Understanding CNNS in NLP
Peadar Coyle

Contents
- Convolutional Neural Network
- Has Convolutions (Photoshop idea)
- CNNs are Convolutions in a Neural Network
- Image classification is explained first
- Applied to NLP
What is a Convolution?

A sliding window function applied to a matrix.
Edge Detection

Taking the difference between pixels and its neighbours detects edges

Blurring

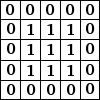
Averaging each pixel with it's neighbours gives blurring
ReLu and Tanh

CNN
- Layers of convolution with non-linear activation functions
- Two function examples are ReLU and Tanh
- In a traditional feed-forward network - we connect each input neuron to each output neuron in the next layer
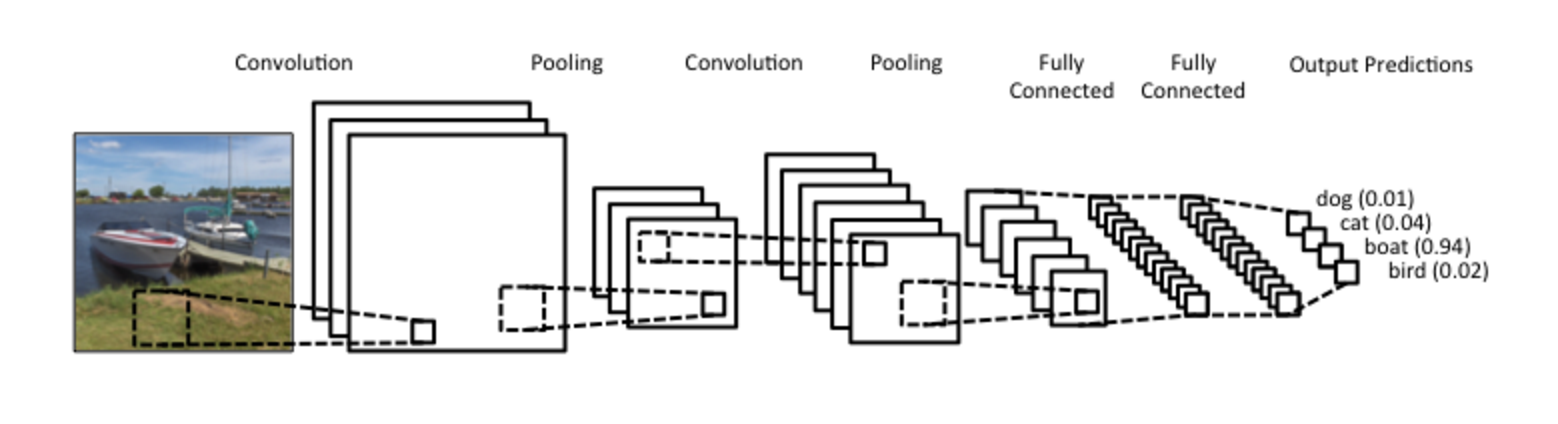
CNN (2)
- In CNNs we use convolutions over the input layer to compute the output
- Local connections - each region of input connected to a neuron in output
- Each layer applies different filters (100s or 1000s) and combines them

Training
A CNN automatically learns the values of its filters based on the task you want it to perform.
Example
A CNN for image classification may learn to detect edges in the first layer -> shapes -> facial shapes. The final layer will be a classifier that uses these high level features.

2 Aspects
Location invariance and compositionality
- Don't care where an elephant is in an image
- Each filter composes a local patch of lower level features into a higher level representation.
- Pixels -> Edges -> Shapes -> Complex Shapes