React
Functional Web Development
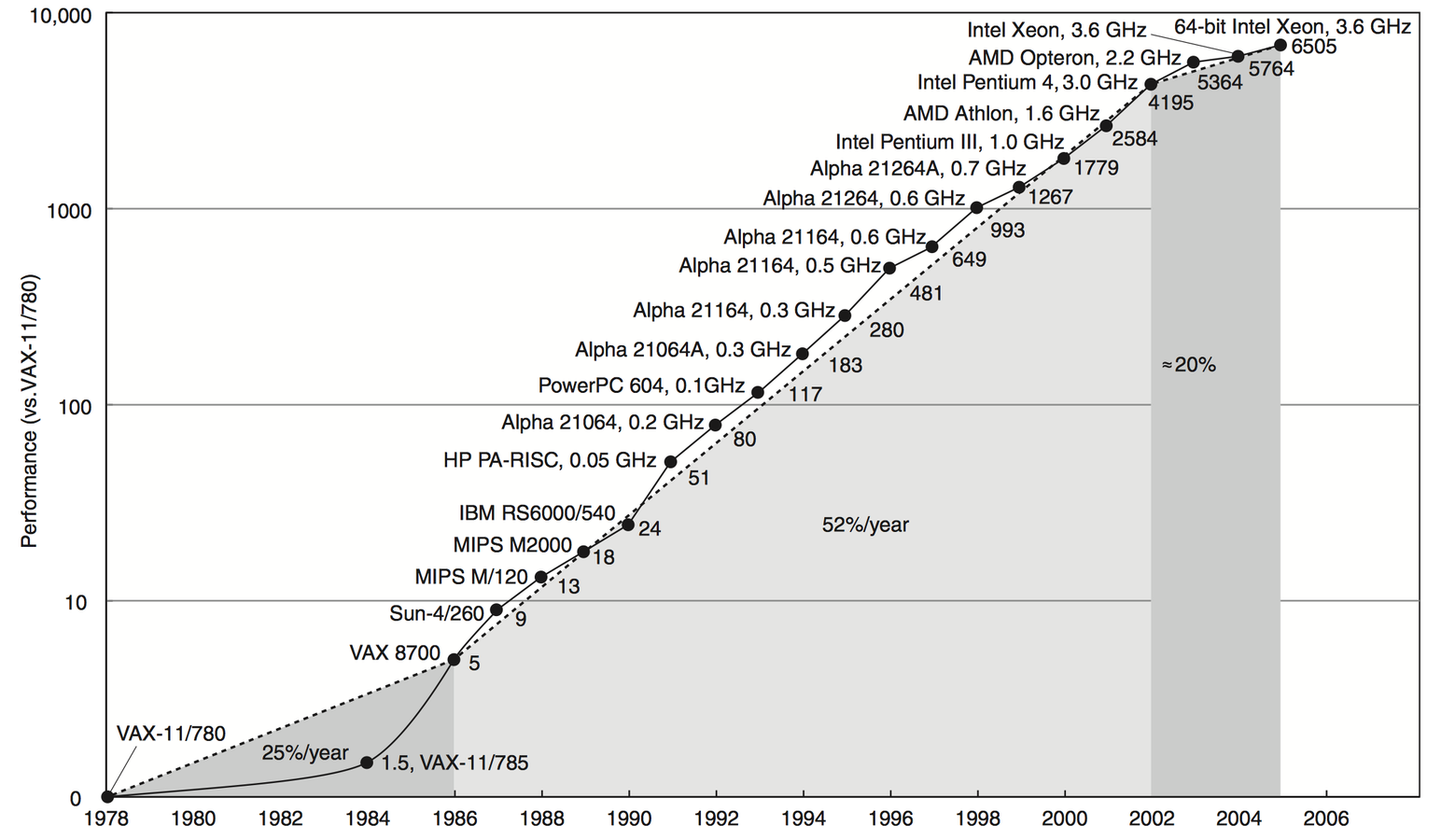
First a bit of history
1978 Model View Controller is born
»MVC was conceived as a general solution to the problem of users controlling a large and complex data set.«
- Trygve Reenskaug [1]
On an abstract level that sounds very promising!
1995 Netscape Navigator 2.0
Introduced the Document Object Model
& JavaScript
Now web pages could be dynamic!
