Researching & writing literature reviews in sociology
SOCI 16 | Professor Suya
Simon Elichko (they/he)
Social Sciences & Data Librarian
What we'll talk about today:
- Developing a rhetorical understanding of how to use sources in your research
- Differentiating literature review from background reading
- Navigating the research literature in sociology
- Citing sources in ASA Style
Intellectual interests
↓↓↓
Topics
↓↓
Research question
↓
Sources
↓
Argument
what you know already
multiple smaller questions
↓
↓
↓
what you need to learn more about
B / E / A / M
Writers rely on background sources, interpret or analyze exhibits, engage arguments, and follow methods.
–Bizup (2008)
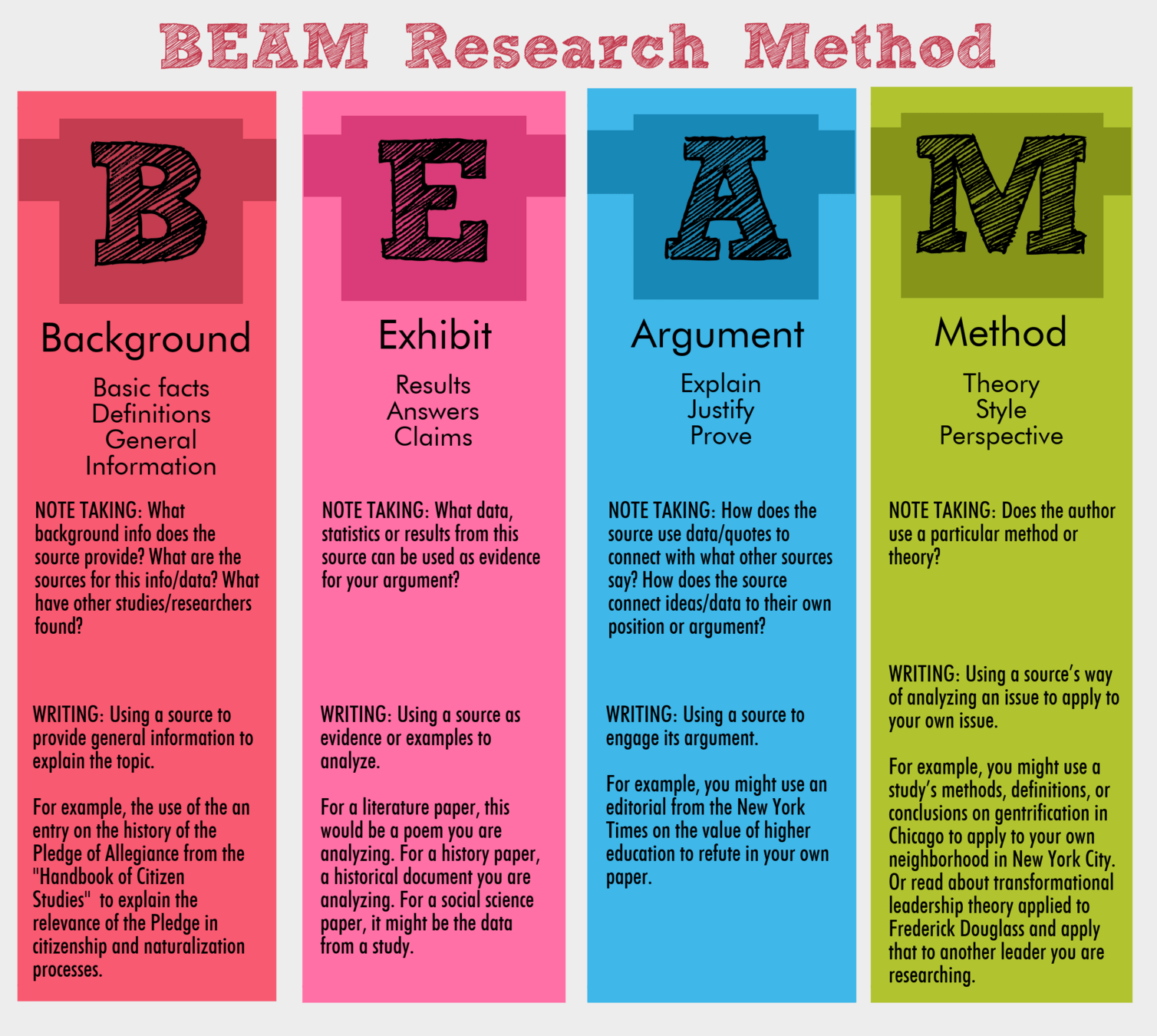
| Source Use | Definition | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Background | Factual information, often used to help introduce a topic and provide context | Often you'll see this in the introduction of a paper Doesn't always need a citation ("common knowledge") |
| Exhibit | Something you're analyzing and interpreting as part of making your main argument. | Can be qualitative or quantitative Commonly referred to as data, primary sources, texts |
| Argument | Claims that you're responding to, building on, or critiquing. | Often these will be scholarly articles and books from your discipline (sociology, chemistry, etc.) |
| Method | Approaches to studying or understanding something, which you are borrowing or adapting for your own research. | Can be practical or theoretical |
Roles that sources can play in your research:
Purpose
- How does it connect with your topic?
- What are you looking for?
- Background information
- Evidence / data
-
Arguments
- Other scholars' arguments that you can critique and build on
-
Methods
- Ideas for how to approach studying your specific question
Quality
- Is it scholarly?
- Does it cite other research?
-
Author expertise
- Author/contributor bios
- If the author's name is too common try adding site:.edu to your search
-
Publisher
- Article: was it published in an academic journal?
-
Book: published by a university press?
-
Routledge, Springer
-
Routledge, Springer
- How often is this article cited? An imperfect metric, but can be helpful. Look up the article in Google Scholar.
