的一段程式碼
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 你的程式寫在這
return 0;
}1. 導入標頭檔,裡面包含各種功能
2. 使用標準命名空間,簡化接下來的程式碼
4. 主函式,在程式中會先被執行
6. // 是註解,可替換成你想寫的程式碼
7. 回傳結束程式
輸出
cout 可以讓電腦印出你想說的話
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Hello, SCIST!";
return 0;
}
文字串請用 " " 包起來
輸出
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Hello SCIST " << 5 << "th";
return 0;
}
可以用 << 串接合併多個東西
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Hello,\nSCIST S5\n";
return 0;
}可以用 \n 換行


隨堂練習
d483
輸入
電腦執行程式時你可以輸入東西給他做運算
但輸入時要儲存在哪裡呢?
變數
變數
可以把變數想像成一個容器,儲存各種資料,且有可變性
每個變數都有以下屬性:
- 型別 type:代表它適合裝什麼,這堂課會介紹不同型別
- 名稱 name :為變數取個名稱,用來區別不同的變數
- 值 value:變數裡頭裝的東西,會是一個符合變數型別的數值
- 位址 address :該變數被放在記憶體的哪裡
(之後如果有機會才會教到 先不用理 address)
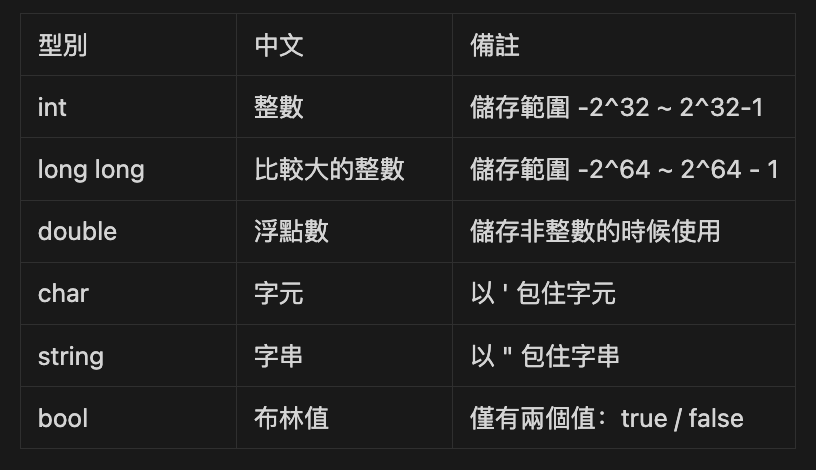
變數 - 型別
簡單用表格介紹一下不同的型別
無法馬上都背起來沒關係
之後會慢慢用到
使用變數之前一定要先宣告
宣告方法:型別 變數名稱
宣告
int number;
string name;賦值 assign
給變數存入值的行為
我們稱為 賦值 ,= 為 賦值運算子
int number = 4;
string name = "ShiYu";初始化:宣告變數同時賦值
注意!變數還沒賦值時 絕對不要讀取這個變數的值
可能會導致無法預期的結果
輸入
輸出是用 cout <<
那輸入呢?
cin >>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
cin >> name;
cout << "Hello, " << name << "!\n";
return 0;
}
隨堂練習
a001
運算子
算術
-
+
-
-
-
*
-
/
-
%
比較
-
>
-
<
-
==
-
>=
-
<=
-
!=
邏輯
-
&&
-
||
-
!
因為 5 / 2 = 2 ... 1
所以 5 % 2 = 1
% (MOD):取餘數
隨堂練習
a002、d827
賦值
-
=
-
+=
-
-=
-
*=
-
/=
-
%=
遞
-
++
-
--
n = n + 1
是 n += 1
也是 n++
出錯了?
- 忘記加分號 ;
- 字拼錯或是全形與半形不分
- 忘記宣告變數
- cin、cout 箭頭方向記相反
- 括號用錯種類、忘記加或加錯地方
常見錯誤
請養成良好的
程式碼撰寫習慣
程式語法和邏輯都沒寫錯
但沒縮排沒空格閱讀起來較困難
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
cout<<a+b+c<<"\n";
return 0;}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
cout << a + b + c << "\n";
return 0;
}適時的空格與縮排有助於閱讀與除錯
題外話(宗教戰爭):
大括號到底要不要下放?
下放
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Hello, SCIST!";
return 0;
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello, SCIST!";
return 0;
}! 下放

