Using Principal Component Analysis to Improve Accessibility
Ben Simondet
University of Minnesota - Morris
April 30, 2016
Outline
Introduction
- What's the problem?
Background
- What is PCA?
- How does PCA work?
Ways PCA Can Help
- Facial Recognition
- Emotion Recognition
- Eye Tracking
Conclusions
Introduction
Background
Methods
Conclusions
Introduction
A Normal Day
- Knock on the door
- What do you do?
- What if that's not easy?

A Normal Day

- What if you go to have a conversation with a friend?
- What if you can't figure out what they're feeling?
What's the problem?

- User Experiences
- Limitations
- Diversity
Introduction
Background
Methods
Conclusions
Background
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Tons of Applications
- Statistics
- Facial Recognition
- Neuroscience
- Increasing Accessibility?
- Data Simplification
- Predictor Models
PCA Algorithm
- Find principal components
- Evaluate eigenvalues
- Re-plot data
Finding Principle Components
Finding Principle Components

Finding Principle Components

First Principal Component
Finding Principle Components

Second Principal Component
Evaluate Eigenvalues

Large eigenvalues = More influence
Large eigenvalues = More influence
Small eigenvalues
= Less influence
Finding Principle Components

Finding Principle Components

x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
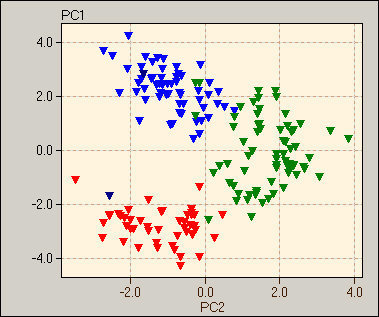
Evaluate Eigenvalues
2-D to 1-D Graph
120-D (not possible as a physical graph)
to 2(or 3)-D Graph
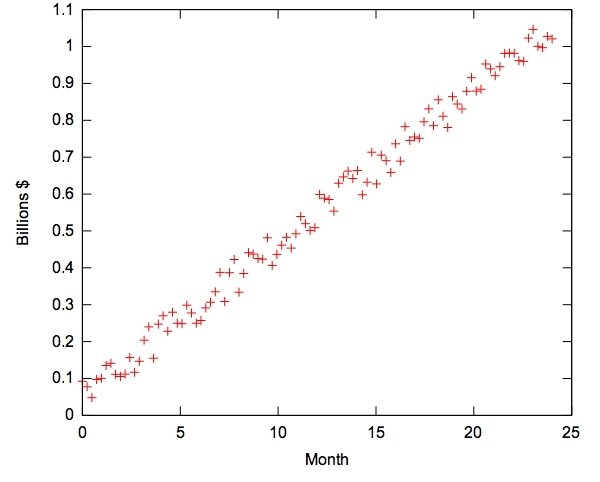
Re-plot Data
| Billions | Month | Eigenvalue |
|---|---|---|
| .66 | 11 | 2 |
X=11*2
Y=.66*2
(22,1.32)
Re-plot Data
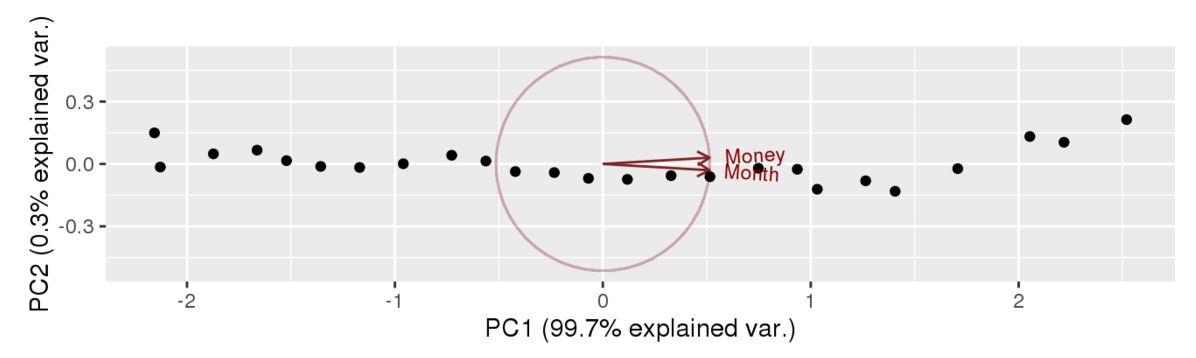
Re-plot Data
Introduction
Background
Methods
Conclusions
Methods
Facial Recognition
Emotion Recognition
Eye Tracking
Method 1:
Facial Recognition
Facial Recognition
- One of the most common uses for PCA
- Human face has a set of features
-
Remote Door Access
- Physical and Memory Assistance

