Notes of
Machine Learning
Chris Hung, Jin Xun
Content
- Classical ML
- An overview (Chris)
- Supervised Learning - Regression (LJX)
- Supervised Learning - Classification (LJX)
- Reinforcement Learning (RL) (Next)
- Training
- Model Design
- Basis of model training
- Adjust learning rate (LJX)
- Batch normalization(LJX)
- Quantum Machine Learning
- Application Examples
Classical ML
An overview of Classical ML
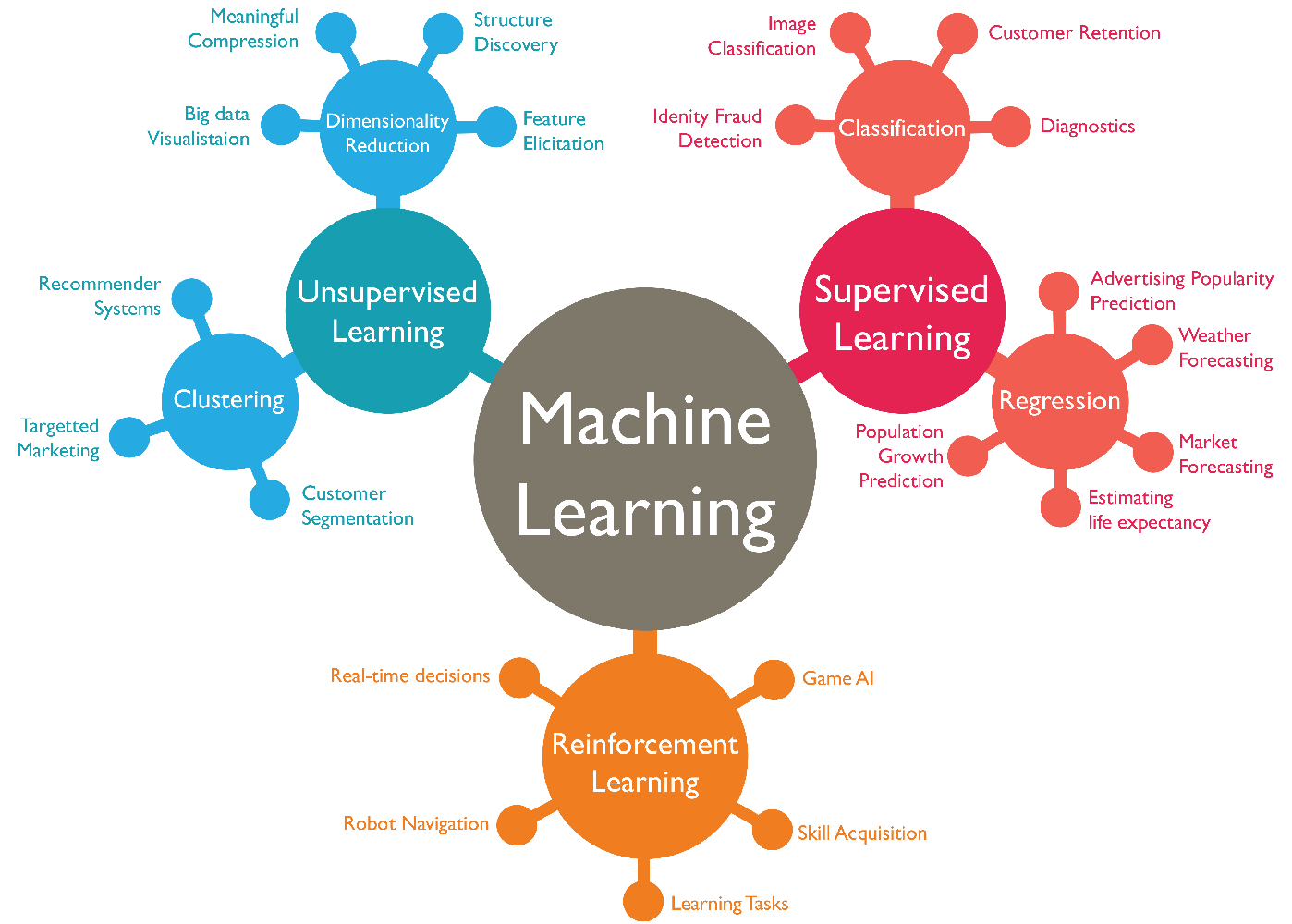
Map of ML
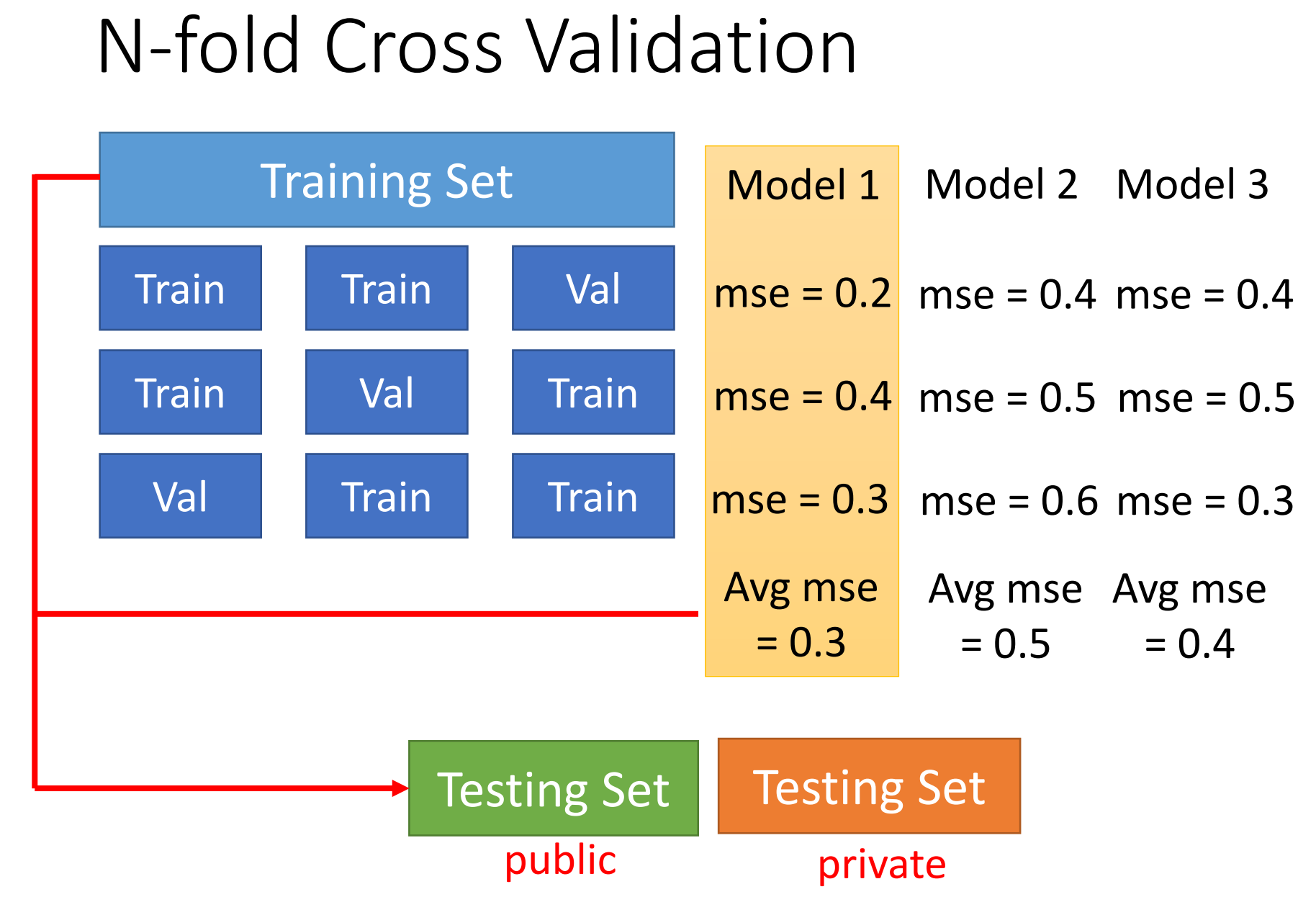
Model Selection
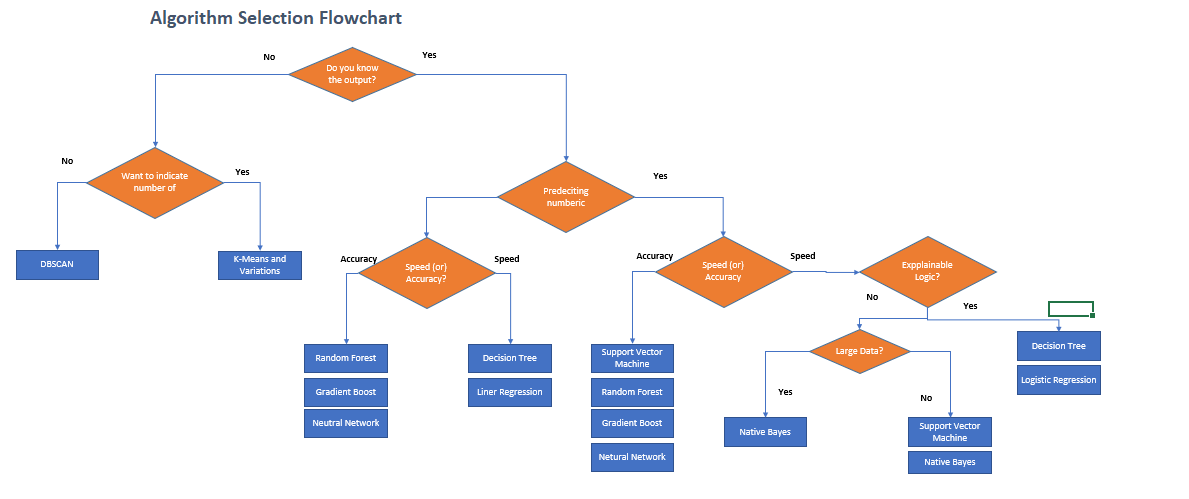
Design Method
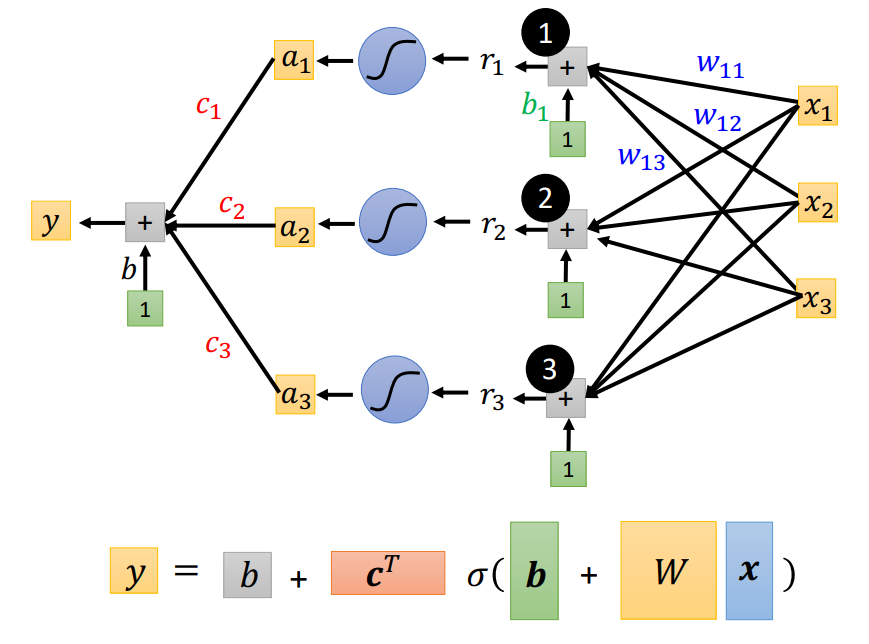
Give some features
Predict another feature
