Web Components.
Are we there yet?
live slides: goo.gl/ofHnzr
<video>
<h1>
<h2>
<h3>
<h4>
<h5>
<DIV>
<p>
<span>
<article>
<A>
<BODY>
<HEAD>
<STRONG>
<input>
<SELECT>
<TEXTAREA>
<IMG>
<UL>
<HTML>
<TITLE>
<meta>
<AUDIO>
<BUTTON>
<video>
<video width="480" controls poster="webmvp8.gif">
<source src="webmvp8.webm" type="video/webm">
<source src="webmvp8_512kb.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="webmvp8.ogv" type="video/ogg">
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 video tag.
</video>attributes
children elements
<VIDEO> HTML
<video> STRUCTURE
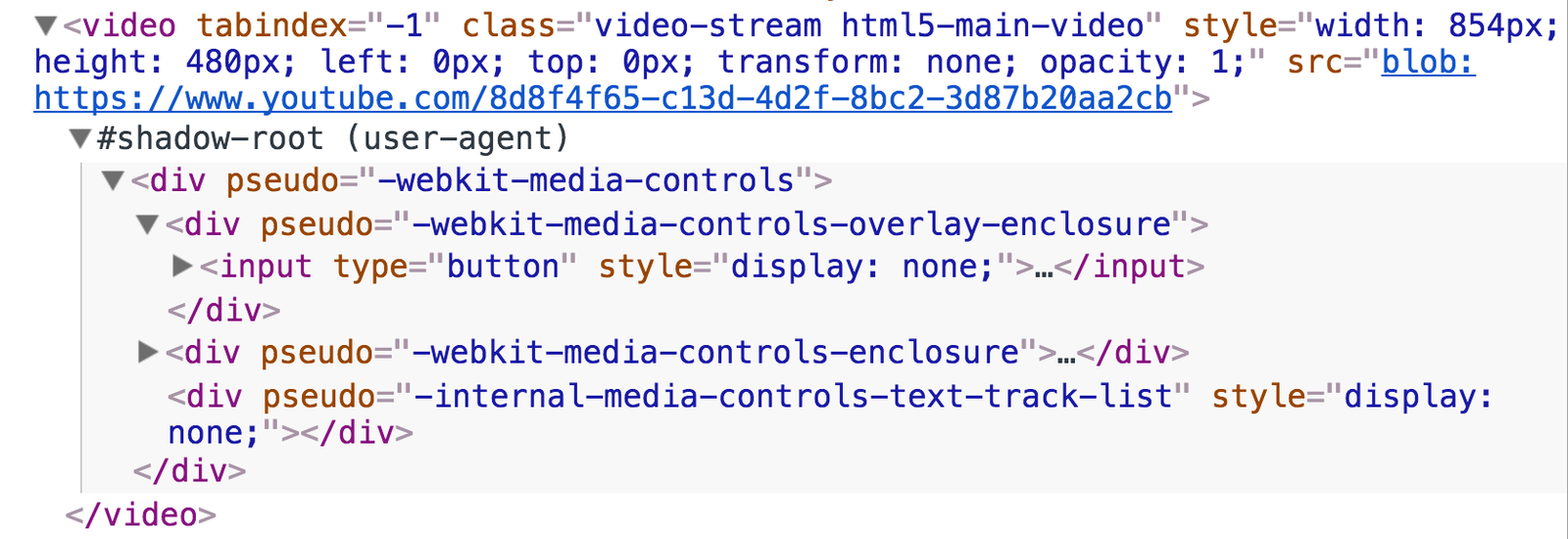
Internal structure
const video = document.createElement('video');video.play();
video.pause();video.addEventListener('loadedmetadata', ...);methods
events
<video> DOM
video.controls = true;
video.poster = 'image.png';properties
<video>
Inputs
Outputs
events
attributes
& properties
methods
play(), pause(),
etc...
src, poster, autoplay, etc..
internal DOM structure
canplay, pause, play, playing, ratechange, timeupdate, volumechange, error, etc...
<video> INTERFACE API
WHAT REALLY ARE
WEB COMPONENTS?
Four emerging specs
Custom Elements
Shadow DOM
Templates
HTML Imports
SHADOW DOM
Shadow DOM
Shadow DOM replaces element content with DOM subtree not directly connected to document.
ELEMENT
<p></p>
SHADOW DOM
ELEMENT
<p></p>
SHADOW DOM
<div>...
Shadow DOM
Style rules are scoped. CSS selectors like id and class do not apply to elements outside.
ELEMENT
<style>
#my-id { color: red }
</style>
<div id="my-id">
Text
</div>Shadow DOM
Shadow DOM Slot API allows flexibly distribute content to Shadow DOM.
ELEMENT
<div id="wrapper">
<slot name="title"></slot>
</div>
<slot></slot>Shadow DOM API
const div = document.createElement('div');
Or 'closed'
const shadowRoot = div.attachShadow({ mode: 'open' });div.shadowRoot === shadowRoot // For 'open' mode
shadowRoot instanceof DocumentFragment === true;
// We can add some content
shadowRoot.innerHTML = '<p>Some paragraph</p>';
div.children.length === 0; // trueCUSTOM ELEMENTS
CUSTOM ELEMENTS
Custom Elements API allows to define new elements.
<my-carousel swipe arrows>
<my-carousel-item name="Item 1">
<img src="image-1.png" />
</my-carousel-item>
<my-carousel-item name="Item 1">
<img src="image-1.png" />
</my-carousel-item>
</my-carousel>CUSTOM ELEMENTS API
class MyElement extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this.textContent = 'Sample text';
}
get something() { ... }
myMethod() { ... }
}customElements.define('my-element', MyElement);CUSTOM ELEMENTS API
- Attributes changes (attributeChangedCallback)
- El. added to DOM (connectedCallback)
- El. removed from DOM (disconnectedCallback)
- El. moved to another document (adoptedCallback)
standards
own standards
v33 (02/2014)
CUSTOM ELEMENTS V0

Shadow DOM V0
v25 (prefix) (02/2013), v35 (05/2014)
v40





in dev
v53
v10
in dev
Shadow DOM V1
v41





in dev
v54
in dev
in dev
Custom Elements V1
TEMPLATES
TEMPLATES
Templates declare fragments of DOM which can be activated later at runtime.
<template id="my-template">
<h1>Title</h1>
<img src="image.png" />
</template>deferred request
TEMPLATES
Templates are implemented in every modern browser.





v15
v22
v26
v7.1
v13
HTML Imports
HTML Imports
HTML Imports are a way of including HTML documents in other documents.
<head>
...
<link rel="import" href="bootstrap.html">
</head>HTML Imports
HTML file may contains styles, templates, scripts, css, etc...
<link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap.css">
<script src="jquery.js"></script>
<script src="bootstrap.js"></script>
...
<template id="my-element">...</template>
<script> customElements.define(...) </script>import 'bootstrap.css';
import jQuery from 'jquery';
import bootstrap from 'bootstrap';
const template = '...';
customElements.define(...);HTML Imports
Mozilla and Webkit will not implement html imports in favor of ES6 Modules.





v23
v36
U/C
Web Components
Web Components
<MY-ELEMENT>
Inputs
Outputs
events
attributes
& properties
prototype methods
attributeChangedCallback,
prototype properties
Shadow DOM
+ Template
custom events dispatched on element
instance
WEB COMPONENTS.
IS IT WORTH?
My THOUGHTS
The most important specifications are shipped,
in development or can be polyfilled/shimmed.
Web components are great way to unify
creating UI libraries.
Web components will never replace JS frameworks.