How do you know if a source is any good?
Open this link:
bit.ly/rias-beam
Background, exhibit, argument, or method?
From the article's introduction: "Class inequality in participation in American politics is a persistent challenge to democratic ideals. People with lower incomes are much less likely to vote than are those with higher incomes (Schlozman, Verba, and Brady 2012; Straughn and Andriot 2011; Wolfinger and Rosenstone 1980), who in turn have a disproportionately large influence on American politics and policy (Gilens 2012). Understandingthe sources of political nonparticipation among poorer people is therefore key to efforts to make American democracy more fully representative."
From: Laurison, D. (2015), The Willingness to State an Opinion: Inequality, Don't Know Responses, and Political Participation. Sociol Forum, 30: 925-948. https://doi.org/10.1111/socf.12202
Background, exhibit, argument, or method?
"My research in both Bosnian and Somalian communities has been anchored primarily in the micro-level context. However, unlike my research with Bosnians, my current project is congruent with several key principles of participatory action research (PAR). Mary Brydon-Miller (2001) identifies three fundamental principles of PAR."
From: Huisman, Kimberly. 2008. “‘Does This Mean You’re Not Going to Come Visit Me Anymore?’: An Inquiry into an Ethics of Reciprocity and Positionality in Feminist Ethnographic Research.”Sociological Inquiry 78(3):372–396.
Background, exhibit, argument, or method?
"Another area of tension with myself centered around feelings of competency. I was fairly comfortable conducting interviews with participants and interacting with various members of the Bosnian community. However, when the interview veered in another direction and people opened up to me about painful and traumatic experiences, as they sometimes did, I felt overwhelmed by their pain and unsure of what to say or do. I wanted to help but did not feel as though I had adequate skills to do so."
From: Huisman, Kimberly. 2008. “‘Does This Mean You’re Not Going to Come Visit Me Anymore?’: An Inquiry into an Ethics of Reciprocity and Positionality in Feminist Ethnographic Research.”Sociological Inquiry 78(3):372–396.