(Output one scalar)
Supervised Learning Regression
Give some features
Classify it
(Output one vector)
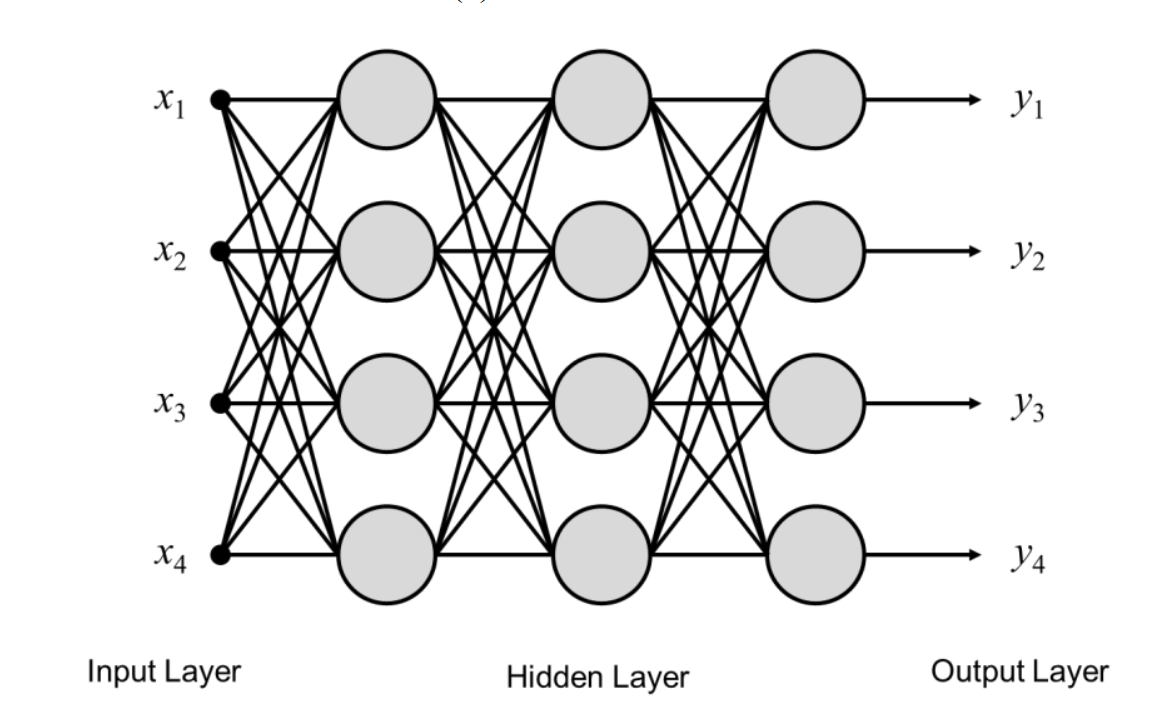
Supervised Learning Classification
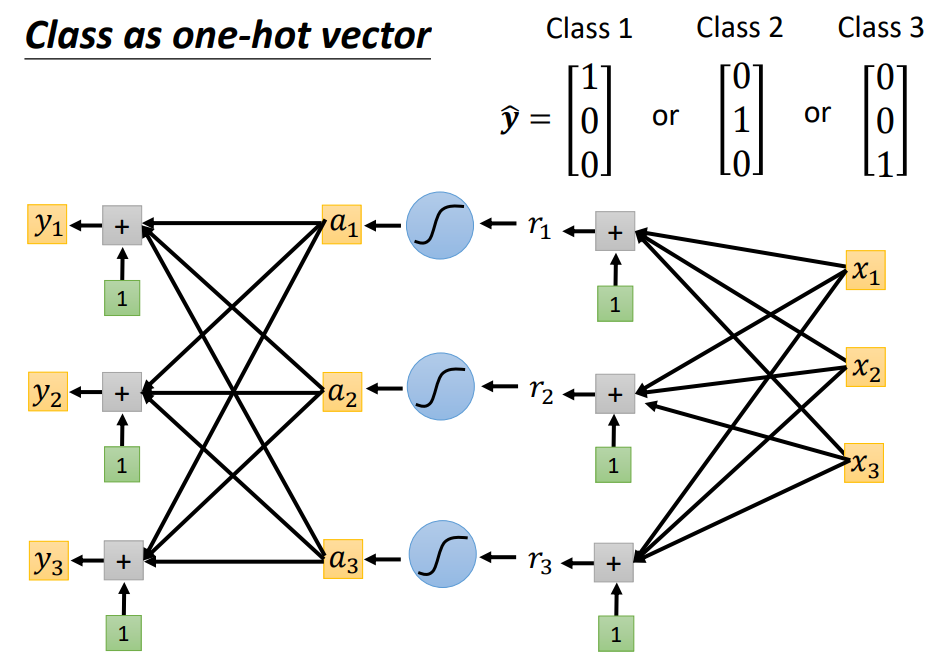
把regression重複做
每次乘上不同的w和加上不同的bias


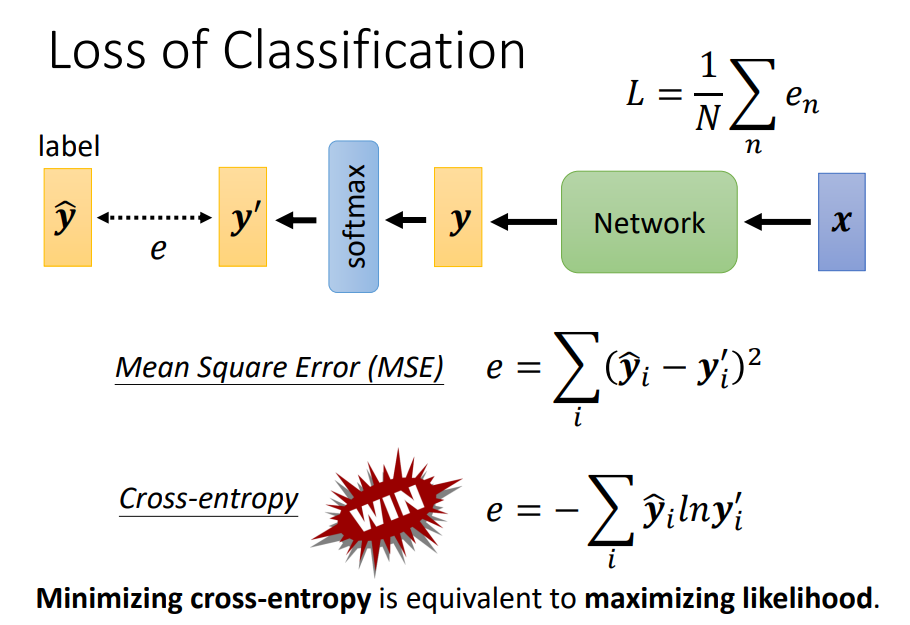
Soft-max
1. Normalization
