Project: A Programming Language
為了練習寫程式語言,所以我們自己寫一個程式語言(X
Lecturer: 土豆
Note & TA: 丰嘉
大綱
- 程式語言運作原理
- 實作目標
- Parsing
- 實作 - if
- 實作 - print
- 實作 - operators
- 實作 - do
- 實作 - define
- 實作 - while
- 實作 - fun
- 課後練習
- 參考資料
測試環境
- Windows 10
- Node.js(13.3.0)
凡例
Egg_lan
JavaScript
do(define(x, 10),
if(>(x, 5),
print("large"),
print("small")))function skipSpace(string) {
let first = string.search(/\S/);
if (first == -1) return "";
return string.slice(first);
}今日程式碼
程式語言運作原理

?
編譯器
編譯器如何運作?
1. Lexing: 將程式碼拆解成Token(e.g. ==, +, -, if, while, x...)
while b ≠ 0
if a > b
a := a − b
else
b := b − a
return awhile
b
!=
0
if
a
>
b
...以下省略...
編譯器如何運作?
2. Parsing: 將Token轉換為parse tree
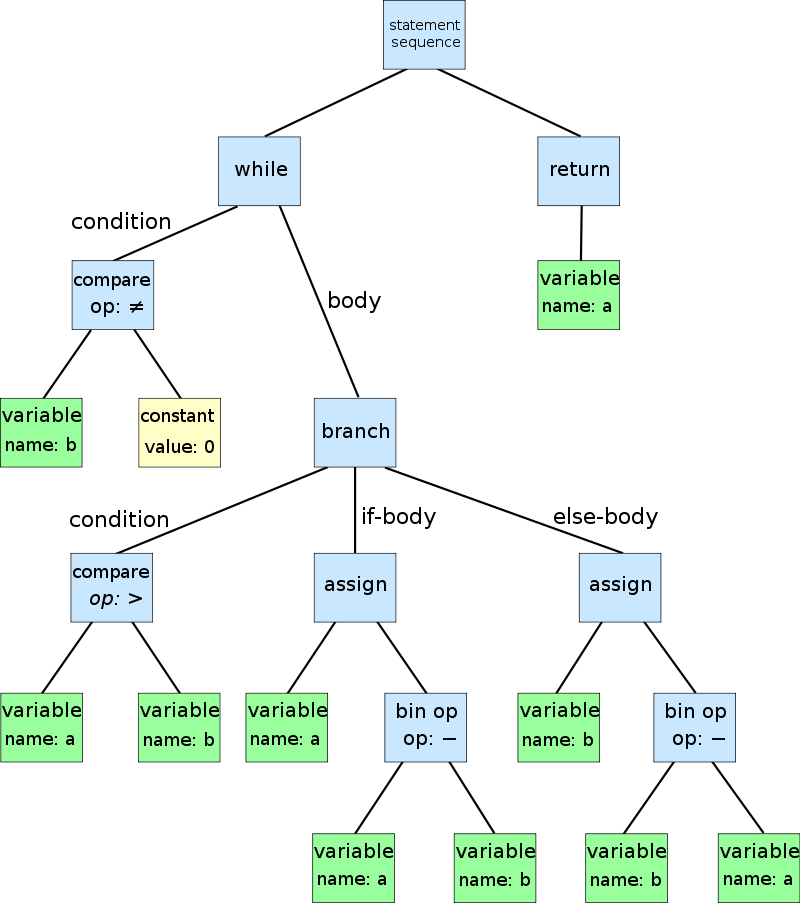
編譯器如何運作?
