\text{Chapter 4}
\text{Chapter 4}
\text{Chapter 4}
\text{Chapter 4}
\text{Dr. Adel Abbout}
\begin{aligned}
& \vec{v}=\vec{v}_0+\vec{a} t \\
& \vec{r}-\vec{r}_0=\vec{v}_0 t+\frac{1}{2} \vec{a} t^2
\end{aligned}
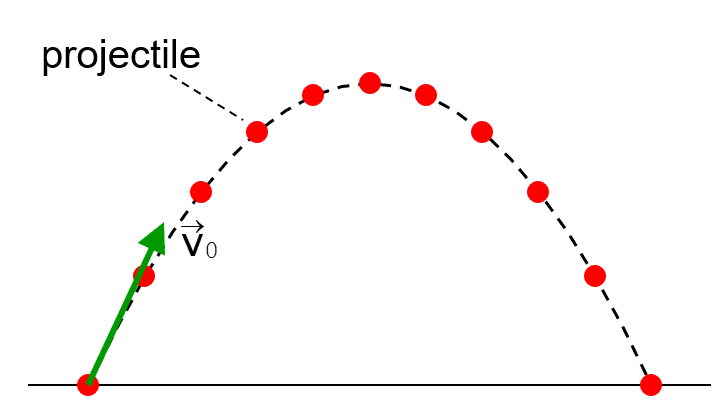
\begin{aligned}
& v_y=v_{0 y}-g t \\
& y-y_0=v_{0 y} t-\frac{1}{2} g t^2
\end{aligned}
x-x_0=v_{0 x} t
\text{Motion along x-axis is \textcolor{red}{uniform}}
v_{x}=\text{constante}=v_{0x}
\text{Trajectory equation}
y=\tan \theta_0 x-\frac{g}{2\left(v_0 \cos \theta_0\right)^2} x^2
R=\frac{v_0^2 \sin 2 \theta_0}{g}
H=\frac{v_0^2 \sin ^2 \theta_0}{2 g}
\text{Range}
\text{Max. Height}
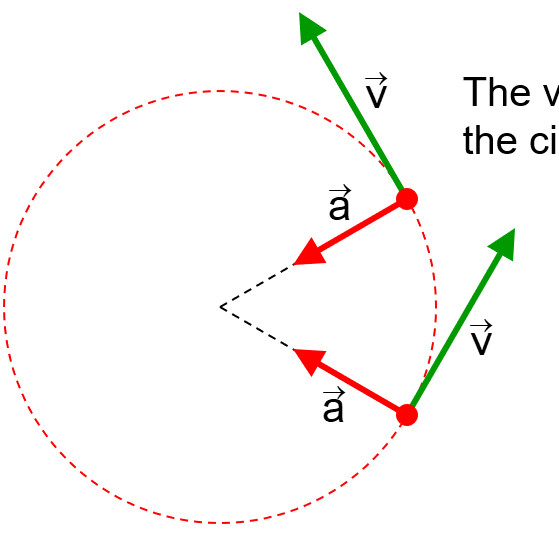
a=\frac{v^2}{r}
\text{Centripetal acceleration}
T=\frac{2 \pi r}{v}
\vec{v}_{P A}=\vec{v}_{P B}+\vec{v}_{B A}
\text{Period}
\text{Circular \textcolor{green}{uniform} motion}
\text{Moving reference}
\text{Constant acceleration motion}
\text{A particle is accelerated by air over a horizontal $xy$-plane with a constant acceleration}
\text{$\vec{a}=$ $(4.00 \hat{\imath}+8.00 \hat{\jmath}) \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^2$. At time $t=0$, the velocity is $(4.00 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}) \hat{\imath}$.}
\text{What is the speed of the particle at $t=1.65 \mathrm{~s}$ ?}
\text{A) 16.9 m/s}\\
\text{B) 16.2 m/s}\\
\text{C) 32.1 m/s}\\
\text{D) 20.4 m/s}\\
\text{E) 14.6 m/s}
\text{\textcolor{red}{A) 16.9 m/s}}\\
\text{B) 16.2 m/s}\\
\text{C) 32.1 m/s}\\
\text{D) 20.4 m/s}\\
\text{E) 14.6 m/s}
v_x=v_x^0+a_x t
v_y=v_y^0+a_y t
v_x=4+4 . 1.65=10.6 \text{ m/s}
v_y=0+8 1.65=13.2 \text{ m/s}
\displaystyle v=\sqrt{v_x^2+v_y^2}=\sqrt{10.6^2+13.2^2}=16.9 \text{ m/s}
\text{Motion with constant acceleration along the two axis:}
\Rightarrow
\text{A particle is accelerated by air over a horizontal $xy$-plane with a constant acceleration}
\text{$\vec{a}=$ $(4.00 \hat{\imath}+8.00 \hat{\jmath}) \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^2$. At time $t=0$, the velocity is $(4.00 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}) \hat{\imath}$.}