2. 放大差距(指數)
y^{'}_i = \frac{exp(y_i)}{\displaystyle \sum_{k=0}^{n}exp(y_k)}
Model Design
Preprocess data
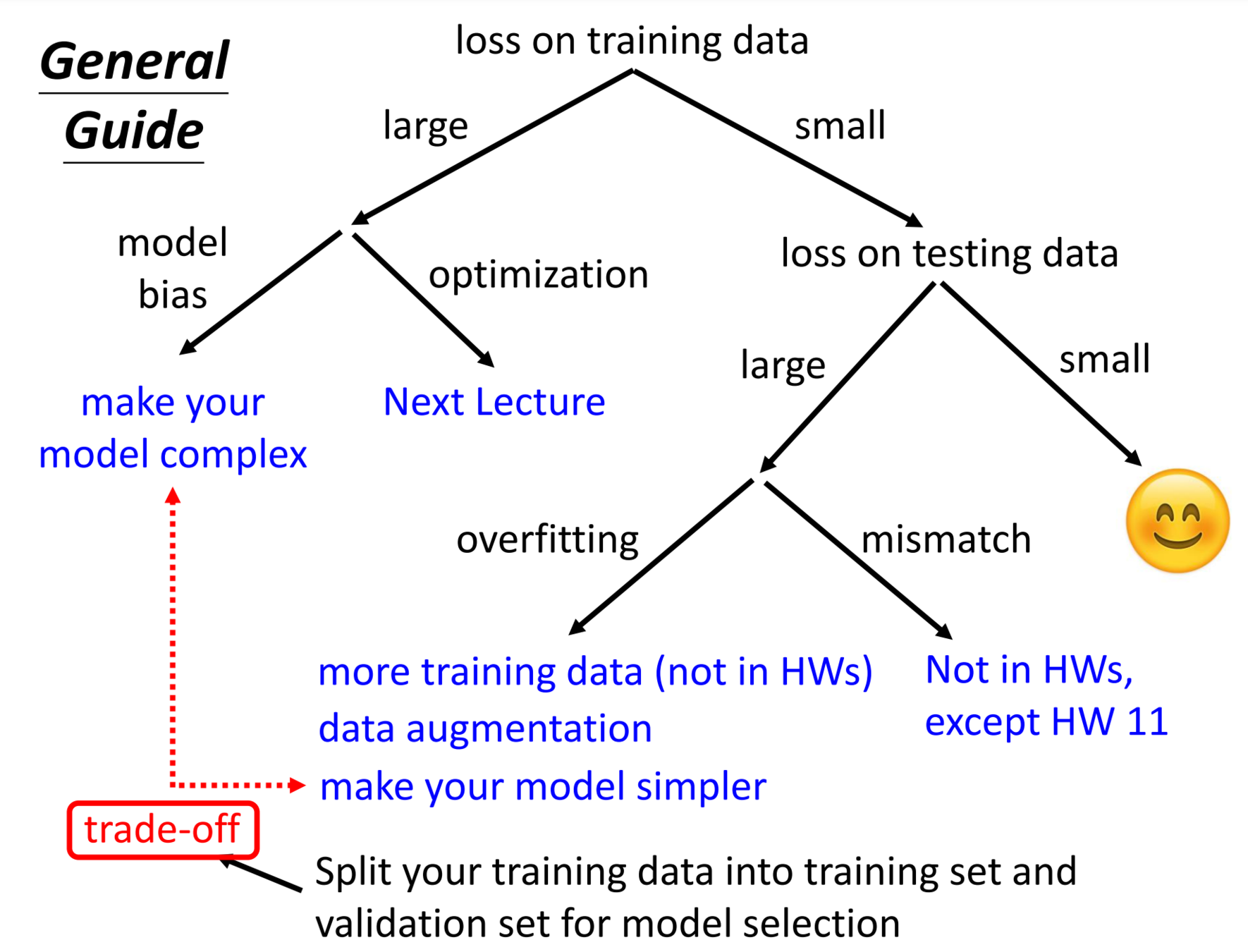
Basis of Model Training
- loss
- Escape Saddle point and Local Minima
- Batch
- Momentum+Gradient Descent
Train Model
Escape Saddle Point
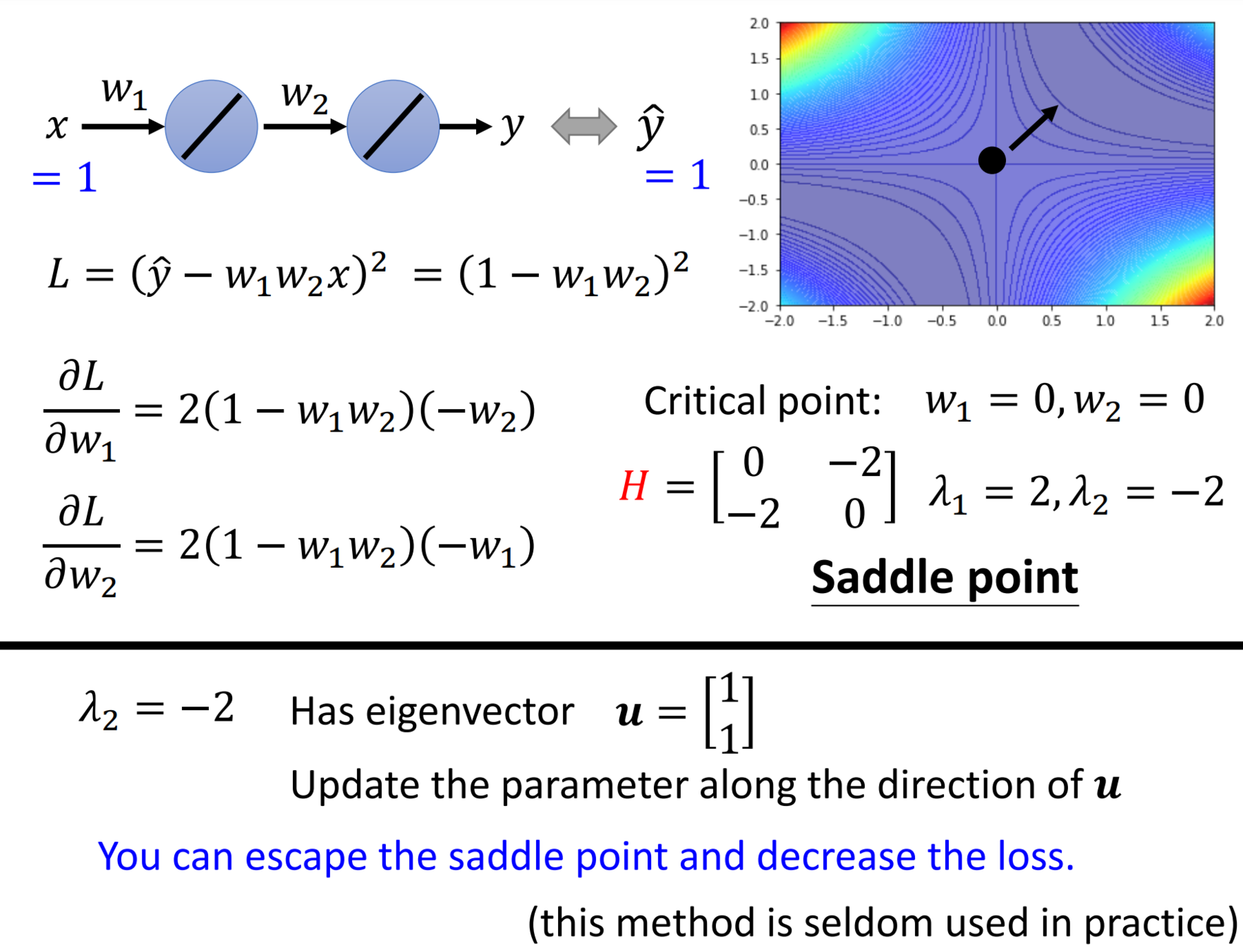