3. Optimization: 優化程式
4. 將parse tree轉換為machine code
創造一個程式語言
=
寫一個編譯器
=
寫一個幫你處理程式碼,並將其轉換為machine code的程式
實作目標
Egg語言
do(define(x, 10),
if(>(x, 5),
print("large"),
print("small")))寫一個程式,解析Egg語言,並輸出其結果
do(define(x, 10),
if(>(x, 5),
print("large"),
print("small")))Output:
"large"
本次實作程式
Egg interpreter
程式架構
- parsing: 解析egg程式碼,轉換為parse tree
- specialForms: 存放if、while、define等功能的物件
- topScope: 存放變數、operator、print的物件
- evaluate: 執行parse tree的function
- 執行程式
程式架構
// TODO Parsing
const specialForms = Object.create(null);
const topScope = Object.create(null);
// TODO evaluate
// runParsing
目標: parse tree
do(define(x, 10),
if(>(x, 5),
print("large"),
print("small")))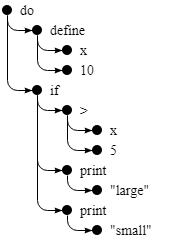
{
type: "apply",
operator: {type: "word", name: ">"},
args: [
{type: "word", name: "x"},
{type: "value", value: 5}
]
}parseExpression
function parseExpression(program) {
program = skipSpace(program);
let match, expr;
if (match = /^"([^"]*)"/.exec(program)) {
expr = {type: "value", value: match[1]};
} else if (match = /^\d+\b/.exec(program)) {
expr = {type: "value", value: Number(match[0])};
} else if (match = /^[^\s(),#"]+/.exec(program)) {
expr = {type: "word", name: match[0]};
} else {
throw new SyntaxError("Unexpected syntax: " + program);
}
return parseApply(expr, program.slice(match[0].length));
}- 跳過開頭多餘空白
- 篩選String、Number、Word
- 處理Application
parseExpression
function skipSpace(string) {
let first = string.search(/\S/);
if (first == -1) return "";
return string.slice(first);
}跳過開頭多餘空白
parseExpression
1. String: /^"([^"]*)"/
2. Number: /^\d+\b/
3. Word: /^[^\s(),#"]+/
Regular Expression
parseApply
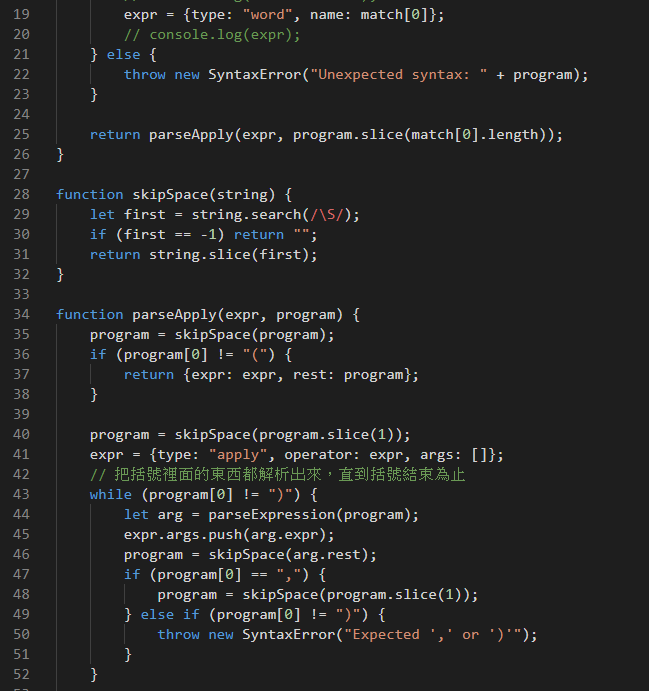
function parseApply(expr, program) {
program = skipSpace(program);
if (program[0] != "(") {
return {expr: expr, rest: program};
}
program = skipSpace(program.slice(1));
expr = {type: "apply", operator: expr, args: []};
// 把括號裡面的東西都解析出來,直到括號結束為止
while (program[0] != ")") {
let arg = parseExpression(program);
expr.args.push(arg.expr);
program = skipSpace(arg.rest);
if (program[0] == ",") {
program = skipSpace(program.slice(1));
} else if (program[0] != ")") {
throw new SyntaxError("Expected ',' or ')'");
}
}
// 再解析一遍,看看後面沒有別的括號
return parseApply(expr, program.slice(1));
}parseApply
- 如果開頭不是左括號,就不處理它
- 解析括號內的東西,直到右括號為止
- 用parseExpression解析出參數
- 再解析一遍,確認後面有沒有別的括號
跑跑看
function parse(program) {
let {expr, rest} = parseExpression(program);
if (skipSpace(rest).length > 0) {
throw new SyntaxError("Unexpected text after program");
}
return expr;
}
console.log(parse("+(a, 10)"));
/*
{type: "apply",
operator: {type: "word", name: "+"},
args: [{type: "word", name: "a"},
{type: "value", value: 10}]}
*/用腦袋跑跑看
// e.g.
parse("+(a, 10)")
parseExpression("+(a, 10)")
parseApply({type: "word", name: "+"}, "(a, 10)")
expr = {
type: "apply",
operator: {type: "word", name: "+"},
args: []
}
parseExpression(...)
expr = {
...