\text{What is the speed of the particle at $t=1.65 \mathrm{~s}$ ?}
\text{A projectile is fired from level ground with a speed of $12.0 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ at a target located at a height }
\text{\textcolor{black}{A) }}55.1^0\\
\text{B) }33.2^0\\
\text{C) }41.5^0\\
\text{D) }64.3^0\\
\text{E) }44.7^0
\text{$h=5.00 \mathrm{~m}$ above the ground as shown in Figure 2. The projectile's velocity to be horizontal}
\text{at the instant it reaches the target. }
\text{At what angle above the horizontal must the projectile be fired?}
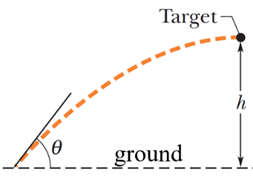
\displaystyle \theta=\sin^{-1}0.82=55.1^0
\text{The velocity at the target is horizontal. This means that } v_y=0
\text{We conclude that the target is the \textcolor{red}{maximum height} we can reach}
\displaystyle h=\frac{v_0^2 \sin^2\theta}{2 g}
\displaystyle \sin\theta=\sqrt{\frac{2 g h}{v_0^2 }}
\Rightarrow
\Rightarrow
\displaystyle \sin\theta=\sqrt{\frac{2\times9.8\times5}{12^2 }}=0.82
\Rightarrow
\text{Answer A}

\text{A projectile is fired from level ground with a speed of $12.0 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ at a target located at a height }
\text{$h=5.00 \mathrm{~m}$ above the ground as shown in Figure 2. The projectile's velocity to be horizontal}
\text{at the instant it reaches the target. }
\text{At what angle above the horizontal must the projectile be fired?}
\text{A ball thrown horizontally at $2.5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ travels a horizontal distance of $1.6 \mathrm{~m}$ before hitting }
\text{\textcolor{black}{A) }}3.7\text {m}\\
\text{B) }4.1\text {m}\\
\text{C) }3.2\text {m}\\
\text{D) }2.0\text {m}\\
\text{E) }1.7\text {m}
\text{the ground. From what height was the ball thrown?}
\text{(old exam)}
\displaystyle y=x\tan\theta+\frac{1}{2}g \frac{x^2}{(v_0 \cos\theta)^2}
x_0=0,y_0=0, \theta=0
\text{We choose a reference at the point the object was fired.}
\Rightarrow
\displaystyle y=-\frac{1}{2}9.8 \frac{1.6^2}{(2.5)^2}=-2.0 \text{ m}
\text{The object hits the ground with }y=-2.0 \text{ m} ,\text{ so the height is } 2.0\text{ m}