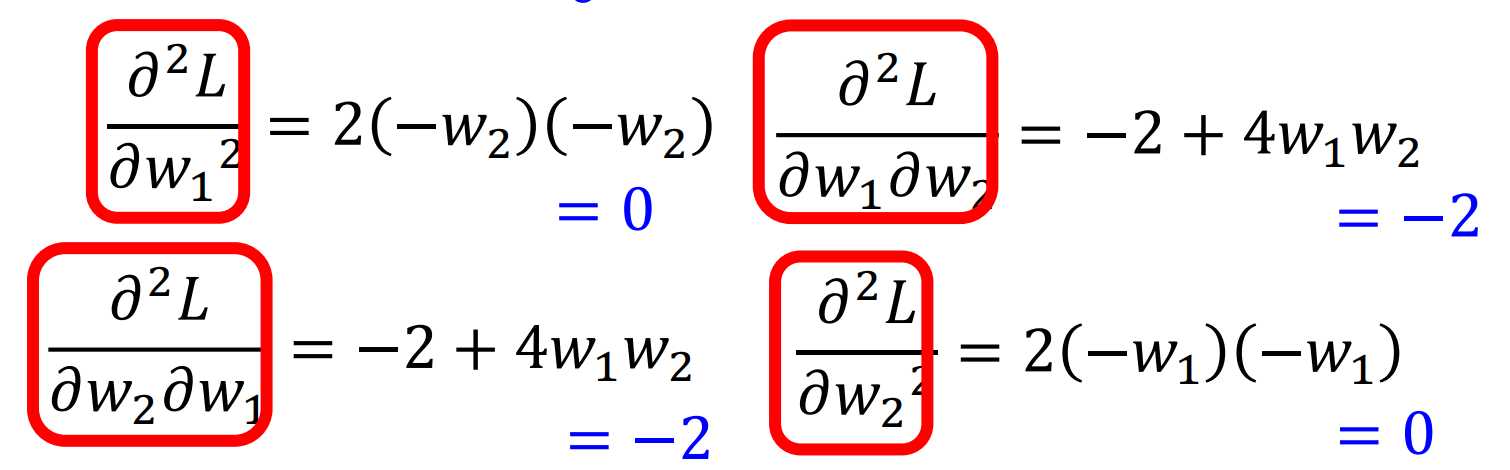
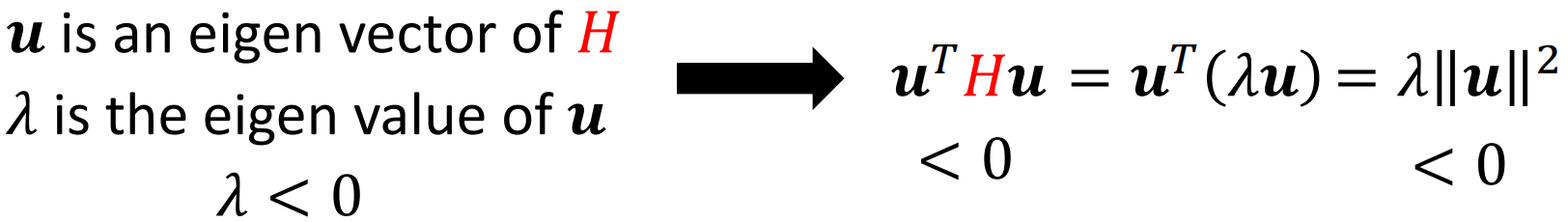
Batch Size And
Momentum
Help Escape from
Crtical Points
Batch
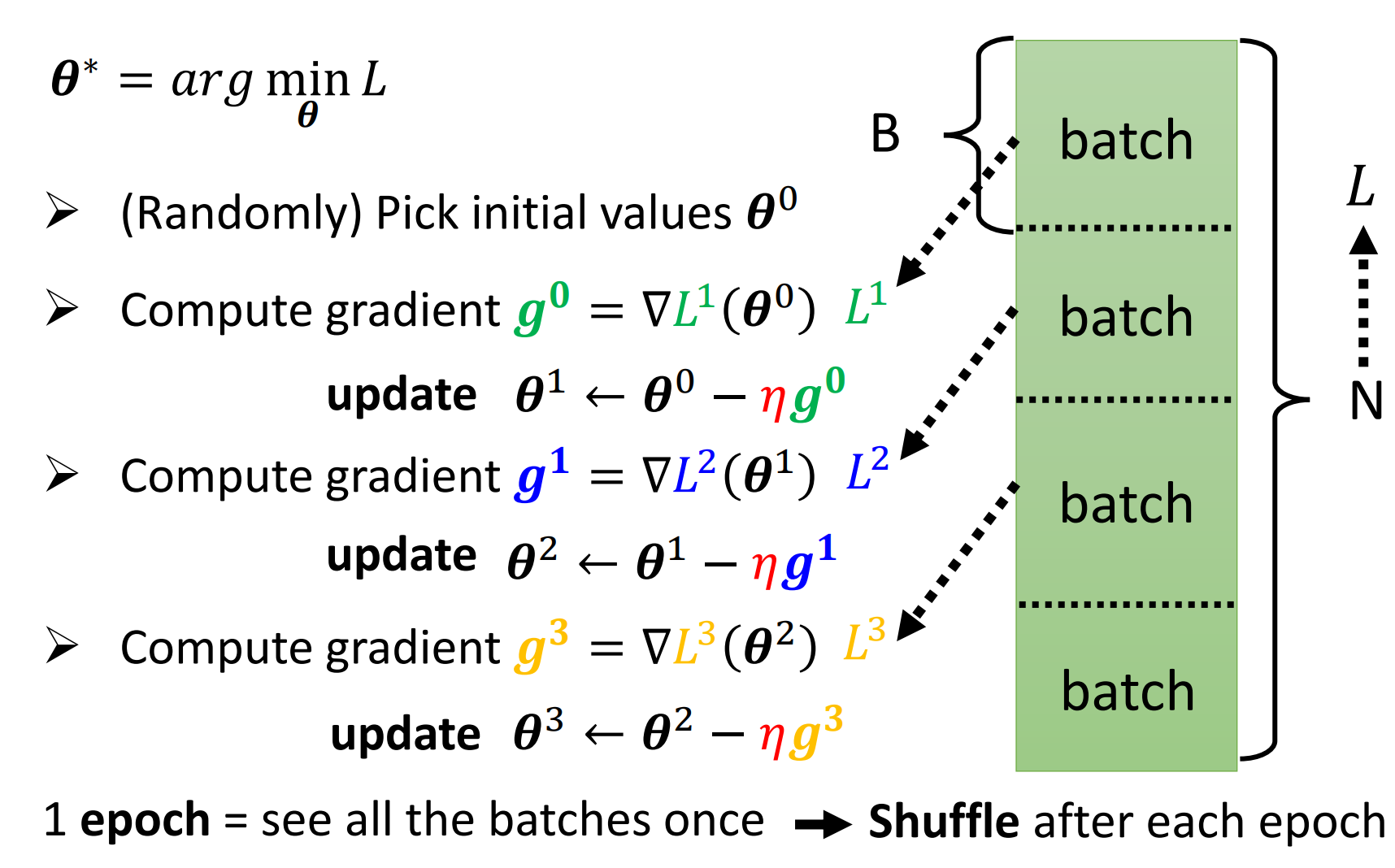
Batch Size
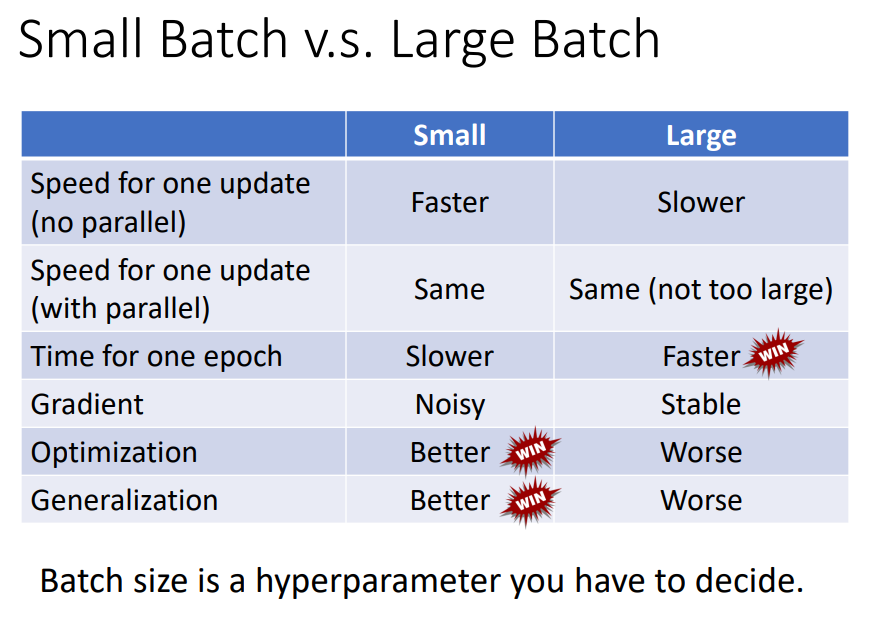
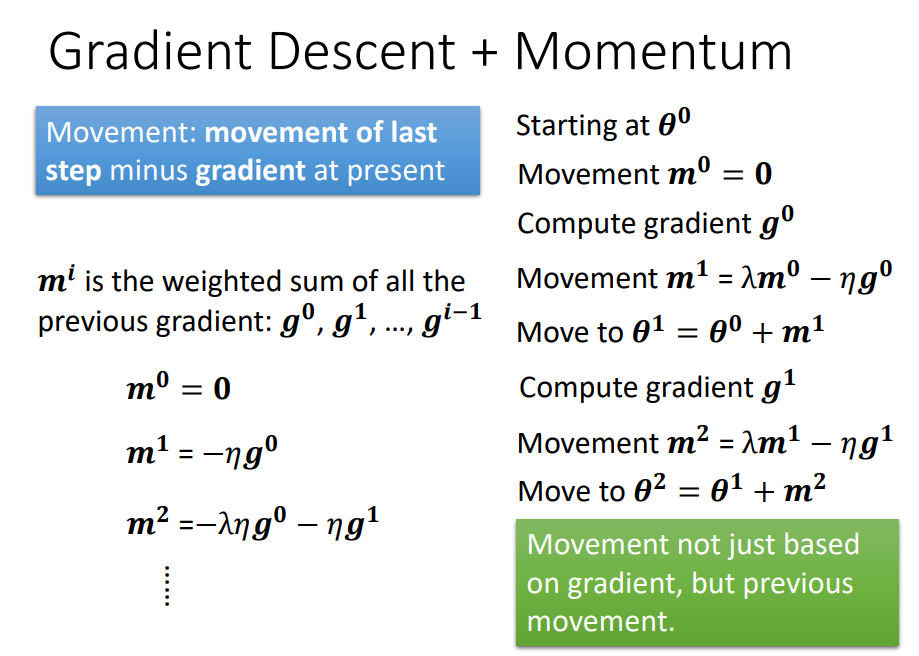
Momentum
-Gradient(n)+movement(n-1)
