{ "super": "API" }
Un (tout) petit rappel
pour commencer
HTTP
GET /path/to/foo?type=bar HTTP/1.1 Host: api.example.com
url = scheme://host:port/path?query_string
(version simplifée)
méthode = GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, ...
Constat
- les XHR sont souvent codées directement dans les vues,
- les urls sont très souvent codées en dur,
- parfois sous forme de variables,
- comment faire lorsqu'on doit pointer différents environnements donc différentes url entre le test, la recette, la preprod, la prod ?
- la création des query string se fait souvent "à la main",
- etc,
=> qu'en est-il des bonnes pratiques ?
Petit aperçu
d'appels à une API ?
Quelques exemples avec jQuery
Construction du path
var request = $.ajax({
url: "https://api.navitia.io/v1/" + path,
method: "get",
dataType: "json"
});var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
var path = "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/" + point.lng + ";" + point.lat + "/stop_schedules";
var request = $.ajax({
url: "https://api.navitia.io/v1/" + path,
method: "get",
dataType: "json"
});Appel API
var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
var path = "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/" + point.lng + ";" + point.lat + "/stop_schedules";
var request = $.ajax({
url: "https://api.navitia.io/v1/" + path,
method: "get",
dataType: "json",
xhrFields: {
withCredentials: true
}
})
request.done(function (data, textStatus, jqXHR) { /* do something */ });
request.fail(function (jqXHR, textStatus, error) { /* do something */ });
var authKey = "XXXXXXX";
var lang = "fr";
var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
Création d'une query string
Data
Building query: concatenate
var authKey = "XXXXXXX";
var lang = "fr";
var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
var query =
"key=" + authKey +
"&lang=" + lang +
"&position=" + point.lat + "," + point.lng;
Building service url
var authKey = "XXXXXXX";
var lang = "fr";
var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
var query =
"key=" + authKey +
"&lang=" + lang +
"&position=" + point.lat + "," + point.lng;
var path = "/position";
$.ajax({
url: "http://api.what3words.com" + path + (query ? "?" + query : ""),
method: "get",
dataType: "json"
})
var request = queryWords({
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
});
Création d'une query: refactoring
Il est toujours possible de faire un refactoring
On cache la complexité avec une fonction queryWords
function queryWords(point) {
var authKey = "XXXXXXX";
var lang = "fr";
var path = "/position";
var query =
"key=" + authKey +
"&lang=" + lang +
"&position=" + point.lat + "," + point.lng;
return $.ajax({
url: "http://api.what3words.com" + path + (query ? "?" + query : ""),
method: "get",
dataType: "json"
});
}
var request = queryWords({
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
});
var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
var path = "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/" + point.lng + ";" + point.lat + "/stop_schedules";
var request = $.ajax({
url: "https://api.navitia.io/v1/" + path,
method: "get",
dataType: "json",
});Authentification HTTP
var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
var path = "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/" + point.lng + ";" + point.lat + "/stop_schedules";
var request = $.ajax({
url: "https://api.navitia.io/v1/" + path,
method: "get",
dataType: "json"
});var username = "username";
var password = "very-secret-password";
// generate base64 encoded string "Basic XXXXXX"
var authorization = btoa(username + ":" + password);
var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
var path = "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/" + point.lng + ";" + point.lat + "/stop_schedules";
var request = $.ajax({
url: "https://api.navitia.io/v1/" + path,
method: "get",
dataType: "json"
});var username = "username";
var password = "very-secret-password";
// generate base64 encoded string "Basic XXXXXX"
var authorization = btoa(username + ":" + password);
var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
var path = "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/" + point.lng + ";" + point.lat + "/stop_schedules";
var request = $.ajax({
url: "https://api.navitia.io/v1/" + path,
method: "get",
dataType: "json",
beforeSend: function (xhr) {
xhr.setRequestHeader("Authorization", authorization);
}
});Problématiques
- quelle gestion des URLS ?
- comment construire le path ?
- quelle gestion des queries ?
- quelle gestion de l'authentification ?