}
...把每個function call的參數,還有expr的變化寫出來
用腦袋跑跑看
expr = {
type: "apply",
operator: {type: "word", name: "+"},
args: []
}+(a, 10)
(a, 10)
a, 10)
10)
{type: "word", name: "+"}expr = {
type: "apply",
operator: {type: "word", name: "+"},
args: [{type: "word", name: "a"}]
}expr = {
type: "apply",
operator: {type: "word", name: "+"},
args: [{type: "word", name: "a"},
{type: "value", value: 10}]
}實作 - if
if(true, true, false)完整程式碼
evaluate
function evaluate(expr, scope) {
if (expr.type == "value") {
return expr.value;
} else if (expr.type == "word") {
if (expr.name in scope) {
return scope[expr.name];
} else {
throw new ReferenceError(`Undefined binding: ${expr.name}`);
}
} else if (expr.type == "apply") {
let {operator, args} = expr;
if (operator.type == "word" &&
operator.name in specialForms) {
return specialForms[operator.name](expr.args, scope);
} else {
let op = evaluate(operator, scope);
if (typeof op == "function") {
return op(...args.map(arg => evaluate(arg, scope)));
} else {
throw new TypeError("Applying a non-function.");
}
}
}
}evaluate
- 如果是value就直接回傳value的值
- 如果是word,在scope中尋找符合的結果
- 如果是apply
- 如果type是word,而且operator是合法的
- 執行特定動作
- 如果是function則執行function,否則跳error
- 如果type是word,而且operator是合法的
specialForms.if
specialForms.if = (args, scope) => {
if (args.length != 3) {
throw new SyntaxError("Wrong number of args to if");
} else if (evaluate(args[0], scope) !== false) {
return evaluate(args[1], scope);
} else {
return evaluate(args[2], scope);
}
}定義if
topScope
topScope.true = true;
topScope.false = false;定義true、false
執行
let prag = parse(`if(false, false, true)`);
/*
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'if' },
args: [
{ type: 'word', name: 'false' },
{ type: 'word', name: 'false' },
{ type: 'word', name: 'true' }
]
}
/*先取得parse tree
console.log(evaluate(prag, topScope));evaluate運算
實作 - print
if(false, print("It's true!"), print("It's false!"))完整程式碼
topScope加上這段就行
topScope.print = value => {
console.log(value);
return value;
}執行
let prag = parse(`if(false, print("It's true!"), print("It's false!"))`);
/*
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'if' },
args: [
{ type: 'word', name: 'false' },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] }
]
}
args[1]
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'print' },
args: [ { type: 'value', value: "It's true!" } ]
}
args[2]
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'print' },
args: [ { type: 'value', value: "It's false!" } ]
}
*/先取得parse tree
執行
// 因為有print了,就不用console.log
evaluate(prag, topScope);evaluate運算
執行
// -------------Add run-------------------
function run(program) {
let parse_tree = parse(program);
return evaluate(parse_tree, Object.create(topScope));
}
// ------------------------------------------
run(`if(false, print("It's true!"), print("It's false!"))`); // Modify this 把執行流程寫成function
實作 - operators
print(+(1, 2))完整程式碼
topScope
for (let op of ["+", "-", "*", "/", "==", "<", ">"]) {
topScope[op] = Function("a, b", `return a ${op} b;`)
}定義operators
Function物件可產生動態function
parse tree
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'print' },
args: [
{ type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: '+' },
args: [ { type: 'value', value: 1 },
{ type: 'value', value: 2 } ]
}
]
}evaluate
function evaluate(expr, scope) {
if (expr.type == "value") {
return expr.value;
} else if (expr.type == "word") {
if (expr.name in scope) {
return scope[expr.name];
} else {
throw new ReferenceError(`Undefined binding: ${expr.name}`);
}
} else if (expr.type == "apply") {
let {operator, args} = expr;
if (operator.type == "word" &&
operator.name in specialForms) {
return specialForms[operator.name](expr.args, scope);
} else {
let op = evaluate(operator, scope);
if (typeof op == "function") {
return op(...args.map(arg => evaluate(arg, scope)));
} else {
throw new TypeError("Applying a non-function.");
}
}
}
}{ type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: '+' },
args: [ { type: 'value', value: 1 },
{ type: 'value', value: 2 } ]
}實作 - do
do(print(+(1, 2)),
print(==(2, 2)),
print(-(3, 2))
)完整程式碼
parse tree
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'do' },
args: [
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] }
]
}
args[0]
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'print' },
args: [ { type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: '+' },
args: [ { type: 'value', value: 1 },
{ type: 'value', value: 2 } ]
} ]
}
args[1]
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'print' },
args: [ { type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: '==' },
args: [ { type: 'value', value: 2 },
{ type: 'value', value: 2 } ]
} ]
}
args[2]
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'print' },
args: [ { type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: '-' },
args: [ { type: 'value', value: 3 },
{ type: 'value', value: 2 } ]
} ]
}specialForms.do
