Design Patterns in Laravel

Md. Sohel Amin
Sr. Software Engineer
Mailforge
Github: sohelamin, appzcoder
Twitter: sohel_amin
Email: sohelamincse at gmail dot com
What is Design Pattern?
Design patterns are solutions to recurring problems, guidelines on how to tackle certain problems.
In other words, It is a description or template for how to solve a problem.
Why should use Design Patterns?
- To reuse codes in multiple projects
- Proven & tested by expert developers
- To follow best practices
- Maintenance
- Documentation
- Readability
Types of Design Pattern
1. Creational Design Patterns
These patterns deal with object creation mechanisms.
2. Structural Design Patterns
These design patterns concern class and object composition.
3. Behavioral Design Patterns
These patterns describe interactions between objects and focus on how objects communicate with each other.
Design Patterns used in Laravel
- Builder/Manager Pattern (eg. AuthManager)
- Factory Pattern (eg. Validator)
- Repository Pattern (eg. UserRepository)
- Strategy Pattern (eg. Config/LoaderInterface)
- Provider Pattern (eg. AuthServiceProvider)
- Facade Pattern (eg. DB, Session)
To be discussed
- Facade Pattern
- Repository Pattern
- Provider Pattern
Facade Pattern
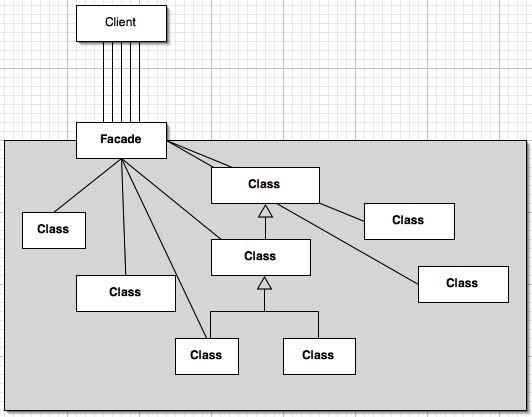
Facade pattern provides a simplified interface to a complex subsystem.
When to use Facade Pattern?
- A simple interface is required to access a complex system.
- A system is very complex or difficult to understand.
- An entry point is needed to each level of layered software.
Facade Pattern
class Cart
{
public function addProducts($products)
{
// Product adding codes goes here
}
public function getProducts()
{
// Product retrieval codes goes here
}
}
class Order
{
public function process($products)
{
// Order processing codes goes here
}
}Facade Pattern
class Payment
{
public function charge($charge)
{
// Additional charge codes goes here
}
public function makePayment()
{
// Payment method verify & payment codes goes here
}
}
class Shipping
{
public function calculateCharge()
{
// Calculation codes goes here
}
public function shipProducts()
{
// Ship process codes goes here
}
}Facade Pattern
class CustomerFacade
{
public function __construct()
{
$this->cart = new Cart;
$this->order = new Order;
$this->payment = new Payment;
$this->shipping = new Shipping;
}
public function addToCart($products)
{
$this->cart->addProducts($products);
}
public function checkout()
{
$products = $this->cart->getProducts();
$this->totalAmount = $this->order->process($products);
}
public function makePayment()
{
$charge = $this->shipping->calculateCharge();
$this->payment->charge($charge);
$isCompleted = $this->payment->makePayment();
if ($isCompleted) {
$this->shipping->shipProducts();
}
}
}Facade Pattern
$customer = new CustomerFacade;
$products = [
[
'name' => 'Polo T-Shirt',
'price' => 40,
],
[
'name' => 'Smart Watch',
'price' => 400,
],
];
$customer->addToCart($products);
$customer->checkout();
$customer->makePayment();Facade Pattern in Laravel
Example: Config, Input, URL, Route, View, DB etc
return [
'aliases' => [
'DB' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB::class,
]
]Step1. Open the config file config/app.php
// become
DB::select();Facade Pattern in Laravel
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Support\Facades;
/**
* @see \Illuminate\Database\DatabaseManager
* @see \Illuminate\Database\Connection
*/
class DB extends Facade
{
/**
* Get the registered name of the component.
*
* @return string
*/
protected static function getFacadeAccessor()
{
return 'db';
}
}Step2. Let's open Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB.php
Facade Pattern in Laravel
protected function registerConnectionServices()
{
$this->app->singleton('db', function ($app) {
return new DatabaseManager($app, $app['db.factory']);
});
}Step3. Let's open Illuminate/Database/DatabaseServiceProvider.php
public function __call($method, $parameters)
{
return $this->connection()->$method(...$parameters);
}Step4. Let's open Illuminate/Database/DatabaseManager.php
// become
$app['db']Underlying the static method
class_alias('Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB', 'DB');
// we can call DB instead of Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB now// vendor/laravel/framework/src/Illuminate/Support/Facades/Facade.php
abstract class Facade
{
public static function __callStatic($method, $args)
{
$instance = static::getFacadeRoot();
if (! $instance) {
throw new RuntimeException('A facade root has not been set.');
}
return $instance->$method(...$args);
}
}DB::select()Repository Pattern
The Repository pattern is usually used to create an interface between business logic & database access layers of an application

Why should use Repository Pattern?
- To makes code easier to maintain by centralizing the data access logic.
- To separately testing business and data access logic.
- To reduces duplication of code.
- To reduce errors
Repository Pattern
// app/Repositories/PostRepositoryInterface.php
<?php
namespace App\Repositories;
interface PostRepositoryInterface
{
public function getAll();
public function find($id);
}
Repository Pattern
// app/Repositories/PostEloquentRepository.php
<?php
namespace App\Repositories;
use App\Post;
class PostEloquentRepository implements PostRepositoryInterface
{
public function getAll()
{
return Post::all();
}
public function find($id)
{
return Post::findOrFail($id);
}
}
Repository Pattern
// app/Providers/AppServiceProvider.php
public function register()
{
$this->app->bind(
'App\Repositories\PostRepositoryInterface',
'App\Repositories\PostEloquentRepository'
);
}Repository Pattern
// app/Http/Controllers/Admin/PostsController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers\Admin;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use App\Repositories\PostRepositoryInterface;
class PostsController extends Controller
{
protected $postRepository;
public function __construct(PostRepositoryInterface $postRepository)
{
$this->postRepository = $postRepository;
}
public function index()
{
$posts = $this->postRepository->getAll();
return view('admin.posts.index', compact('posts'));
}
}
Provider Pattern
The Provider pattern was formulated by Microsoft. It is a mid layer between an API class and the Business Logic/Data Abstraction Layer of the application.
Provider Pattern
// vendor/laravel/framework/src/Illuminate/Redis/RedisServiceProvider.php
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Redis;
use Illuminate\Support\Arr;
use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;
class RedisServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
protected $defer = true;
public function register()
{
$this->app->singleton('redis', function ($app) {
$config = $app->make('config')->get('database.redis');
return new RedisManager(Arr::pull($config, 'client', 'predis'), $config);
});
$this->app->bind('redis.connection', function ($app) {
return $app['redis']->connection();
});
}
public function provides()
{
return ['redis', 'redis.connection'];
}
}
Provider Pattern
// config/app.php
<?php
return [
'providers' => [
Illuminate\Redis\RedisServiceProvider::class,
],
'aliases' => [
'Redis' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Redis::class,
]
]
References
- https://www.appzcoder.com/category/php-design-patterns/
- https://github.com/domnikl/DesignPatternsPHP
- https://github.com/kamranahmedse/design-patterns-for-humans
- Laravel Design Patterns and Best Practices by Arda Kilicdagi and H Ibrahim Yilmaz