Gestion des URL (1/2)
- Protocole: http ou https
- Gestion de différents environnements: recette, preprod, prod, ...
-
Maintien d'anciennes versions d'API: v0, v1, ...
http://recette.domaine.tld https://preprod.domaine.tld https://prod.domaine.tld/v1 https://prod.domaine.tld/v2
Gestion des URL (2/2)
-
Ou sous forme de variables ?
$.ajax({
url: "http://recette.domaine.tld/foo"
});var apiUrl = "http://recette.domaine.tld";
$.ajax({
url: apiUrl + "/foo"
});-
Hardcodées ?
Gestion des path
-
Comment gérer des paths paramétrés?
// PATH /coverage/fr-idf/coords/<resource>/stop_schedules
var path = "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/_resource_/stop_schedules";-
Où sont stockés les paths ?
-
hardcodées ?
-
variables ?
-
// PATH /coverage/fr-idf/coords/<resource>/stop_schedules
var path = "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/_resource_/stop_schedules";
$.ajax({
url: "https://api.navitia.io/v1" + path
});
// PATH /coverage/fr-idf/coords/<resource>/stop_schedules
var path = "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/_resource_/stop_schedules";
var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
path.replace("_resource_", point.lng + ";" + point.lat);
$.ajax({
url: "https://api.navitia.io/v1" + path
});
Gestion des queries
Comment générer ce genre de query ?
// ?from=2.354255;48.869424&to=2.267189;48.8811491&datetime=20150624T190000
// &datetime_represents=arrival&max_duration_to_pt=300&max_nb_tranfers=2Gestion des queries (1/3)
// ?from=2.354255;48.869424&to=2.267189;48.8811491&datetime=20150624T190000
// &datetime_represents=arrival&max_duration_to_pt=300&max_nb_tranfers=2Par une concaténation de chaînes de caractères ?
var query = "?";
query += "from=" + from.lng + ";" + from.lat;
query += "&to=" + to.lng + ";" + to.lat;
query += "&datetime=" + moment.format(time);
query += "&datetime_represents=arrival";
query += "&max_duration_to_pt=" + duration;
query += "&max_nb_tranfers=" + transfers;Gestion des queries (2/3)
var data = {
from: "2.354255;48.869424",
to: "2.267189;48.8811491",
datetime: "20150624T190000",
datetime_represents: "arrival",
max_duration_to_pt: 300,
max_nb_tranfers: 2
};
Hashmap pour les cas simples ?
var data = {
from: "2.354255;48.869424",
to: "2.267189;48.8811491",
datetime: "20150624T190000",
datetime_represents: "arrival",
max_duration_to_pt: 300,
max_nb_tranfers: 2
};
var queryArgs = [];
for (var param in data) {
queryArgs.push(param + "=" + data[param]);
}
var query = "?" + queryArs.join("&");
var data = {
from: "2.354255;48.869424",
to: "2.267189;48.8811491",
datetime: "20150624T190000",
datetime_represents: "arrival",
max_duration_to_pt: 300,
max_nb_tranfers: 2
};
var queryArgs = [];
for (var param in data) {
queryArgs.push(param + "=" + data[param]);
}
var query = "?" + queryArs.join("&");
// ?from=2.354255;48.869424&to=2.267189;48.8811491&datetime=20150624T190000
// &datetime_represents=arrival&max_duration_to_pt=300&max_nb_tranfers=2Building query
Gestion des queries (3/3)
var from = {lng: 2.354255, lat: 48.869424};
var to = {lng: 2.267189, lat: 48.8811491}
var query = journeyQuery(from, to);
var journeyQuery = function (from, to) {
var data = {
datetime: "20150624T190000",
datetime_represents: "arrival",
max_duration_to_pt: 300,
max_nb_tranfers: 2
};
var queryArgs = [];
for (var param in data) {
queryArgs.push(param + "=" + data[param]);
}
queryArgs.push("from=" + from.lng + ";" + from.lat);
queryArgs.push("from=" + to.lng + ";" + to.lat);
return "?" + queryArs.join("&");
}
Fonction pour les cas plus complexes ?