Background, exhibit, argument, or method?
"Although many feminist scholars continue to grapple with these issues (e.g., see Deem 2002; Deutsch 2004; DeFiore 2002; Henry 2003; Jacobs 2004), much qualitative research continues to be presented in a way that does not acknowledge the struggles and dilemmas behind the work. Mary Waters (2001:347) captures this reality when she writes, “I have found that frank discussions of the reality of the research experience are much rarer than the sanitized discussions of ‘research methods.’” Perhaps because of space limitations, findings are often presented in a way that leaves out the messy and tangled aspects of the work.”
From: Huisman, Kimberly. 2008. “‘Does This Mean You’re Not Going to Come Visit Me Anymore?’: An Inquiry into an Ethics of Reciprocity and Positionality in Feminist Ethnographic Research.”Sociological Inquiry 78(3):372–396.
From a list to a literature review
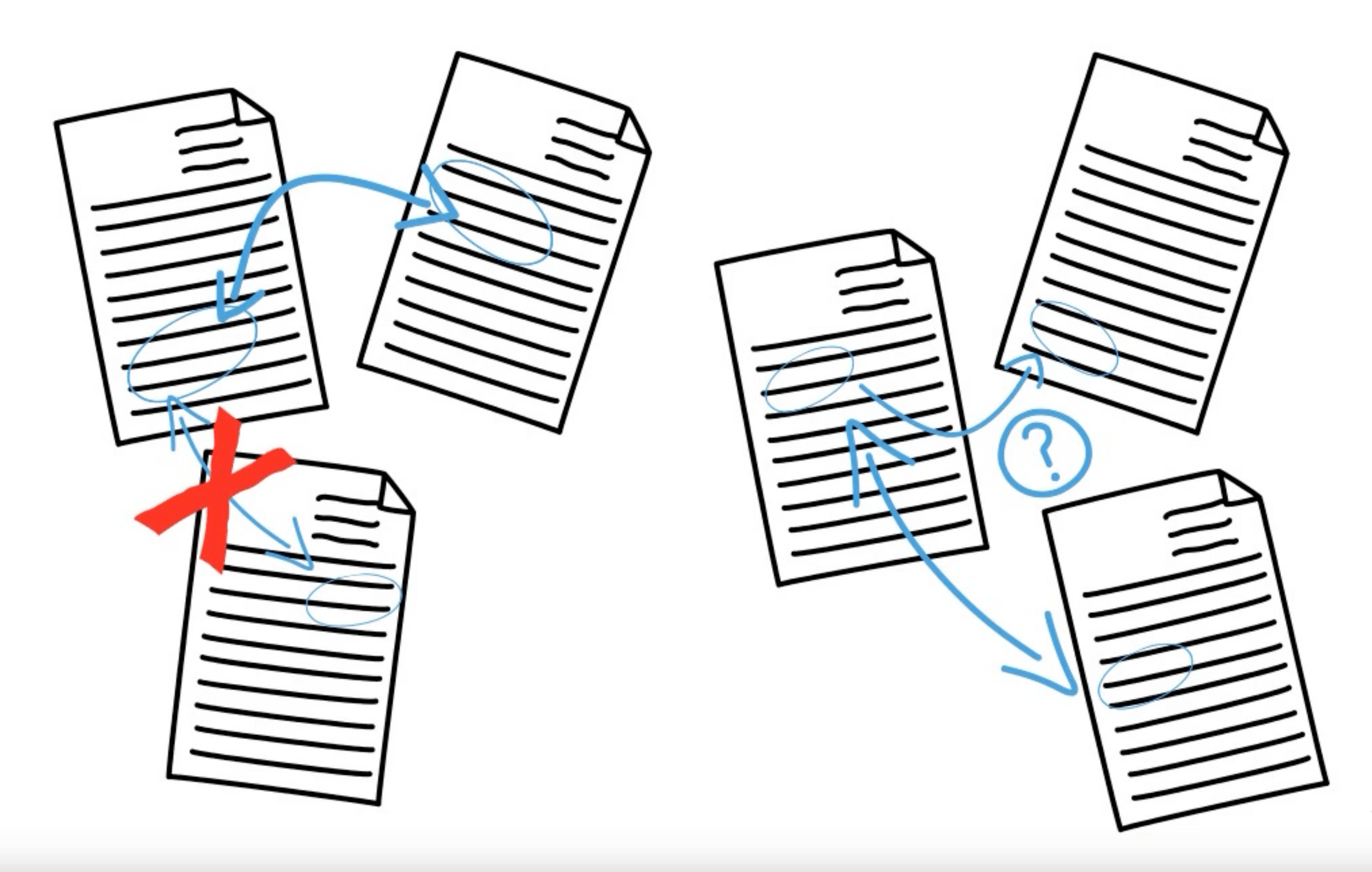


Making informed generalizations about patterns in the literature
Text

When you first look
at a review article:
- Read the abstract
- What is the scope of the review?
