Getting Started with Java


Agenda

-
Hello World Program
-
Variable and Data Types
-
Ranges of Data Types
-
Typecasting
-
Comments
-
Constants in Java - final
-
Reading Input - Scanner




class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}First Program - Hello World

A variable is a container which stores a value in a Java program. Each variable has a type associated with it which is defined at its declaration.

Variables
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int num = 100;
System.out.println(num);
}
}Here num is a variable of integer type storing value 100.
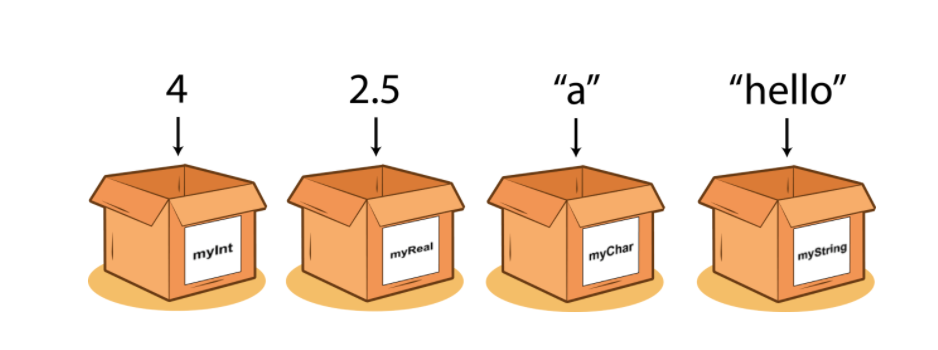


Variables
Variable name: A label for a memory location
Value: The something that would be stored in a variable
Storage: A place where data can be stored
Declaration: Announcing a variable (usually) at the beginning of a program
Naming convention: A set of rules about the names of variables
Assignment: Giving (setting) a variable a value

- For variable name we can use uppercase and lowercase letters, digits from 0 to 9 and underscore(_).
- First character must be underscore or letter.
- Java is a strongly typed language. So every variable needs to be declare before using it

Naming Convention
// Valid variable names
int marks1 = 50;
String student_name = "Naruto";
int id = 2;
// Invalid variable names
int 1_person;
Data Types mean to identify the type of the data and associate operations that can be done on the data values. Data types define the value that a variable can take.

Data Types in Java
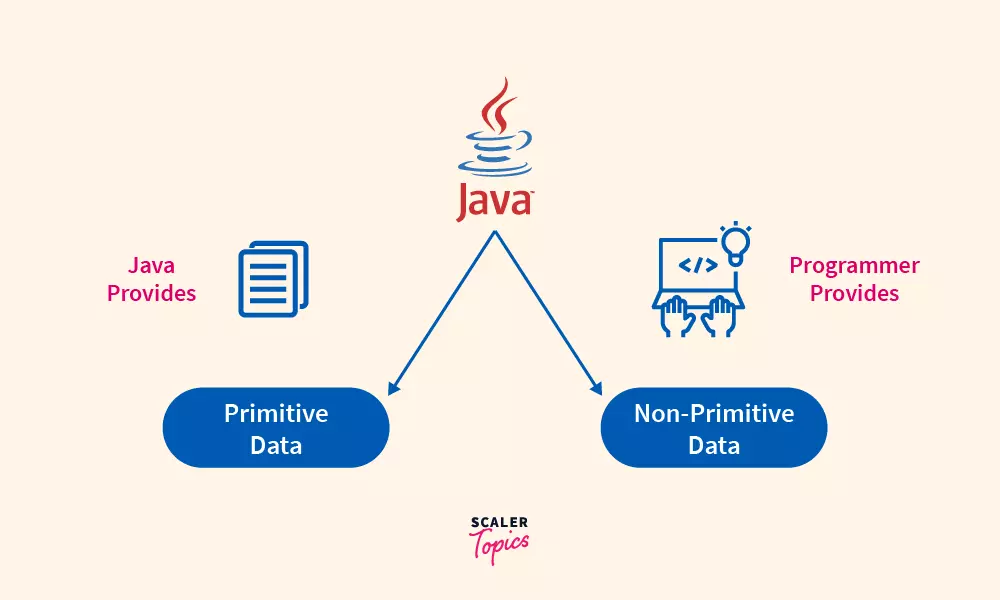
Data types also tell us information about:
- The size of the memory location.
- The maximum and minimum value of range that can store in the memory location.
- Different types of operations can be done on the memory location.