var from = {lng: 2.354255, lat: 48.869424};
var to = {lng: 2.267189, lat: 48.8811491}
var query = journeyQuery(from, to);
var from = {lng: 2.354255, lat: 48.869424};
var to = {lng: 2.267189, lat: 48.8811491}
var query = journeyQuery(from, to);
var journeyQuery = function (from, to) {
var data = {
datetime: "20150624T190000",
datetime_represents: "arrival",
max_duration_to_pt: 300,
max_nb_tranfers: 2
};
var queryArgs = [];
for (var param in data) {
queryArgs.push(param + "=" + data[param]);
}
queryArgs.push("from=" + from.lng + ";" + from.lat);
queryArgs.push("from=" + to.lng + ";" + to.lat);
return "?" + queryArs.join("&");
}
// ?from=2.354255;48.869424&to=2.267189;48.8811491&datetime=20150624T190000
// &datetime_represents=arrival&max_duration_to_pt=300&max_nb_tranfers=2Méthode HTTP
$.get()
$.post()
$.ajax({method: "put"})
$.ajax({method: "delete"})
$.ajax({method: "head"})
request.get()
request.post()
request.put()
request.del()
request.head()
Méthode HTTP
fetch(url, {method: "get"})
https://github.com/github/fetch
fetch(url, {method: "post"})
fetch(url, {method: "put"})
fetch(url, {method: "delete"})
fetch(url, {method: "head"})
Authentification
// https://github.com/what3words/w3w-javascript-wrapper/blob/master/what3words.js
var what3words = new function (language) {
this.API_KEY = 'YOURAPIKEY'; // Change to your what3words API key
this.language = language || 'en'; // Change to your default language
// --
this.postRequest = function (url, data, callback) {
data.key = this.API_KEY;
data.lang = this.language;
$.post('http://api.what3words.com/' + url, data, callback, 'JSON');
};
};Authentification par un paramètre dans la query
- variable ?
- codé en dur ?
https://api.what3words.com/position?key=YOURAPIKEY&lang=en&...
Authentification
ex. Basic Auth
- variable ?
- codé en dur ?
var username = "username";
var password = "very-secret-password";
// generate base64 encoded string "Basic XXXXXX"
var authorization = btoa(username + ":" + password);
$.ajax({
// ...
});var username = "username";
var password = "very-secret-password";
// generate base64 encoded string "Basic XXXXXX"
var authorization = btoa(username + ":" + password);
$.ajax({
// ...
beforeSend: function (xhr) {
xhr.setRequestHeader("Authorization", authorization);
}
});Mais encore ...
- Où stocker des headers dynamiques, par exemple
renvoyés par une API, type CSRF ? - Réponse serveur: callback ou Promise ?
- Différents encodages pour différents appels:
- form
- json
- xml
- Gestion d'appels sur plusieurs API ?
Et pourquoi pas
- des fichiers de configuration
- des appels de méthode simples
- aucune manipulation des URLS
- abstraction sur les appels d'XHR
superapi
Sans superapi
// PATH /coverage/fr-idf/coords/<resource>/stop_schedules
var path = "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/_resource_/stop_schedules";
var point = {
lat: 48.874192
lng: 2.353241
};
path.replace("_resource_", point.lng + ";" + point.lat);
var request = $.ajax({
url: "https://api.navitia.io/v1" + path
});
request.done(function() {
// do something
});superapi
En 3 points ...
superapi
Au commencement, une configuration
1. configuration
{
"baseUrl": "https://api.navitia.io/v1",
"services": {
"stopSchedules": {
path: "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/:lng;:lat/stop_schedules",
method: "GET"
}
},
options: {
type: "form"
},
headers: {
"Authorization": "Basic ZWRkNWYxODQt...."
}
}fichier JSON
superapi
Ensuite, la mise en place
2. initialisation
var api = new superapi.default.Api();
var api = new superapi.default.Api();
api.configure("navitia", navitiaConf);
superapi
Fire!