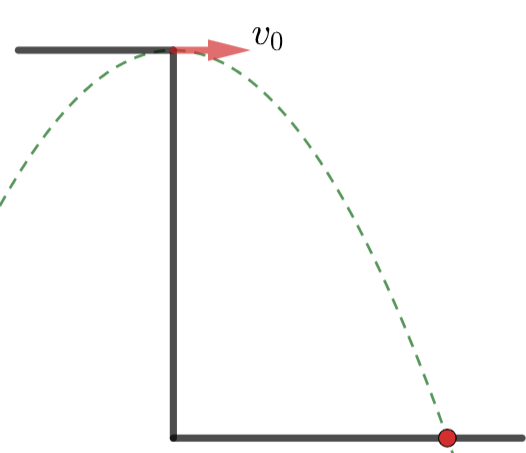
\text{Answer D}
\text{A ball thrown horizontally at $2.5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ travels a horizontal distance of $1.6 \mathrm{~m}$ before hitting }
\text{the ground. From what height was the ball thrown?}
\text{(old exam)}
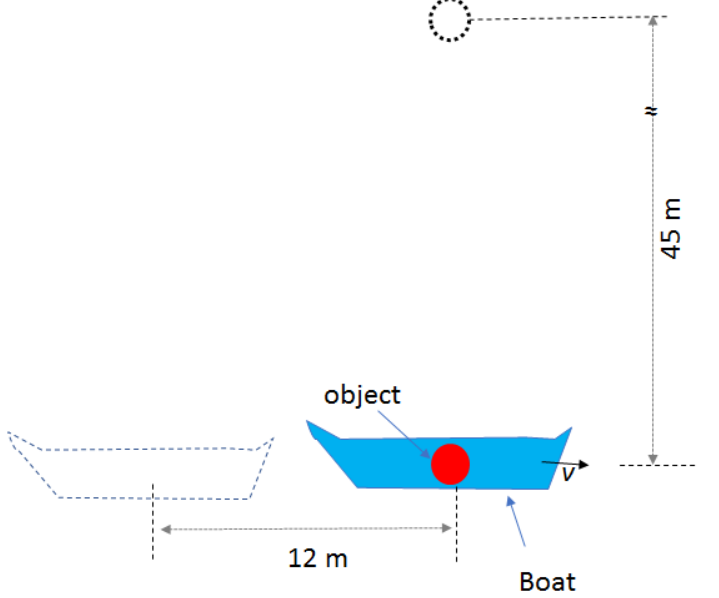
\text{An object falls from a bridge that is $45 \mathrm{~m}$ above the water. It falls directly into a small boat,}
\textcolor{black}{A) \hspace{1mm} 4.0\text { m/s}}\\
\text{B) }8.0\text { m/s}\\
\text{C) }6.0\text { m/s}\\
\text{\textcolor{black}{D) }}5.0\text { m/s}\\
\text{E) }2.5\text { m/s}
\text{(old exam)}
\text{ moving with constant speed $v$ as shown in Figure 2. The boat was $12 \mathrm{~m}$ away from the point }
\text{of impact (the point at which the object falls on the boat) when the object was released.}
\text{ What is the speed $v$ of the boat? [Ignore air resistance.]}
y-y_0=v_0t+\frac{1}{2}at^2
d=x-x_0=v t
\text{For the ball:}
\text{Let us choose the origin of the frame at the position of the ball on the boat}
\Rightarrow
0-h=-\frac{1}{2}gt^2
\Rightarrow
\displaystyle t=\sqrt{\frac{2h}{g}}=\frac{2 45}{9.8}=3.0s
\text{For the boat:}
\Rightarrow
\displaystyle v=d/t=12/3.0=4.0 \text{ m/s}
\text{Answer A}
\text{An object falls from a bridge that is $45 \mathrm{~m}$ above the water. It falls directly into a small boat,}
\text{(old exam)}
\text{ moving with constant speed $v$ as shown in Figure 2. The boat was $12 \mathrm{~m}$ away from the point }
\text{of impact (the point at which the object falls on the boat) when the object was released.}
\text{ What is the speed $v$ of the boat? [Ignore air resistance.]}

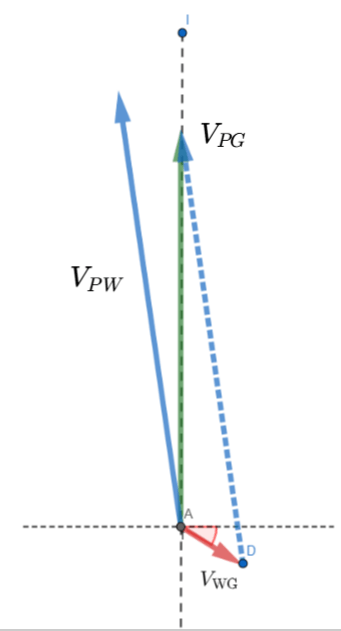
\text{After flying for $15 \mathrm{~min}$ in a wind blowing $44 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$ at an angle of $30^{\circ}$ south of east, an airplane
}
\textcolor{black}{\text{A) $245 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$}}\\
\text{B) $38.1 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$}\\
\text{C) $202 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$}\\