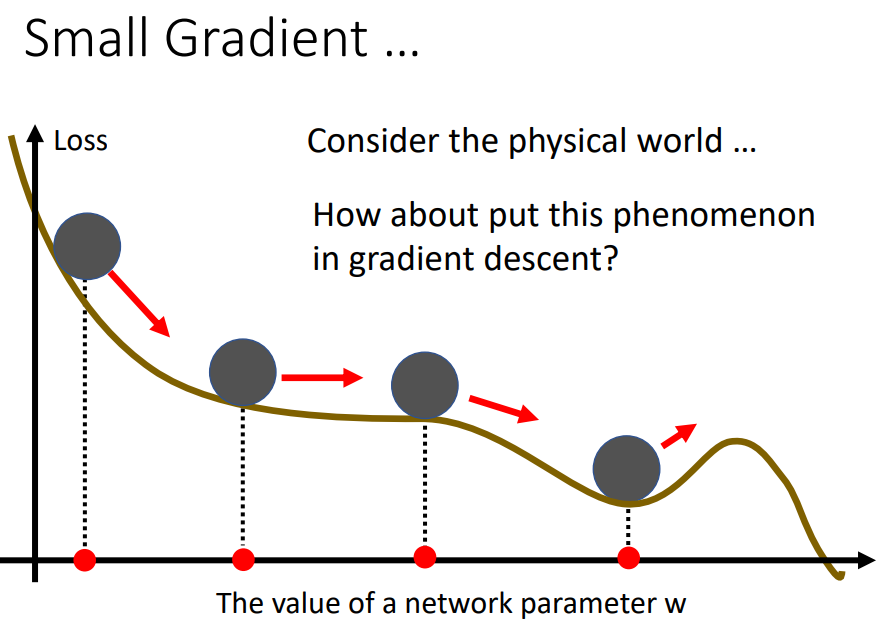
想像球從高處滾下來,帶著之前的動量跑
可能可以翻出local minimum
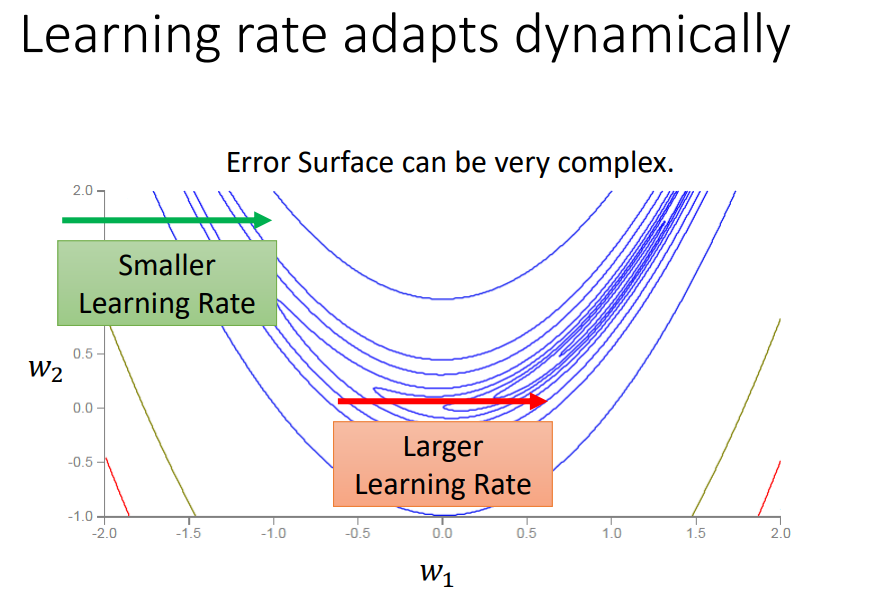
Adjust Learning Rate
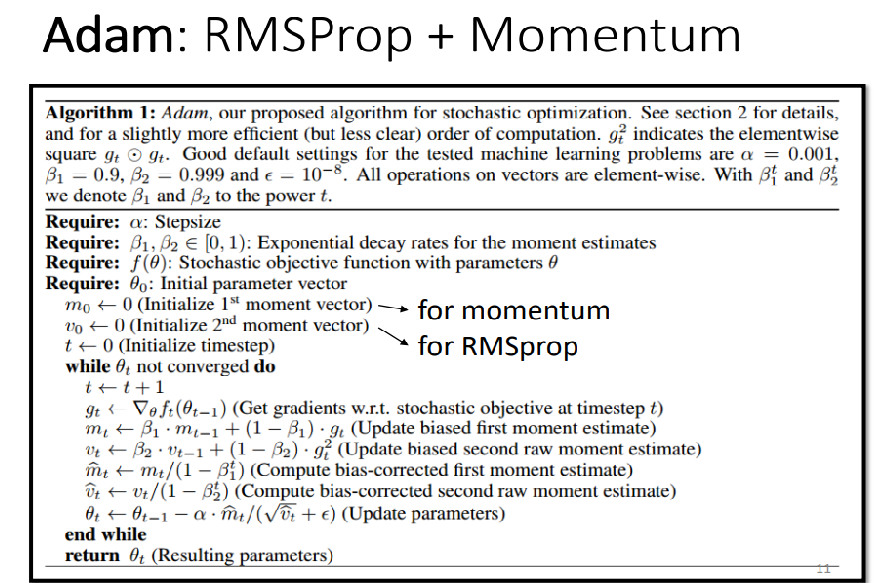
Best Optimizer: Adam=RMSProp + Momentum
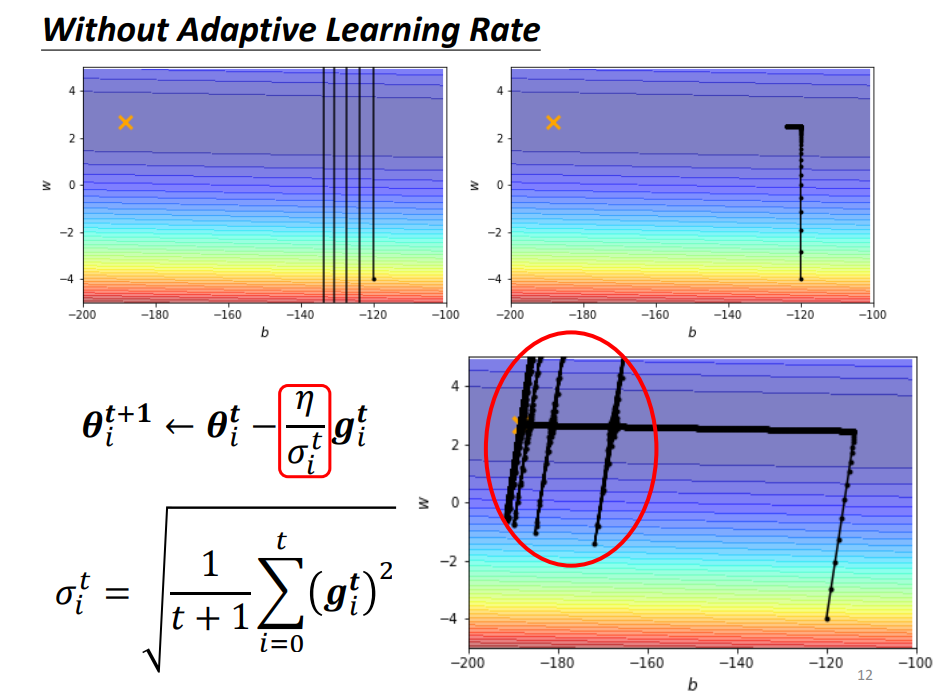
Adagrad
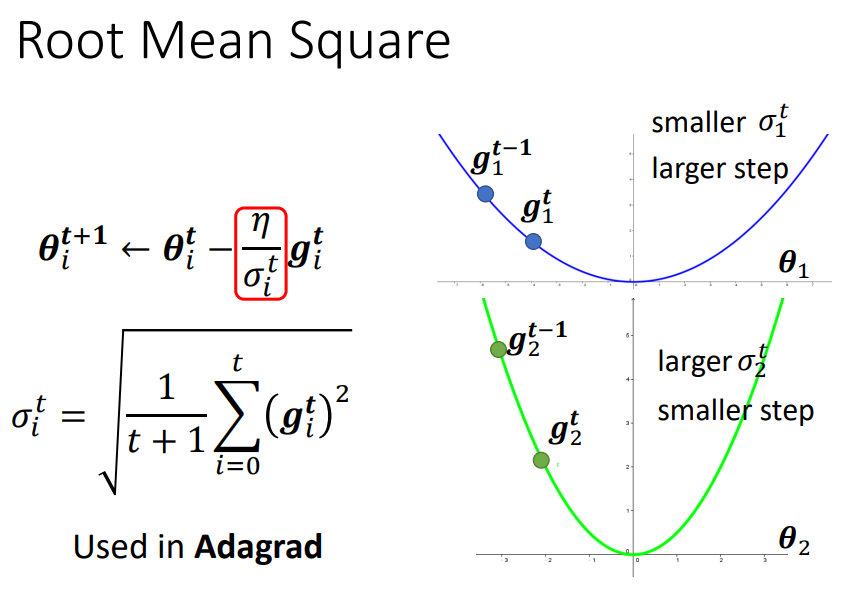
Adagrad consider all gradients before