Times are a changing
Now for a small detour
Path dependence
»Path dependence explains how the set of decisions one faces for any given circumstance is limited by the decisions one has made in the past, even though past circumstances may no longer be relevant«
- Dave Praeger [2]
Your mind is like a canyon formed by raindrops of knowledge!
The problem with MVC
Everything is mutable!
The classic problem of a notification counter being out of sync with the rest of the site was what prompted Facebook to write React
The problem with MVC
MVC as used on the web uses
bindings, observers and templates
Lots and lots of state!
and state is...

The problem with MVC
Communication is... everywhere!
Why write software likes it's 1995?
We don't have to use exclusively mutable APIs
We can make our communication more straight forward
Functional Design
We separate data from behaviour
Which makes it easier to reuse, compose and share that behaviour
UI is our behaviour
We consolidate our data
One source of truth for the hole application, when any part of that data changes -
we rerender
Ideally we would like to treat our UI as
a pure function
(data) -> dom
Full render of everything every time at 60 fps
Unfortunatly that would be slow and impractical
React
Virtual Document Object Model
(props, state) -> v-dom
(props) -> v-dom
Virtual Document Object Model
Diff between previous and new v-dom
Wicked fast and very practical
f(old-dom, new-dom) = Δ
Computes minimal changes and puts them in a queue for batching - like a GPU!
»Retained mode is going to be used by at least ten times as many programmers as immediate mode. On the other hand, the world class applications that really step to new levels are going to be done in an immediate mode graphics API.«