\text{D) $220 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$}\\
\text{E) $44.0 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$}
\text{(old exam)}
\text{pilot is over a town that is $55 \mathrm{~km}$ due north of the starting point.}
\text{What is the speed of the airplane relative to the wind? }
\vec{V}_\text{PG}=\vec{V}_\text{PW}+\vec{V}_\text{WG}
\text{We project over the x-axis}
{V}_\text{PW}^x={V}_\text{PG}^x-{V}_\text{WG}^x
\vec{V}_\text{PW}=\vec{V}_\text{PG}-\vec{V}_\text{WG}
{V}_\text{PW}^x=0-44 \cos(-30^0)=-22\sqrt{3} \text{ km/h}
\text{We project over the y-axis}
{V}_\text{PW}^y={V}_\text{PG}^y-{V}_\text{WG}^y
{V}_\text{PW}^y=220-44 \sin(-30^0)=242\text{ km/h}
V_\text{PW}=\sqrt{(22\sqrt{3})^2+242^2}=245 \text{ km/h}
{V}_\text{PG}=55\text{ km}/0.25\text{h}=220 \text{ km/h}
\text{After flying for $15 \mathrm{~min}$ in a wind blowing $44 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$ at an angle of $30^{\circ}$ south of east, an airplane
}
\text{(old exam)}
\text{pilot is over a town that is $55 \mathrm{~km}$ due north of the starting point.}
\text{What is the speed of the airplane relative to the wind? }
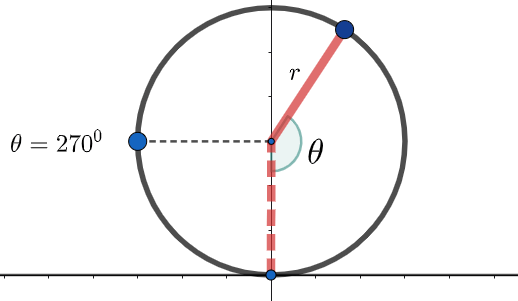
\text{A particle $P$ travels with constant speed on a circle of radius $r=3.00 \mathrm{~m}$ as shown in Figure 2 }
\text{and completes one revolution in $20.0 \mathrm{~s}$. The particle passes through $O$ at time $t=0$.}
\text{With respect to $O$, find the particle's position vector and acceleration at the time $t=15 \mathrm{~s}$. }
\text{(old exam)}
\text{The distance travelled on the circle is}
d=v t =\frac{2\pi r}{T} t
d=r\theta
\text{The length of an arc of circle is:}
\displaystyle \theta=2 \pi\frac{t}{T}=\frac{3 \pi}{2}= 270^0
\text{We deduce that:}
\text{From the figure, we see that when $\theta =270$,}
x=-r=-3.00\text{ m}
y=r=3.00 \text{ m}
\displaystyle a=\frac{v^2}{r}=\frac{(2\pi r/T)^2}{r}=\frac{(2\pi)^2 r}{T^2}=(2\times 3.14)^2/20^2 \times3=0.296 \text{ $m/s^2$}
\text{The particle is at $270^0$. The acceleration points out towards the center.}
\vec{r}=-3.00 \hat{i}+3.00 \hat{j} (m)