3. appel XHR
api.navitia.stopSchedule({
params: point,
query: {
distance: distance
}
});api.navitia.stopSchedule();superapi
Quelques explications
1. superapi: configuration
{
"baseUrl": "",
"services": {},
"headers": {},
"options": {}
}1. superapi: configuration
{
"baseUrl": "https://api.navitia.io/v1",
"services": {
"stopSchedules": {
"path": "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/:lng;:lat/stop_schedules",
"method": "GET",
"options": {
"type": "json"
}
}
},
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic ZWRkNWYxODQt...."
}
}API endpoint
1. superapi: configuration
{
"baseUrl": "https://api.navitia.io/v1",
"services": {
"stopSchedules": {
"path": "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/:lng;:lat/stop_schedules",
"method": "GET",
"options": {
"type": "json"
}
}
},
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic ZWRkNWYxODQt...."
}
}Services
services est un hash map de services configurés
1. superapi: configuration
{
"baseUrl": "https://api.navitia.io/v1",
"services": {
"stopSchedules": {
"path": "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/:lng;:lat/stop_schedules",
"method": "GET",
"options": {
"type": "json"
}
}
},
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic ZWRkNWYxODQt...."
}
}Service id
- Le service id doit être préférablement en camelCase
- Le service id est le nom de la fonction générée (curry)
1. superapi: configuration
{
"baseUrl": "https://api.navitia.io/v1",
"services": {
"stopSchedules": {
"path": "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/:lng;:lat/stop_schedules",
"method": "GET",
"options": {
"type": "json"
}
}
},
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic ZWRkNWYxODQt...."
}
}Service path
- Peut-être un chemin paramétré
- Les paramètres doivent suivre le patron :param
- Ce patron est configurable
1. superapi: configuration
{
"baseUrl": "https://api.navitia.io/v1",
"services": {
"stopSchedules": {
"path": "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/:lng;:lat/stop_schedules",
"method": "GET",
"options": {
"type": "json"
}
}
},
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic ZWRkNWYxODQt...."
}
}Service method
- Valeur par défaut: "GET"
- Support des différents verbes HTTP
1. superapi: configuration
{
"baseUrl": "https://api.navitia.io/v1",
"services": {
"stopSchedules": {
"path": "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/:lng;:lat/stop_schedules",
"method": "GET",
"options": {
"type": "json"
}
}
},
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic ZWRkNWYxODQt...."
}
}Service options
- hash map des différentes options par défaut
1. superapi: configuration
{
"baseUrl": "https://api.navitia.io/v1",
"services": {
"stopSchedules": {
"path": "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/:lng;:lat/stop_schedules",
"method": "GET",
"options": {
"type": "json"
}
}
},
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic ZWRkNWYxODQt...."
}
}global headers
1. superapi: configuration
{
"baseUrl": "https://api.navitia.io/v1",
"services": {
"stopSchedules": {
"path": "/coverage/fr-idf/coords/:lng;:lat/stop_schedules",
"method": "GET"
}
},
"options": {
"type": "json",
"accept": "json"
},
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic ZWRkNWYxODQt...."
}
}global options
Also supported : global options
2. superapi: initialisation
var api = new superapi.default.Api();
api.withSuperagent(superagent);
api.configure("navitia", navitiaConf);
1. setup API wrapper
3. add configuration
// controllers/api.js
define([
"superapi",
"superagent",
"json!config/api/navitia.json"
],
function (superapi, superagent, navitiaConf) {
"use strict";
var api = new superapi.default.Api();
api.withSuperagent(superagent);
api.configure("navitia", navitiaConf);
return api;
});2. add XHR agent
3. superapi: appel XHR
return function(point, distance) {
return api.navitia.stopSchedule({
params: point,
query: {
distance: distance
}
});
};
XHR call
Exemple avec utilisation d'un wrapper
// api/stopSchedule.js
define([
"controllers/api"
],
function (api) {
"use strict";
return function(point, distance) {
return api.navitia.stopSchedule({
params: point,
query: {
distance: distance
}
});
};
});
3. superapi: appel XHR
var point = {
lat: 48.874192,
lng: 2.353241
};
stopSchedule(point, 500).then(/* */);
calling our XHR wrapper
// somewhere in your code
define([
"api/stopSchedule"
], function (stopSchedule) {
// ...
var point = {
lat: 48.874192,
lng: 2.353241
};
stopSchedule(point, 500).then(/* */);
// ...