- What disciplines are mentioned?
- What sense do you get for the trajectory of the review article and the research it describes?
- Look at the section headings
ABSTRACT
The decisions employers make are of critical importance to sociological understandings of labor market stratification. While contemporary research documents employment outcomes with ever-growing precision, far less work examines how employers actually make decisions. In this article, I review research on the process of employer decision making, focusing on how employers evaluate, compare, and select workers in personnel decisions. I begin by summarizing the most prevalent theories of employer decision making in sociology, grouping them into competency-based, status-based, and social closure–based approaches. A common thread underlying much of this work is the assumption that employers are utility maximizers who base decisions on systematic, even if flawed, cognitive calculations of worker skill and workforce productivity. I then turn to recent research from sociology and beyond that challenges this notion and highlights the importance of understanding how employers themselves—their emotions, identities, and environments—affect decisions. I conclude by suggesting directions for future research.
why this review is interesting and distinctive
ABSTRACT
The decisions employers make are of critical importance to sociological understandings of labor market stratification.
While contemporary research documents employment outcomes with ever-growing precision, far less work examines how employers actually make decisions. In this article, I review research on the process of employer decision making, focusing on how employers evaluate, compare, and select workers in personnel decisions.
I begin by summarizing the most prevalent theories of employer decision making in sociology, grouping them into competency-based, status-based, and social closure–based approaches.
A common thread underlying much of this work is the assumption that employers are utility maximizers who base decisions on systematic, even if flawed, cognitive calculations of worker skill and workforce productivity. I then turn to recent research from sociology and beyond that challenges this notion and highlights the importance of understanding how employers themselves—their emotions, identities, and environments—affect decisions. I conclude by suggesting directions for future research.
scope (what's
on-topic)
outlining the key groups (aka "schools of thought")
characterizations of the literature
ABSTRACT
The decisions employers make are of critical importance to sociological understandings of labor market stratification.
While contemporary research documents employment outcomes with ever-growing precision, far less work examines how employers actually make decisions. In this article, I review research on the process of employer decision making, focusing on how employers evaluate, compare, and select workers in personnel decisions.
I begin by summarizing the most prevalent theories of employer decision making in sociology, grouping them into competency-based, status-based, and social closure–based approaches.
A common thread underlying much of this work is the assumption that employers are utility maximizers who base decisions on systematic, even if flawed, cognitive calculations of worker skill and workforce productivity. I then turn to recent research from sociology and beyond that challenges this notion and highlights the importance of understanding how employers themselves—their emotions, identities, and environments—affect decisions. I conclude by suggesting directions for future research.
trajectory
cues
Planning your literature review
Helpful questions to ask:
- What existing scholarly research is the closest match to your topic and question?
- Is there a scholar whose name keeps coming up?
- Who has done research that's similar to your project, even if it's different in one or two significant aspects?