\text{A particle $P$ travels with constant speed on a circle of radius $r=3.00 \mathrm{~m}$ as shown in Figure 2 }
\text{and completes one revolution in $20.0 \mathrm{~s}$. The particle passes through $O$ at time $t=0$.}
\text{With respect to $O$, find the particle's position vector and acceleration at the time $t=15 \mathrm{~s}$. }
\text{(old exam)}
\text{the position is:}

\begin{align*}
&\text{A particle moves in uniform circular motion about the origin of an }xy\text{ coordinate system,}\\
&\text{clockwise, with a period of }10\,\mathrm{s}.\\
&\text{At one instant, its position vector (from the origin) is }
\vec r = (-4.0\,\hat{\imath}+3.0\,\hat{\jmath})\,\mathrm{m}.\\
&\text{At that instant, what is the velocity (in m/s) of the particle?}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
\text{A)}\ & \vec v = +1.9\,\hat{\imath}+2.5\,\hat{\jmath}\\
\text{B)}\ & \vec v = -2.5\,\hat{\imath}+1.9\,\hat{\jmath}\\
\text{C)}\ & \vec v = -0.4\,\hat{\imath}+0.3\,\hat{\jmath}\\
\text{D)}\ & \vec v = +2.5\,\hat{\imath}-1.9\,\hat{\jmath}\\
\text{E)}\ & \vec v = -1.9\,\hat{\imath}-2.5\,\hat{\jmath}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
&\text{A particle moves in uniform circular motion about the origin of an }xy\text{ coordinate system,}\\
&\text{clockwise, with a period of }10\,\mathrm{s}.\\
&\text{At one instant, its position vector (from the origin) is }
\vec r = (-4.0\,\hat{\imath}+3.0\,\hat{\jmath})\,\mathrm{m}.\\
&\text{At that instant, what is the velocity (in m/s) of the particle?}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
\vec r &= (-4\,\hat{\imath}+3\,\hat{\jmath})\ \mathrm{m},
\qquad R=\|\vec r\|=\sqrt{(-4)^2+3^2}=5\ \mathrm{m},\\[2pt]
\omega &= \frac{2\pi}{T}=\frac{2\pi}{10}=0.628\ \mathrm{rad/s},
\qquad \vec\omega=-\,\omega\,\hat{\mathbf k}\ \text{(clockwise)},\\[2pt]
\vec v &= \vec\omega\times\vec r
= (-\omega\hat{\mathbf k})\times(-4\,\hat{\imath}+3\,\hat{\jmath})
= 3\omega\,\hat{\imath}+4\omega\,\hat{\jmath}\\[2pt]
&= 3(0.628)\,\hat{\imath}+4(0.628)\,\hat{\jmath}
\approx \boxed{\,1.9\,\hat{\imath}+2.5\,\hat{\jmath}\ \mathrm{m/s}\,}.