Facial Recognition
- Physical
- Allow user to know who is at the door
- Automatically let in specific people
- Grant people door access without needing to go to the door
- Memory
- Ability to assign friendly nicknames to visitors to improve future memory
Application: Web Based Door Access
Facial Recognition
- Very similar to base PCA algorithm
- Image processing steps to accomplish
Algorithm Change

Facial Recognition
- Eigenfaces
- Mean Face
Algorithm Change

Facial Recognition
Emotion Recognition
Eye Tracking
Method 2:
Emotion Recognition
Emotion Recognition
- Similar to face recognition
- Specific parts of the face
- Change faces to make emotions
- Tons of applications
- Augmented Reality - Identify emotions of those around the user
- Emotion Training - Identify emotions in a flash card format

Emotion Recognition
Application: Assistance with Emotion Recognition
- Adults and children with Autism Spectrum Disorder tend to struggle when identifying emotions of others (Rump, Giovannelli, 2011)
- After some practice, this can improve
- Augmented Reality
- Practice
Emotion Recognition
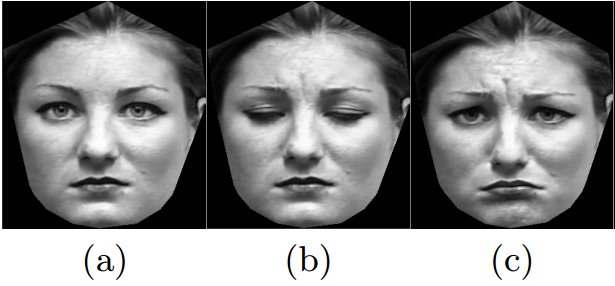
Application: Assistance with Emotion Recognition

- 94 points on each face
- Same people make different emotions
- Joy, Surprise, Disgust, Fear, Anger, Sorrow
Emotion Recognition
Application: Assistance with Emotion Recognition
- Currently existing face databases don't show emotion
- Modifying emotion increases access
- Also provides labeled data for flash cards
Facial Recognition
Emotion Recognition
Eye Tracking
Method 3:
Eye Tracking
Eye Tracking
- Eyes move differently in those with ASD
- Pupil movement can be plotted using PCA
- Early detection and diagnosis of ASD (Mlouka and Martineau, 2014)
- Replacement for mouse/keyboard
Eye Tracking
Application: Assistance with ASD Diagnosis
- Measuring gaze patterns/blinks
- Focus times
- Reaction times
Eye Tracking
Application: Assistance with ASD Diagnosis
Introduction
Background
Methods
Conclusions
Conclusions
Conclusions
Current Obstacles
- Lack of commercial solutions
- Homemade/small-scale
- Availability
- Large data sets

Conclusions
What does the future hold?
- Smart homes
- Wider availability
- More computing power
- Endless possibilities!

References
- "Synthesis of emotional expressions specific to facial structure" - Agarwal, Chatterjee, Mukherjee
- "Face recognition using face-autocropping and facial feature points extraction" - Karmakar, Murthy
- "Face recognition and facial expression identification using pca" - Meher, Maben
- "Principal component analysis of eye-tracking data during visual perception of human faces in aduls and children with autism" - Mlouka, Martineau
- "The development of emotion recognition in individuals with autism" - Rump, Giovannelli
- "Web-based online embedded door access control and home security system based on face recognition" - Sahani, Nanda, Sahu, and Pattnaik