- Potential aspects include geographic area, methodology, identity and demographics, time period, theme(s) emphasized
- What theoretical frameworks could enhance your understanding? Highlight something about this topic that might otherwise be overlooked?
Research mapping + making a synthesis matrix can help with your literature review, and overall organization
Active Reading: Synthesis Matrix
| Article 1 |
Article 2 | Article 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Question 1: |
|||
|
Question 2: |
|||
|
Theme 1: |
Top journals:
- American Sociological Review
- American Journal of Sociology
- Social Forces
- Social Problems

How do you read articles from a journal?
Search for the journal title on Tripod. Follow links to get access through Swarthmore's subscription.
Tripod: tripod.swarthmore.edu
Reviewing the literature:
Navigating sociology research
Browzine (link on guide)
How do you find articles and books on your topic that are scholarly?
Searching for sources using a database that emphasizes scholarly books and journal articles (peer-reviewed), and evaluating your results carefully.
3 good tools for finding sociology research, all linked from the
SOC 16 research guide:
- Web of Science
- Sociological Abstracts
- Tripod
Reviewing the literature:
Navigating sociology research
Let's try searching the Sociological Abstracts database for articles related to your topic.
Keep it simple! Just choose 2-3 keywords for now.
- For example: disaster inequality
To expand your results, add a synonym or related word:
Reviewing the literature:
Sociological Abstracts database

Tip: Put related words in one box and write OR in between them.
Reviewing the literature:
Sociological Abstracts database
How do you get the PDF for
an article you find in
Sociological Abstracts?
In your search results, click
on the article you want.
Use the FindIt button to search Tripod.
In Tripod, follow the Download PDF
or View Online link.


Use the search filters to narrow down your results to more relevant articles. (Click on More > to view the full lists.)
- Publication title
- Location
- Subject
Reviewing the literature:
