Web Components
Syed Saad Qamar
Software Engineer
at IOmechs






/SyedSaadQamar96
/in/syed-saad-qamar
/saadqamar01
/saadqamar96

What is Components?
- A piece of code that is reusable
- A component is a modular building block for computer software
- It can communicate and collaborate with another component
What is Web Components?
- Web components are a set of web platform APIs that allow you to create new custom, reusable, encapsulated HTML tags to use in web pages and web apps.
- Custom components and widgets build on the Web Component standards, will work across modern browsers, and can be used with any JavaScript library or framework that works with HTML
- Web components are based on existing web standards, web developers easily extend HTML with new elements with encapsulated styling and custom behavior
Without component

Without component

Without component
With component

Web components are based on three main specifications
Custom Elements:
The Custom Elements specification lays the foundation for designing and using new types of DOM elements.
class MyToolBar extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
...
}
...
}
window.customElements.define('my-tool-bar', MyToolBar); <my-tool-bar></my-tool-bar>Web components are based on three main specifications
Shadow DOM:
The shadow DOM specification defines how to use encapsulated style and markup in web components.
- Shadow Host: is the DOM element which is hosting the Shadow DOM subtree or it is the DOM node which contains the Shadow Root.
- Shadow Root: is the root of the DOM subtree containing the shadow DOM nodes. It is a special node, which creates the boundary between the normal DOM nodes and the Shadow DOM nodes. It is this boundary, which encapsulates the Shadow DOM nodes from any JavaScript or CSS code on the consuming page.
Most Basic Usage of shadow DOM
HTML:
<div class="my-element">
</div>
<p>Regular element</p>CSS:
p {
font-family: sans-serif;
color: green;
}Most Basic Usage of shadow DOM
JS:
let myElement = document.querySelector('.my-element');
let shadow = myElement.attachShadow({
mode: 'closed'
});
shadow.innerHTML = `
<style>
p {
color: red;
}
</style>
<p>Element with Shadow DOM</p>
`;Result:

Most Basic Usage of shadow DOM
Shadow Tree:
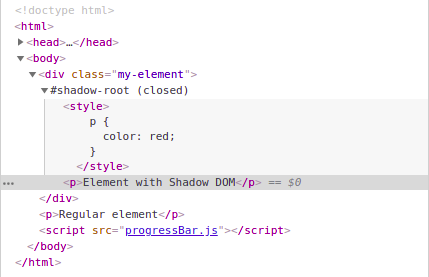
Web components are based on three main specifications
HTML Template:
The template element holds HTML code without displaying it.
<template id="my-paragraph">
<style>
p {
color: white;
background-color: #666;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
<p>My paragraph</p>
</template>HTML:
<my-paragraph></my-paragraph>JS:
customElements.define('my-paragraph',
class extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
let template = document.getElementById('my-paragraph');
let templateContent = template.content;
const shadowRoot = this.attachShadow({mode: 'open'})
.appendChild(templateContent.cloneNode(true));
}
})Now we can use it by just adding it to our HTML document:
Now it's time to do some coding

Run that component in Angular
Follow the following steps
- Create a project using that command
ng new progressbar-angular
2. Coping component file in the project
3. Add that file path in the script to the angular.json file
4. Add CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA in your module
Run that component in React
Follow the following steps
- Create a project using that command
npx create-react-app my-app
2. Coping component file in the project
3. Add that file path in the script to the App.js