specialForms.do = (args, scope) => {
let value = false;
for (let arg of args) {
value = evaluate(arg, scope);
}
return value;
};加上這段
specialForms.do
specialForms.do = (args, scope) => {
let value = false;
for (let arg of args) {
value = evaluate(arg, scope);
}
return value;
};{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'do' },
args: [
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] }
]
}實作 - define
do(define(x, 10),
if(>(x, 5),
print("x is greater then 5"),
print("x is smaller then 5")
)
)完整程式碼
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'define' },
args: [ { type: 'word', name: 'x' }, { type: 'value', value: 10 } ]
}parse tree
specialForms.define = (args, scope) => {
if (args.length != 2 || args[0].type != "word") {
throw new SyntaxError("Incorrect use of define");
}
let value = evaluate(args[1], scope);
scope[args[0].name] = value;
return value;
};specialForms.define
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'define' },
args: [ { type: 'word', name: 'x' }, { type: 'value', value: 10 } ]
}實作 - while
do(define(x, 0),
while(<(x, 10),
do(define(x, +(x, 1)),
print(x)
)
)
)完整程式碼
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'while' },
args: [
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] }
]
}
args[0]
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: '<' },
args: [ { type: 'word', name: 'x' },
{ type: 'value', value: 10 } ]
}
args[1]
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'do' },
args: [
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] }
]
}parse tree
specialForms.while = (args, scope) => {
if (args.length != 2) {
throw new SyntaxError("Wrong number of args to while");
}
while (evaluate(args[0], scope) !== false) {
evaluate(args[1], scope);
}
return false;
};specialForms.while
實作 - fun
do(define(plusOne, fun(a, +(a, 1))),
print(plusOne(10)))完整程式碼
parse tree
{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'fun' },
args: [
{ type: 'word', name: 'a' },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] }
]
}specialForms.fun
specialForms.fun = (args, scope) => {
if (!args.length) {
throw new SyntaxError("Functions need a body");
}
let body = args[args.length - 1];
let params = args.slice(0, args.length - 1).map(expr => {
if (expr.type != "word") {
throw new SyntaxError("Parameter names must be words");
}
return expr.name;
});
return function() {
if (arguments.length != params.length) {
throw new TypeError("Wrong number of arguments");
}
let localScope = Object.create(scope);
for (let i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
localScope[params[i]] = arguments[i];
}
return evaluate(body, localScope);
};
};specialForms.fun
specialForms.fun = (args, scope) => {
if (!args.length) {
throw new SyntaxError("Functions need a body");
}
let body = args[args.length - 1];
let params = args.slice(0, args.length - 1).map(expr => {
if (expr.type != "word") {
throw new SyntaxError("Parameter names must be words");
}
return expr.name;
});
// return ...
};{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'fun' },
args: [
{ type: 'word', name: 'a' },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] }
]
}specialForms.fun
specialForms.fun = (args, scope) => {
// ...
return function() {
if (arguments.length != params.length) {
throw new TypeError("Wrong number of arguments");
}
let localScope = Object.create(scope);
for (let i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
localScope[params[i]] = arguments[i];
}
return evaluate(body, localScope);
};
};{
type: 'apply',
operator: { type: 'word', name: 'fun' },
args: [
{ type: 'word', name: 'a' },
{ type: 'apply', operator: [Object], args: [Array] }
]
}global
true
false
opt
if
local
a
課後練習
實作Array
// Modify these definitions...
topScope.array = "...";
topScope.length = "...";
topScope.element = "...";
run(`
do(define(sum, fun(array,
do(define(i, 0),
define(sum, 0),
while(<(i, length(array)),
do(define(sum, +(sum, element(array, i))),
define(i, +(i, 1)))),
sum))),
print(sum(array(1, 2, 3))))
`);
// → 6實作Comments
// This is the old skipSpace. Modify it...
function skipSpace(string) {
let first = string.search(/\S/);
if (first == -1) return "";
return string.slice(first);
}
console.log(parse("# hello\nx"));
// → {type: "word", name: "x"}
console.log(parse("a # one\n # two\n()"));
// → {type: "apply",
// operator: {type: "word", name: "a"},
// args: []}參考資料
1. Project: A Programming Language. Eloquent JavaScript. 2019/12/14 from: https://eloquentjavascript.net/12_language.html
2. How Does A Compiler Work? [closed]. stackexchange. 2019/12/14 from: https://softwareengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/118586/how-does-a-compiler-work
3. Abstract syntax tree. Wikipedia. 2019/12/14 from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abstract_syntax_tree
4. Programming language. Wikipedia. 2019/12/14 from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Programming_language