});superapi
En quelques lignes
superapi
- La promesse d'une réponse
- Gestion de multiples API
- Modification de la requête
La promesse d'une réponse
// somewhere in your code
define([
"api/stopSchedule"
], function (stopSchedule) {
// ...
var point = {
lat: 48.874192,
lng: 2.353241
};
stopSchedule(point, 500)
.then(function (res) {
// success
})
.catch(function (error) {
// error!
});
// ...
});returning a Promise
sous forme d'une promesse
// api/stopSchedule.js
define([
"controllers/api"
],
function (api) {
"use strict";
return function(point, distance) {
return api.navitia.stopSchedule({
params: point,
query: {
distance: distance
}
});
};
});
La promesse d'une réponse
// somewhere in your code
define([
"api/stopSchedule"
], function (stopSchedule) {
// ...
var point = {
lat: 48.874192,
lng: 2.353241
};
var callback = function (err, res) {
// do something
};
stopSchedule(point, 500, callback);
// ...
});passing a callback
ou d'un bon vieux callback
// api/stopSchedule.js
define([
"controllers/api"
],
function (api) {
"use strict";
return function(point, distance, cb) {
return api.navitia.stopSchedule({
params: point,
query: {
distance: distance
},
callback: cb
});
};
});
Gestion de multiples API
il suffit d'ajouter autant de configurations que nécessaires
var api = new superapi.default.Api();
api.withSuperagent(superagent);
// controllers/api.js
define([
"superapi",
"superagent",
"json!config/api/navitia.json",
"json!config/api/uber.json"
],
function (superapi, superagent, navitia, uber) {
"use strict";
var api = new superapi.default.Api();
api.withSuperagent(superagent);
api.configure("navitia", navitia);
api.configure("uber", uber);
return api;
});
var api = new superapi.default.Api();
api.withSuperagent(superagent);
api.configure("navitia", navitia);
var api = new superapi.default.Api();
api.withSuperagent(superagent);
api.configure("navitia", navitia);
api.configure("uber", uber);
Modification de la requête
Accéder à la requête
api.navitia.stopSchedule({
params: point,
query: {
distance: distance
}
})api.navitia.stopSchedule({
params: point,
query: {
distance: distance
},
edit: function (req) {
// before xhr call
}
})ROADMAP
Actuellement
version 0.10.5
- Support callback / promise
- Une seule configuration
- Gestion des headers dynamiques
- Un seul agent supporté : superagent (historique)
Juillet
version 1.0.0
- Réécriture complète
- La même chose que la 0.10.5 :)
- Multiples configurations
- Multiples agents ($.ajax, ...)
- Meilleure documentation
- plugins API ?
Et Backbone ?