Might not be dynamic
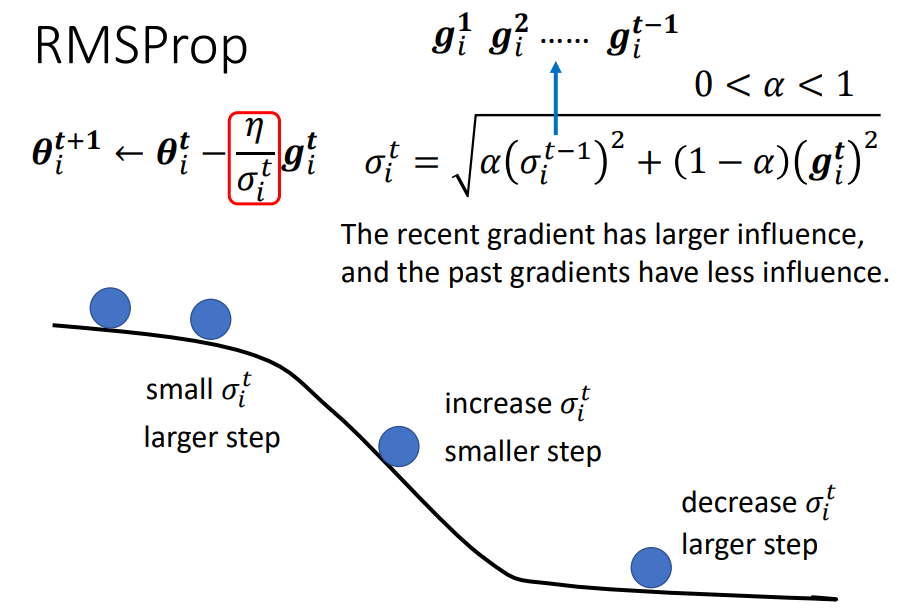
RMSProp
Adam
Original paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980.pdf
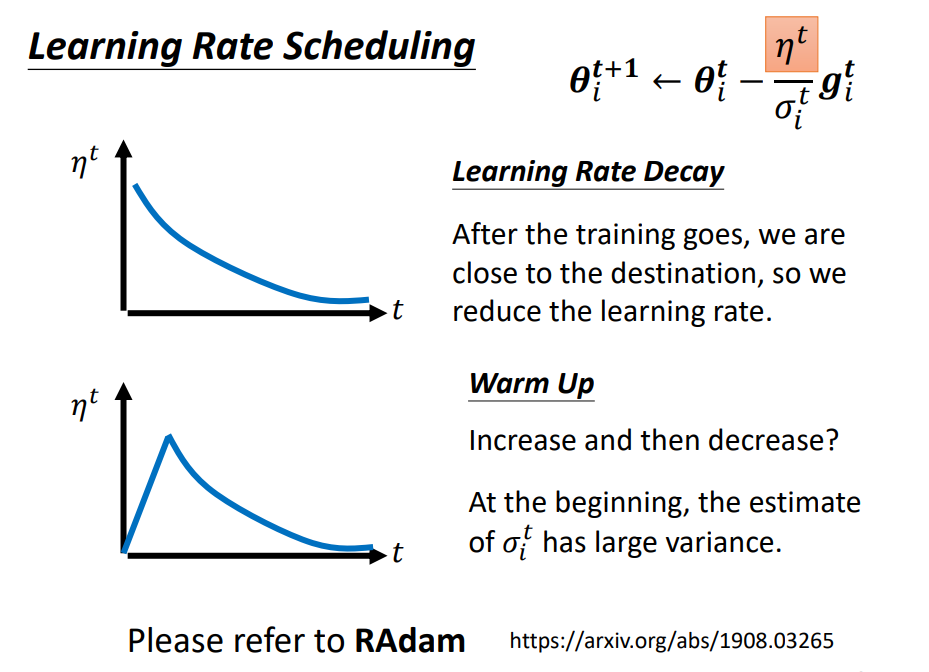
Learning Rate Scheduling
從頭到尾用一個learning rate, 可能前面累積的參數會影響前進
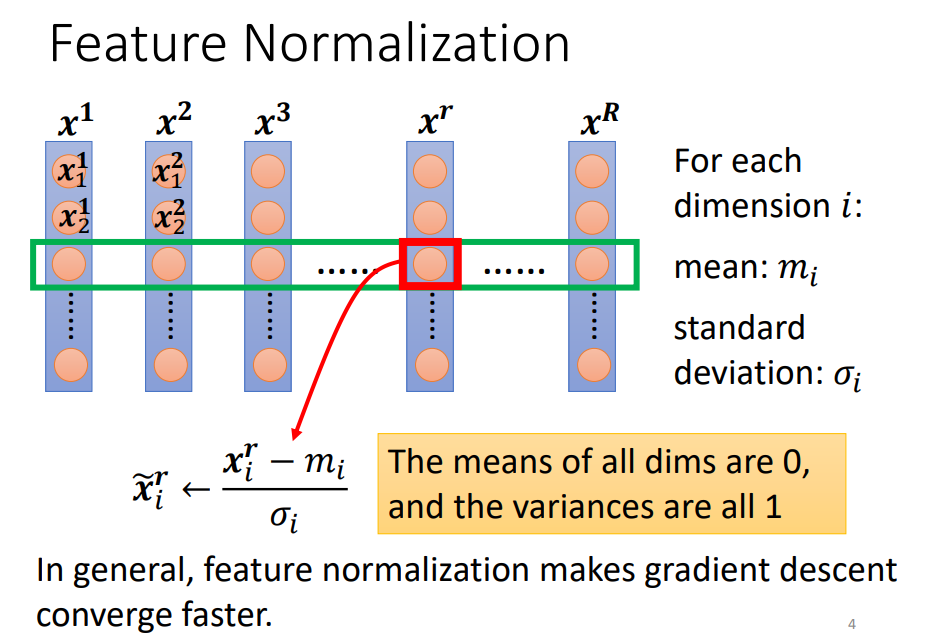
Batch normalization