- John Carmack [3]
Demo Time
React Component
var App = React.createClass({
render: function () {
return React.DOM.h1(null, "Hello, world!");
}
});React Rendering
var App = React.createClass({
render: function () {
return React.DOM.h1(null, "Hello, world!");
}
});
React.renderComponent(App(), document.getElementById('main'));React Props
var App = React.createClass({
render: function () {
return React.DOM.h1(null, "Hello, " + this.props.name + "!");
}
});
React.renderComponent(App({ name: "Cetrea" }), document.getElementById('main'));React DOM Attributes
var App = React.createClass({
render: function () {
return React.DOM.h1({ className: "header" }, "Hello, " + this.props.name + "!");
}
});
React.renderComponent(App({ name: "Cetrea" }), document.getElementById('main'));React Events
var App = React.createClass({
onClickHandler: function (event) {
console.log("Clickidyclick");
},
render: function () {
return React.DOM.h1({ className: "header",
onClick: this.onClickHandler },
"Hello, " + this.props.name + "!");
}
});
React.renderComponent(App({ name: "Cetrea" }), document.getElementById('main'));React State
var App = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function() {
return {value: 'Hello!'};
},
handleChange: function(event) {
this.setState({value: event.target.value}); //Merges with current state
},
render: function() {
var value = this.state.value;
return React.DOM.input({ type="text", value=value,
onChange=this.handleChange}, null);
}
});
React.renderComponent(App(), document.getElementById('main'));React JSX
var App = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function() {
return {value: 'Hello!'};
},
handleChange: function(event) {