請在 Discord 投票並在聊天室說出理由
成大邀請賽的 Judge 要下放才會 AC
條件判斷式
符合特定條件就執行特定程式碼
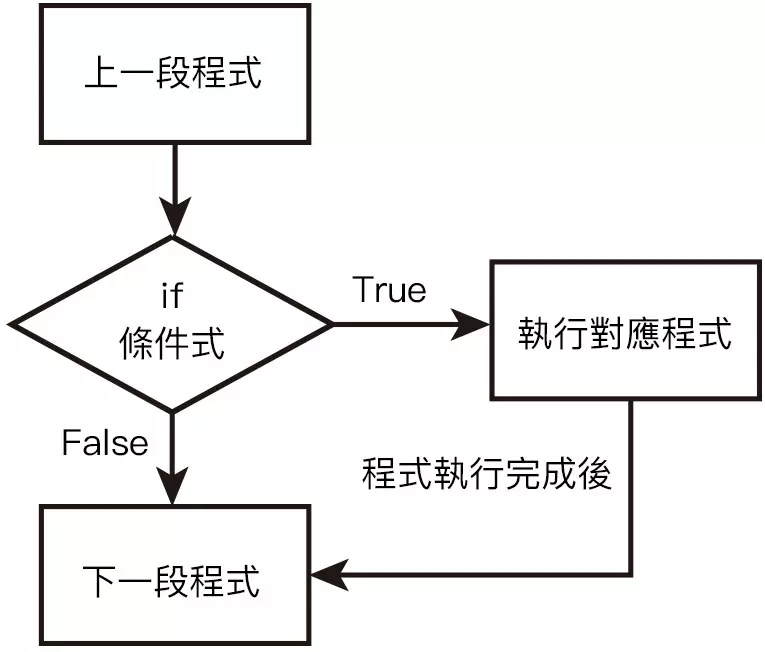
條件判斷式
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int score;
cin >> score;
if (score >= 60) {
cout << "你及格了!\n";
} else if (score < 40){
cout << "你被死當了\n哈哈";
} else {
cout << "你要去補考\n加油!";
}
return 0;
}隨堂練習
d064、d058
輸出 1 ~ 10
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout << "1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10\n";
}輸出 1 ~ 100
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout << "1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45
46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75
76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90
91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100\n";
}

迴圈
for 迴圈
重複執行
固定次數
while 迴圈
重複執行直到不符合條件為止
輸出 1 ~ n
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n; cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i <= n; i++){
cout << i << ' ';
}
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n; cin >> n;
int i = 1;
while(i <= n){
cout << i << ' ';
i++;
}
}for 迴圈
while 迴圈
隨堂練習
d498、d046
迴圈的流程控制
continue
跳過此次
繼續執行下一次
break
中斷並退出迴圈
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
for (int i=1; i<=15; i++){
if (i % 3 == 0){
continue;
} else {
cout << i << ' ';
}
}
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
for (int i=1; i<=15; i++){
if (i*i >= 100){
break;
} else {
cout << i * i << ' ';
}
}
}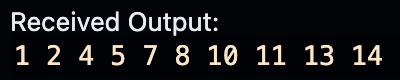
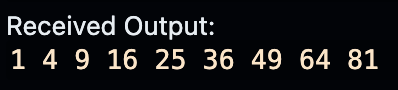
可以用 continue 跳過某個倍數
可以用 break
在數字滿 100 時結束迴圈
輸入 3 個數字
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
}輸入 100 個數字
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j,k,l,m,n,o,p,q,r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d >> e >> f >> g
>> h >> i >> j >> k >> l >> m >> n
>> o >> p >> q >> r >> s >> t >> u
>> v >> w >> x >> y >> z;
}

英文字母都不夠用了
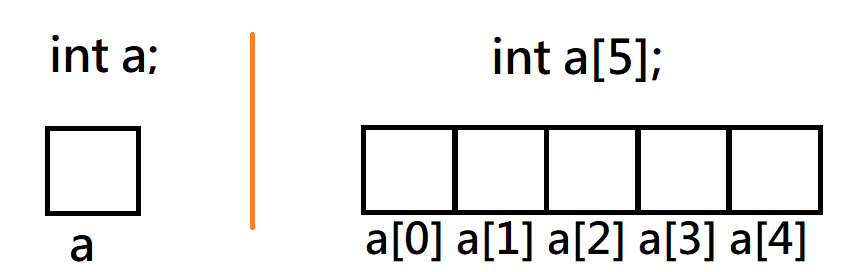
陣列
變數
陣列
可連續儲存大量相同型別的資料
宣告與輸入
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a;
cin >> a;
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[100];
for (int i=0; i<100; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
}