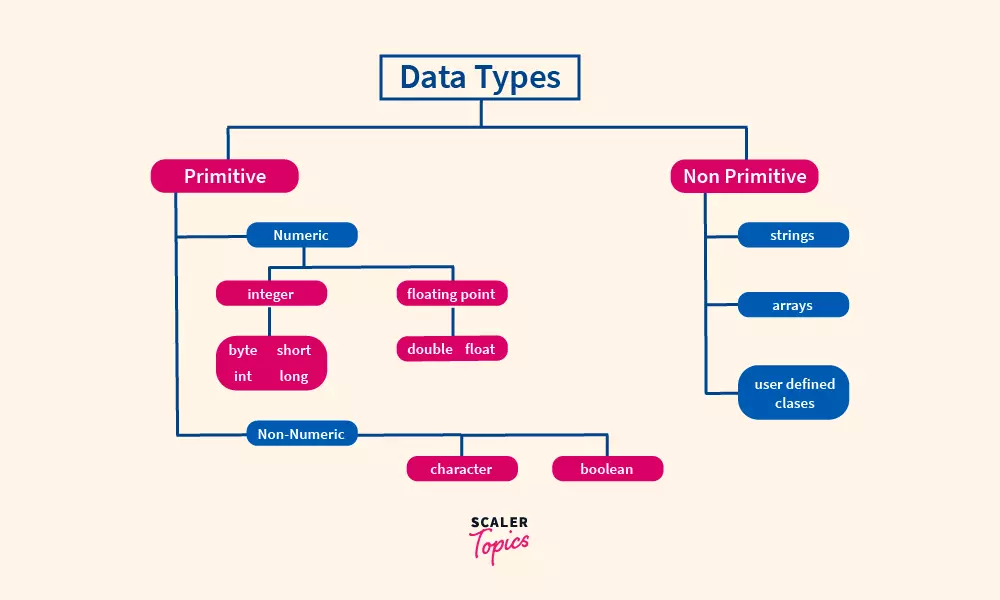


Numeric Data Types and their ranges
| Data Type | Range | Size |
|---|---|---|
| byte | [-128 : 127] | 8 bits |
| short | [-32,768 : 32767] | 16 bits |
| int | [-2,147,483,648 : 2,147,483,647] | 32 bits |
| long | [-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 : 9,223,372,036,854,775,807] | 64 bits |
| float | [1.40239846 x 10^-45 : 3.40282347 x 10^38] |
32 bits |
| double | [4.9406564584124654 x 10^-324 : 1.7976931348623157 x 10^308] |
64 bits |


Strings in Java
- A String is a sequence of characters in Java.
- Single line Strings are defined with double quotes.
- Multiline Strings are defined with triple-double quotes (""")
- Java Strings have several methods available to them.

public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "I love Java";
String str2 = "Programming is awesome";
}
}

Comments are program text used to explain the program logic. They are ignored by the compiler. Comments help to make our code more readable and maintainable. The compiler and interpreter ignore comments, so they do not affect the program's behaviour or performance.

Comments
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// This is a single line comment
/*
This is
a
multiline
comment
*/
}
}
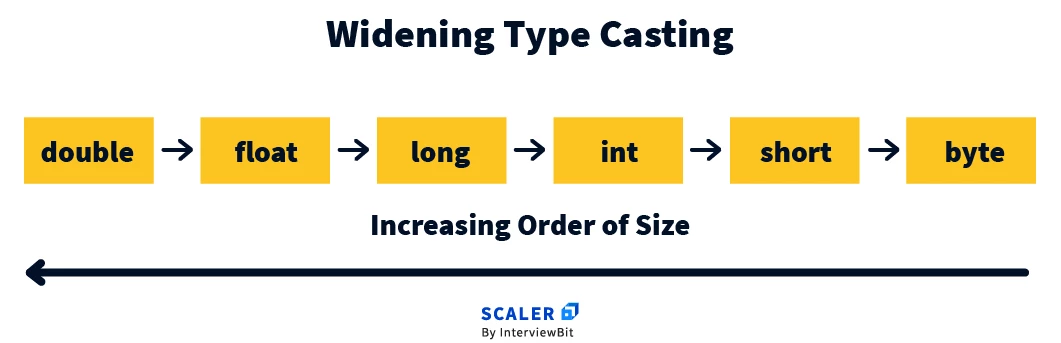
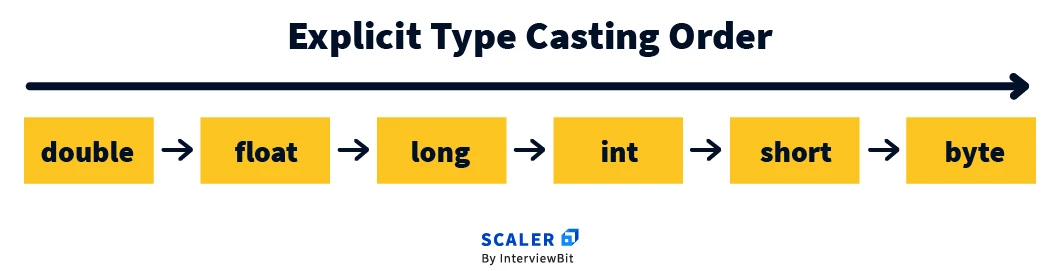
Typecasting refers to changing the type of data from one type to other.

Typecasting
It is of two types:
-
Widening Type Casting :
Automatically done by Java
-
Explicit Type Casting :
User defined

- The final keyword is used to declare constant variables in Java.
- A variable must be declared final at the time of declaration and they cannot be reassigned to a new value.
- A final variable can only be assigned a value once.

Final variables
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
final int num = 100;
System.out.println(num);
// num = 200; Error !!
}
}Here num is a variable of integer type storing value 100.
100
num

Java offers a variety of solutions for reading inputs.
The simplest and the easiest way of reading input is through Scanner class.

Scanner Class in Java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class scannerInput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter an integer");
int a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter a string");
String s=sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("String is "+ s);
}
}


Time to try!



Simple Interest Calculator
Given the values of principle, rate and interest, compute the Simple Interest.
Sample Input
P = 100
R = 5
T = 2
Sample Output
10



Homework
Write a program to read two numbers and print the sum of their squares.
Input:
3 4
Output:
25