\end{align*}
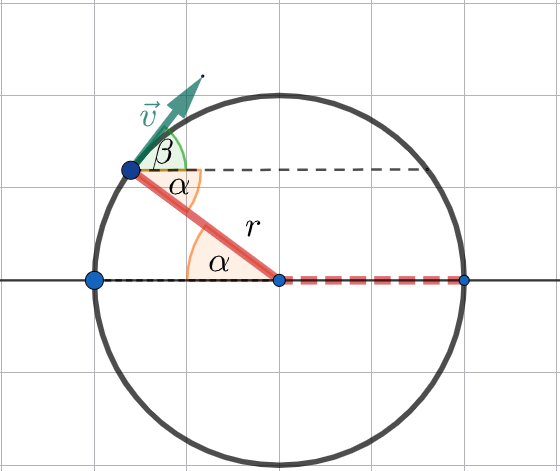
\text{from $\vec{r}$, we can extract $\alpha$}
\alpha=\tan^{-1}(\frac{3}{4})=36.87^0
\beta=90^0-\alpha=54.13^0
v=\omega r=0.628\times5=3.14 \mathrm{~m/s}
\vec{v}=v\cos\beta \hat{i}+v\sin\beta \hat{j}=(1.9 \hat{i}+2.5 \hat{j}) \mathrm{~m/s}
\text{Second method:}
\text{A projectile is thrown from a height H with a speed of 10.0 $\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}$ at an angle of 30 degrees}
\text{below horizontal as shown in Fig 10. Find H, if the horizontal distance $\mathrm{x}=20.0 \mathrm{~m}$.}
\begin{align*}
A) &37.7 \mathrm{~m} &\\
B) &98.0 \mathrm{~m} &\\
C) &49.0 \mathrm{~m} &\\
D) &20.0 \mathrm{~m} &\\
E) &67.8 \mathrm{~m} &
\end{align*}
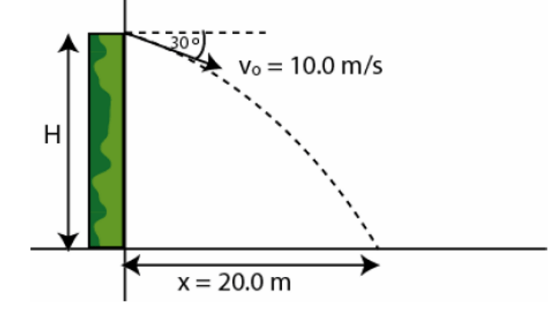
\text{A projectile is thrown from a height H with a speed of 10.0 $\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}$ at an angle of 30 degrees}
\text{below horizontal as shown in Fig 10. Find H, if the horizontal distance $\mathrm{x}=20.0 \mathrm{~m}$.}
\text{Hint: use the equation of trajectory with $\theta=-30^\circ$}

\text{Challenge:}
\text{An object is thrown with a speed $v_0$ with an angle $\theta$ from the horizontal. It reaches }
\text{a maximum height $H=5 $ m and a range $R=10 $ m.}
\text{Find $v_0$ and $\theta$.}
\displaystyle H=\frac{v_0^2 \sin^2\theta}{2 g}
\displaystyle R=\frac{v_0^2 \sin2\theta}{g}
\displaystyle \frac{H}{R}=\frac{\sin^2 \theta}{2\sin2\theta}=\frac{\sin^2 \theta}{4\sin\theta\cos\theta}=\frac{\tan\theta}{4}
\displaystyle \theta=\tan^{-1}\Big(\frac{4H}{R}\Big)
\displaystyle \theta=\tan^{-1}\Big(\frac{4\times 5}{10}\Big)=63.43^0
\Rightarrow
\Rightarrow
\Rightarrow
\text{Challenge:}
\text{An object is thrown with a speed $v_0$ with an angle $\theta$ from the horizontal. It reaches }
\text{a maximum height $H=5 $ m and a range $R=10 $ m.}
\text{Find $v_0$ and $\theta$.}
\begin{aligned}
&\text { Then } \sin ^2 \theta=\frac{4}{5} \text {, so from } v_0^2 \sin ^2 \theta=2 g H \text { : }\\
&\begin{aligned}
& v_0^2=\frac{2 g H}{\sin ^2 \theta}=\frac{2 g H}{4 / 5}=\frac{5}{2} g H=\frac{5}{4} g R=122.5 \\
& v_0=\sqrt{122.5} \approx (11.1 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s})
\end{aligned}
\end{aligned}
\sin2\theta =2\sin\theta \cos\theta
\text{To be updated}