this.setState({value: event.target.value}); //Merges with current state
},
render: function() {
var value = this.state.value;
return <input type="text" value={value} onChange={this.handleChange} />;
}
});
React.renderComponent(App(), document.getElementById('main'));React JSX
var Nav = React.createClass({
render: function() {
var links = this.props.links.map((link) => {
var classes = "link" + window.hash === link.href ? " active" : "";
return <li className={classes}><a href={link.href}>{link.title}</a></li>;
});
return <ul className="links">{ links }</ul>;
}
});
React.renderComponent(Nav({ links: [...] }), document.getElementById('navigation'));React Component Specification
- render
- getInitialState
- getDefaultProps
- propTypes
- mixins
- statics
- displayName
React Component Lifecycle
- componentWillMount
- componentWillUnmount
- componentDidMount
- shouldComponentUpdate
- componentWillReceiveProps
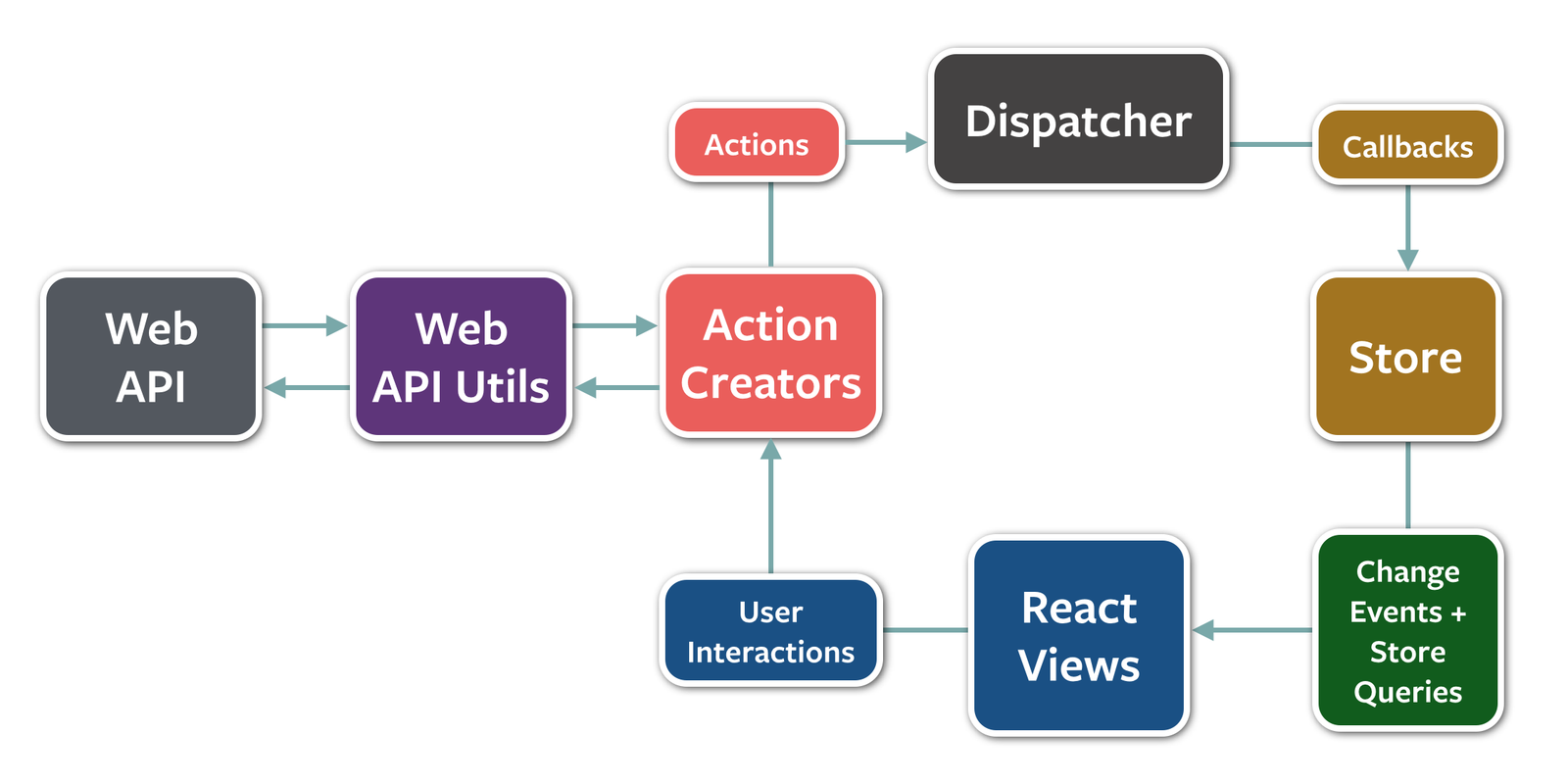
React Architecture
Flux
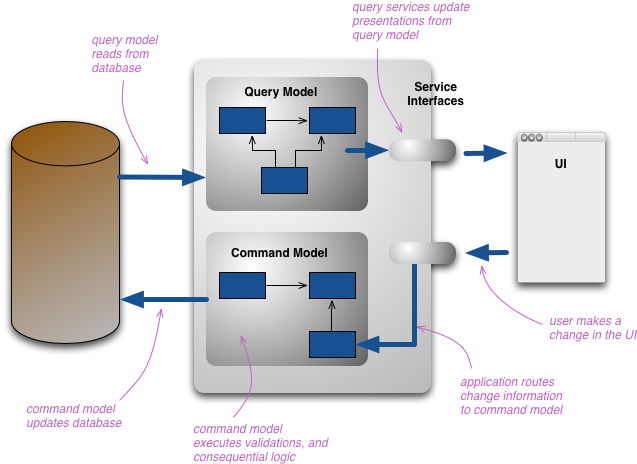
React Architecture
Command Query Responsibility Segregation
React Architecture
React Architecture
f(state, event) -> state
React Architecture
f(state, event) -> seq<state>
React Architecture
Immutable stream of read models
Flowing them into React
React Architecture
Fits very well with Event Sourcing
React Architecture
React Advantages
Straight forward communication
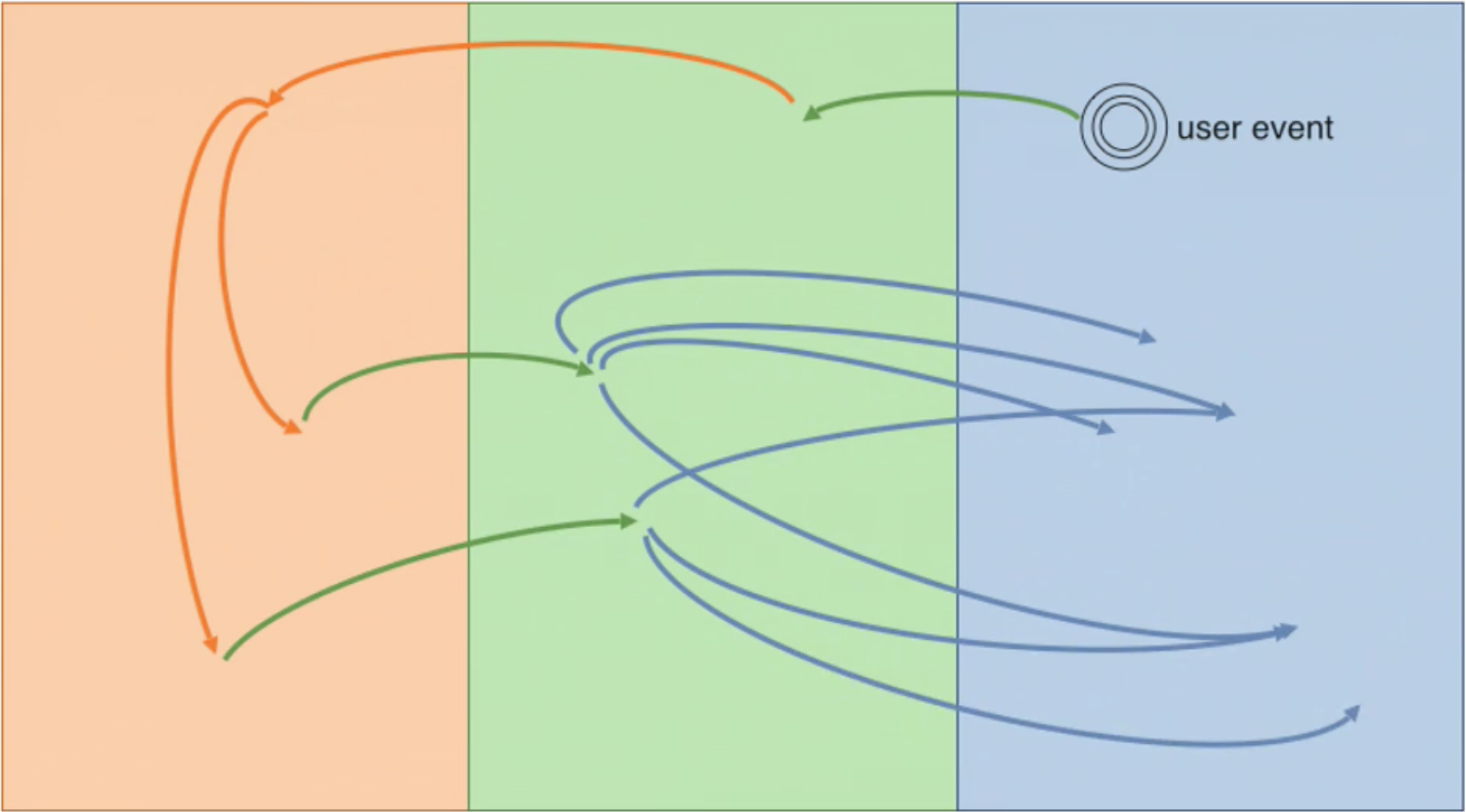
React Advantages
Indempotence
React Advantages
Immutability
Makes it trivial to support undo and redo
Makes it trivial to do performance optimisations
React Advantages
Testability
The virtual DOM let's you fake events very easily and you can very easily verify the desired markup would be generated. It's just JS!