Sociological Abstracts database


What's another way to limit your search
results to certain journals?
Go to Modify Search
Choose + Add a row
Change the drop-down menu
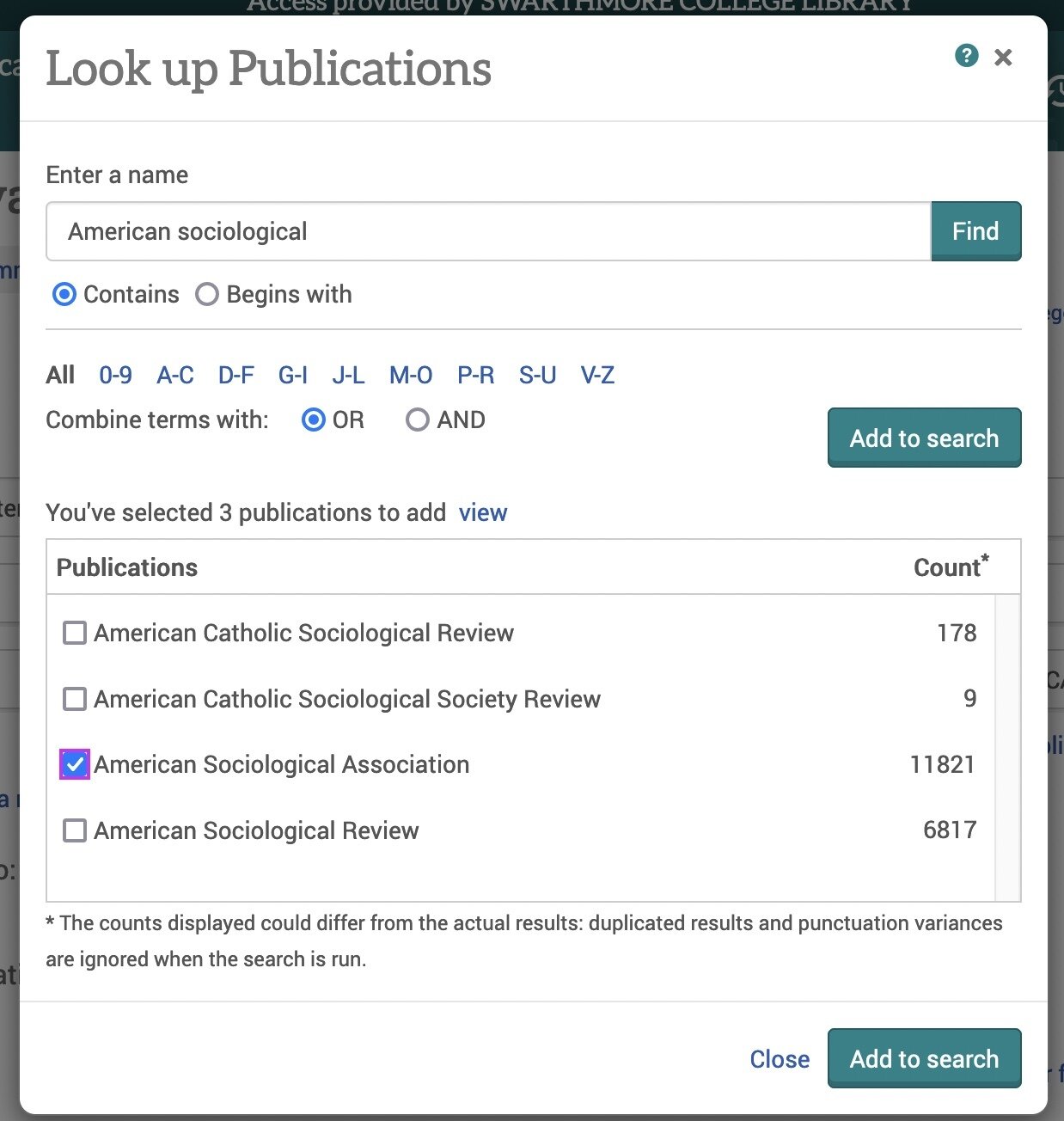
from Anywhere -> Publication title
Use Look up Publications to find
and add each journal. (Search for the
journal, check the box, then Add to search.)
Reviewing the literature:
Sociological Abstracts database

Improve your results:
- Make your results more precise by putting any
two-word phrases inside quotation marks- Hurricane Katrina --> "Hurricane Katrina"
This will only give you articles that include the exact phrase. Otherwise you'll get articles about hurricanes written by someone named Katrina.
- Hurricane Katrina --> "Hurricane Katrina"
- Use the "Peer Reviewed" limit if you're getting non-scholarly results
- See this link on the research guide: Improve Your Searches
Reviewing the literature:
Navigating sociology research
Other ways to find research:
- Use review articles + scholarly bibliographies
- Follow citation networks
- Use book reviews to evaluate books
Reviewing the literature:
Navigating sociology research
Staying organized
-
Document your process
Consider keeping a simple log of what you work on each day. Some students find it helpful to keep a list of questions and keywords.
-
Be consistent
Save your sources to the same folder so you can find everything even if you forget what's in an article. Descriptive filenames help.
-
Annotate or categorize sources
Group similar sources together when you find them, so it's easier to write your literature review. (See Organizing Sources)
Citing Sources
- Publication styles provide guidelines for writing, citing, and formatting
- Common academic styles include MLA, APA, and Chicago
- Who creates publication styles?
- Scholarly societies like ASA, MLA (Literature), APA (Psychology) APSA (Poli Sci)
- Publishers like University of Chicago Press
- Journals: Some journals have a custom style for authors to follow. Other journals specify a common style, e.g. Social Forces uses Chicago Author-Date.
What about outside of academia?