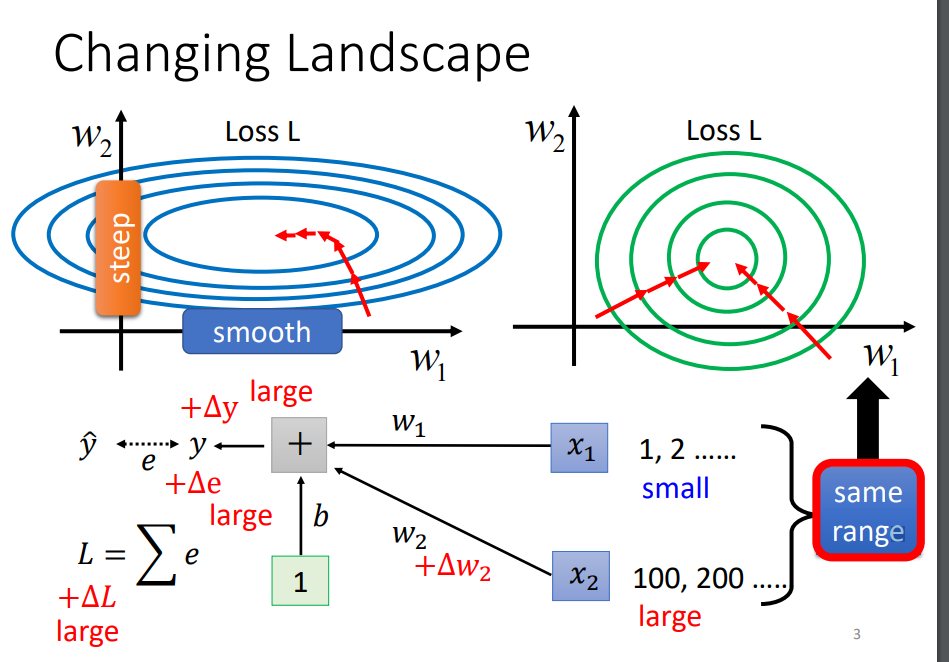
Make it easier to train
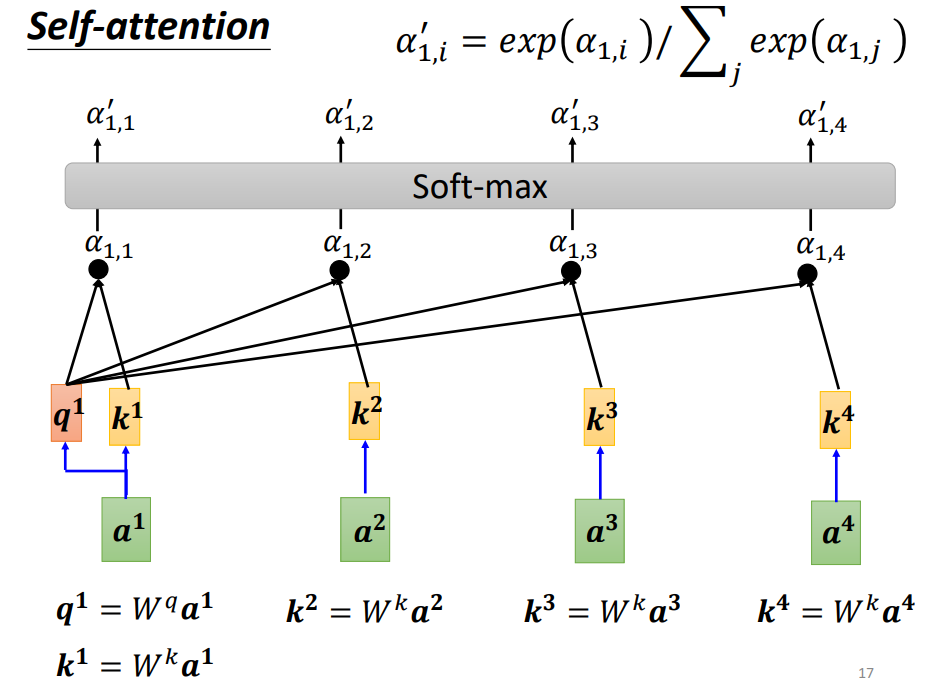
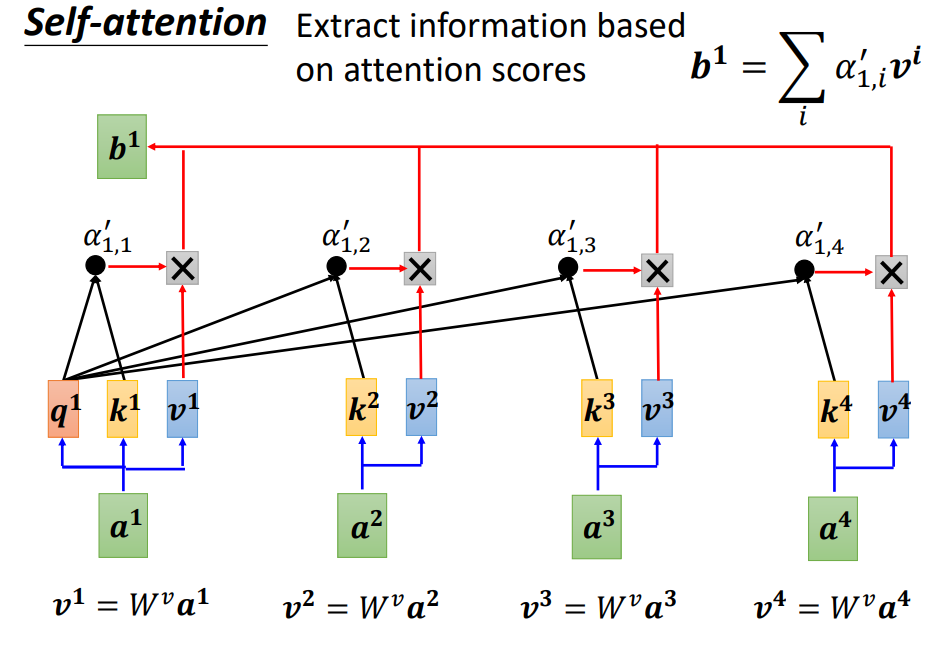
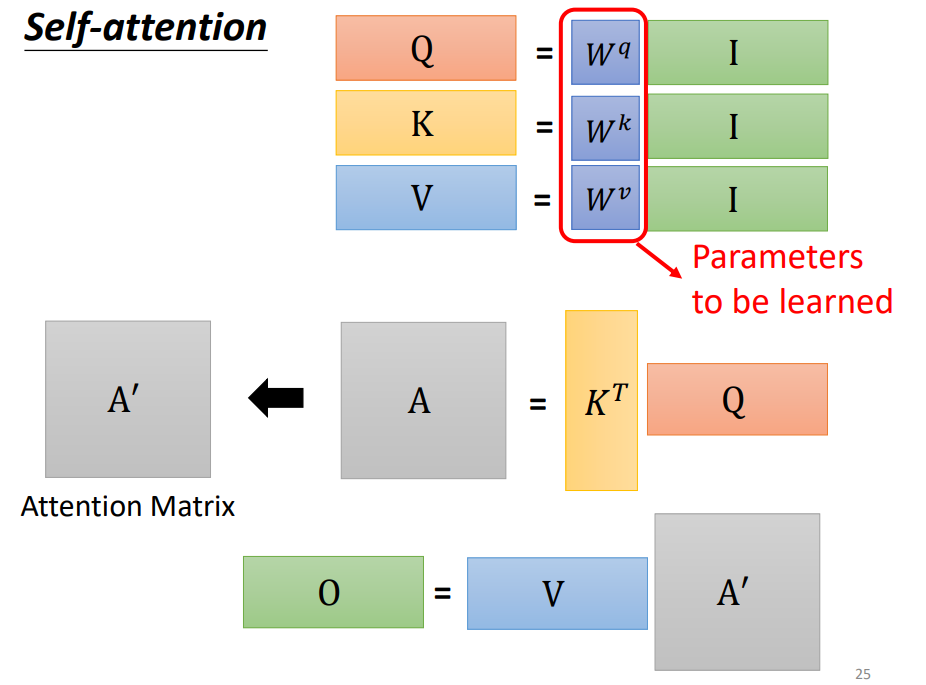
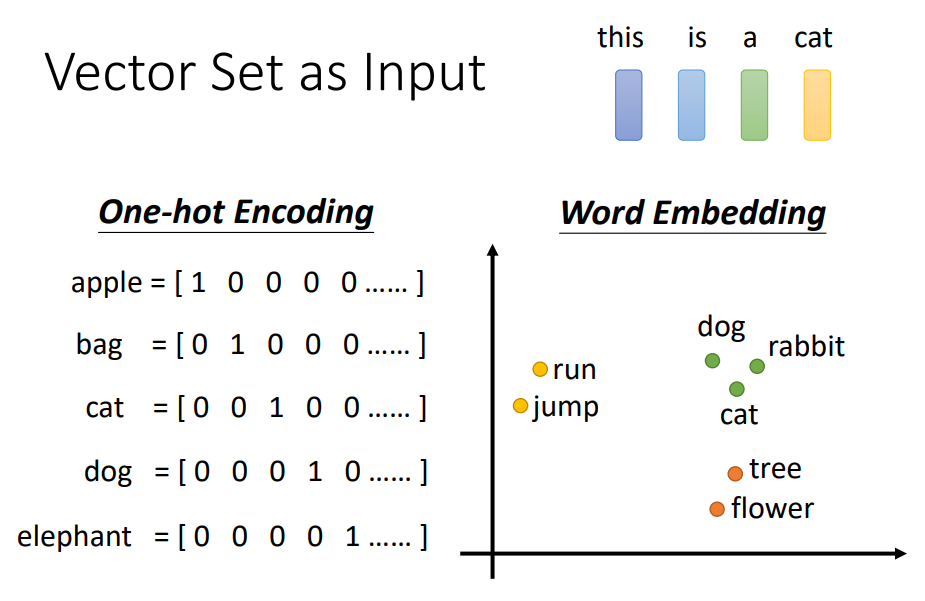
Self-attention
Input is a set of vectors
may change length
為了考慮前後的資料
Text
No correlation
Better!!