backbone-superapi-sync
https://github.com/stephanebachelier/backbone-superapi-sync
backbone-superapi-sync
define([
'backbone',
'backbone.superapiSync',
'controllers/api',
],
function (Backbone, backboneSuperapiSync, superapi) {
'use strict';
return Backbone.Collection.extend({
sync: function (method, model, options) {
return backboneSuperapiSync(superapi).call(this, method, model, options);
}
});
});
backbone-superapi-sync
define([
'backbone',
'controllers/api'
],
function (Backbone, api) {
'use strict';
return Backbone.Collection.extend({
url: function () {
var query = {
q: this.q,
offset: this.offset,
limit: this.size,
'filters[type]': 'entities',
};
return api.buildUrl('search', undefined, query);
}
});
});
/!\ code 0.10.5
Encore plus fort
APItools.com

PROXY sur VOS API
- Réécriture de HTTP queries
- Injection de headers HTTP
- Cache
- Un bon moyen de pallier les limites d'appels
- Réécriture de réponse
PROXY sur VOS API
- Open source
- Stack en ruby
- Des middlewares en LUA
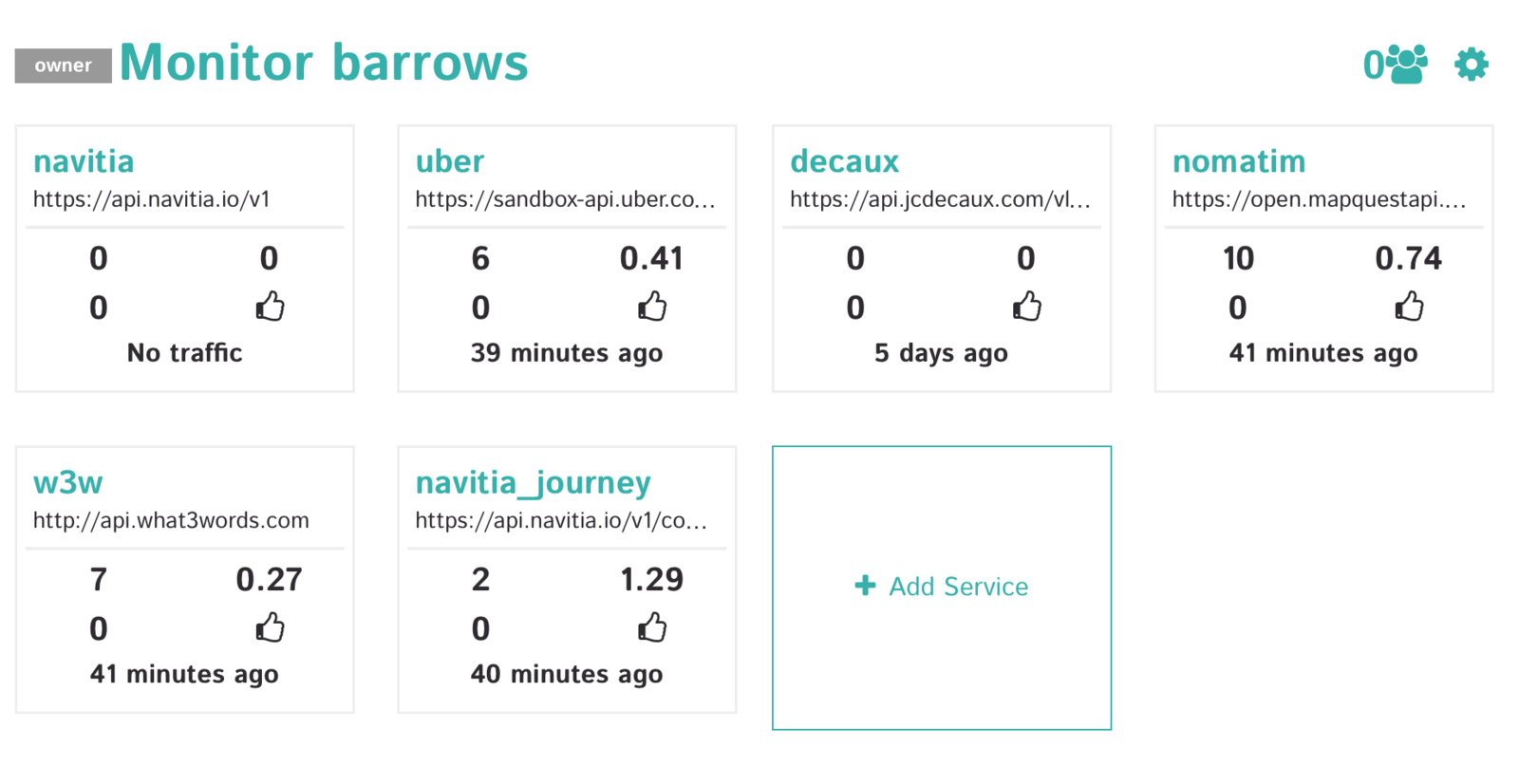
DASHBOARD
PIPELINE
Your app
AN API
Some middlewares