- Associated Press Style is widely used in journalism (Chicago vs. AP; also see TJA)
- Companies and organizations often have detailed style and content systems, including guidelines on writing, formatting, voice and tone, design and branding
Citing Sources in American Sociological Association Style
Official guide: ASA Style Guide (7th ed, 2022)
You can find a copy on the first floor of McCabe
near Simon's office. Shelved at this call number: REF HM 73 .A54
Good online guides include ASA Citation Formatting
(CSU CI) and ASA Style (UCSB)
Key Elements of ASA Style Citation
In-text citations
While writing, cite a work using the author's last name, the year of publication, and page number.
-
"Freedom only has meaning when one becomes conscious of the idea of freedom" (Rousseau 2014:11).
If you mention the author's last name in the sentence, cite them using just date and page:
- Rousseau (2014:11) points out that a person must understand the idea of freedom to truly appreciate it.
References
At the end of your paper, include a list of your references. Use double-spacing and organize references alphabetically by author's last name.
Bergesen, Albert, and Max Herman. 1998. “Immigration, Race, and
Riot: The 1992 Los Angeles Uprising." American Sociological
Review 63(1):39-54. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2657476.
Rousseau, Nathan. 2014. Society Explained. Lanham, MD: Rowman &
Littlefield.
Van Veelen, Bregje, Annabel Pinker, Margaret Tingey, Gerald Taylor
Aiken, and Will Eadson. 2019. “What Can Energy Research Bring to
Social Science?” Energy Research & Social Science 57:1-6.
doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2019.101240.
Example Citations & References in ASA Style
| Type of Source | In-Text Citations | References |
|---|---|---|
|
Book Edited collection with multiple editors - use this to cite the entire book (instead of a specific chapter) |
To cite the work as a whole: Sociologists have explored the development of citizenship practices and identities through education (Lee et al 2004). Cite a specific page: (Lee et al 2004:3) |
Lee, W.O. Grossman, David L., Kerry J. Kennedy, and Gregory P. Fairbrother, eds. 2004. Citizenship Education in Asia and the Pacific: Concepts and Issues. New York: Springer. |
|
Book Chapter (from an edited collection) Use this to cite a chapter from an edited collection. Generally, each chapter in an edited collection will have different authors. |
To cite the work as a whole: Recent research on has highlighted the particular food access issues faced by farmworkers and others central to the production of food in the United States (Brown and Getz 2011). Cite a specific page: (Brown and Getz 2011:124) |
Brown, Sandy, and Christy Getz. 2011. "Farmworker Food Insecurity and the Production of Hunger in California." Pp. 121-46 in Cultivating Food Justice: Race, Class and Sustainability, edited by A.H. Alkon and J. Agyeman. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. |
| Journal Article |
To cite the work as a whole: Social scientists have approached defining "good jobs" and "bad jobs" from a variety of perspectives (Kalleberg, Reskin, and Hudson 2000). Cite a specific page: (Kalleberg, Reskin, and Hudson 2000:256) |
Kalleberg, Arne L., Barbara F. Reskin, and Ken Hudson. 2000. “Bad Jobs in America: Standard and Nonstandard Employment Relations and Job Quality in the United States.” American Sociological Review 65(2):256-78. http:// www.jstor.org/stable/2657440. |
Useful tools for citing sources
Zotero
- Desktop + mobile app for creating a personal research library
- Tag and organize your sources
- Highlight and add notes to PDFs
- Generate citations in virtually any style - including ASA!
- Unlimited file storage while you're at Swat
- Some set-up required

Important caveat: Always double-check any citation you download from Zotero, Tripod, Google Scholar, or anywhere else. Automated systems (sadly) don't usually get all of the details right.
Image credit
Chau, Joe. 2021. Guangzhou City, blue, yellow, and white concrete staircase. Unsplash. https://unsplash.com/photos/6vTw1T0l9gw
Research Help
Reach out to talk about your research interests and your project. Discussing your work and asking questions is a great way to build skills.
Simon Elichko (social sciences & data librarian)
- Make an appointment: bit.ly/selichk1
-
Email selichk1@swarthmore.edu
Research librarians
- For quick questions, try chat in Tripod
- Email librarian@swarthmore.edu