React Advantages
Debugability
You can recreate the UI in the exact state that it was in when the user encountered an error
You can easily record how the user is using your application. Simply save the app state in a stream of states and replay that later. Can give you great insight!
React Advantages
Battlehardened on the biggest sites on the web
Khan Accademy
Yahoo & more
React Advantages
Integrates well with existing frameworks since all React cares about is the View.
No reason to not get started on existing projects :)
Immutable datastructures
Immutable.js is a library by Facebook
Gives you immutable vectors, maps and sets
var vec1 = Immutable.Vector(1, 2);
var map1 = Immutable.Map({a:1, b:2, c:3});
var set1 = Immutable.Set(1,2,3);
Immutable.js is a library by Facebook
Vectors
var vect1 = Immutable.Vector(1, 2);
var vect2 = vect1.push(3, 4, 5);
var vect3 = vect2.unshift(0);
var vect4 = vect1.concat(vect2, vect3);
assert(vect1.length === 2);
assert(vect2.length === 5);
assert(vect3.length === 6);
assert(vect4.length === 13);
assert(vect4.get(0) === 1);Immutable.js is a library by Facebook
Maps
var nested = Immutable.fromJS({a:{b:{c:[3,4,5]}}});
// Map { a: Map { b: Map { c: Vector [ 3, 4, 5 ] } } }
var nested2 = nested.mergeDeep({a:{b:{d:6}}});
// Map { a: Map { b: Map { c: Vector [ 3, 4, 5 ], d: 6 } } }
nested2.getIn(['a', 'b', 'd']);
// 6
var nested3 = nested2.updateIn(['a', 'b', 'd'], value => value + 1);
// Map { a: Map { b: Map { c: Vector [ 3, 4, 5 ], d: 7 } } }
var nested4 = nested3.updateIn(['a', 'b', 'c'], vect => vect.push(6));
// Map { a: Map { b: Map { c: Vector [ 3, 4, 5, 6 ], d: 7 } } }Immutable.js is a library by Facebook
Structural Equality
var map1 = Immutable.Map({a:1, b:1, c:1});
var map2 = Immutable.Map({a:1, b:1, c:1});
assert(map1 !== map2);
assert(Immutable.is(map1, map2) === true);Immutable.js is a library by Facebook
Cursors
var data = Immutable.fromJS({ a: { b: { c: 1 } } });
var cursor = data.cursor(['a', 'b', 'c'], newData => {
data = newData;
});
// ... elsewhere ...
cursor.deref(); // 1
cursor = cursor.update(x => x + 1);
cursor.deref(); // 2
// ... back to data ...
data.getIn(['a', 'b', 'c']); // 2Immutable.js is a library by Facebook
Batching Mutations
var vect1 = Immutable.Vector(1,2,3);
var vect2 = vect1.withMutations(function (vect) {
vect.push(4).push(5).push(6);
});
assert(vect1.length === 3);
assert(vect2.length === 6);Time to glass
Mobile web
Giving people browsing your page on their phone a good experience is important
One measure is time-to-glass
With traditional server side rendered apps it was easier - luckily React components can be rendered server side
Mobile web
What happens when you have loads of client-side JS that renders your UI?
Mobile web
With traditional server side rendered apps it was easy
Luckily React components can be rendered server side
React server side rendering
var Header = React.createClass({ render: () => <div>this.props.title</div> });
var Content = React.createClass({ render: () => <div>this.props.content</div> });
var App = React.createClass({ render: () => {
return <div>
<Header title={this.props.data.title} />
<Content content={this.props.data.content} />
</div>;
}});
function reqHandler(req, res) {
fetchDataForRoute(req, (data) => {
res.send("<html><body>" +
React.renderComponentToString(<App data={data} />)) + "</body></html>");
});
}
app.get('/', reqHandler);References
[1] Trygve/MVC by Trygve Reenskaug
[2] Our Love Of Sewers: A Lesson in Path Dependence by Dave Praeger
[3] OpenGL and Direct3D by John Carmack
- Flux