Linked Lists
Tarun Luthra




Agenda

What you will learn?
-
Classes & Objects Revision
-
What are Linked Lists ?
-
Basic Functionality


Classes & Objects Revision
class Node:
x = 0
y = 0

Classes & Objects Revision
class Node:
x = 0
y = 0
def main():
n1 = Node()
main()


Classes & Objects Revision
class Node:
x = 0
y = 0
def main():
n1 = Node()
print(n1.x) # 0
print(n1.x) # 0
main()


Classes & Objects Revision
class Node:
x = 0
y = 0
def main():
n1 = Node()
n1.x = 50
n1.y = 20
print(n1.x) # 50
print(n1.y) # 20
main()


Classes & Objects Revision
class Node:
x = 0
y = 0
def main():
n1 = Node()
n1.x = 50
n1.y = 20
n2 = n1
print(n1.x)
print(n1.y)
main()


Classes & Objects Revision
class Node:
x = 0
y = 0
def main():
n1 = Node()
n1.x = 50
n1.y = 20
n2 = n1
n2.x = 100
print(n1.x)
print(n1.y)
main()


class Node:
x = 0
y = 0
def main():
n1 = Node()
n1.x = 50
n1.y = 20
n2 = n1
n2.x = 100
n3 = n1
print(n3.x) # 100
print(n3.y) # 20
main()


class Node:
x = 0
y = 0
def main():
n1 = Node()
n1.x = 50
n1.y = 20
n2 = n1
n2.x = 100
n3 = n1
print(n3.x) # 100
print(n3.y) # 20
n4 = Node()
main()


Constructors
class Node:
x = 0
y = 0
def main():
n1 = Node()
n1.x = 50
n1.y = 20
n2 = Node()
n2.x = -20
n2.y = 10
main()


Constructors
class Node:
x = 0
y = 0
def main():
n1 = Node()
n1.x = 50
n1.y = 20
n2 = Node()
n2.x = -20
n2.y = 10
main()
class Node:
x = 0
y = 0
def __init__(self, a, b):
self.x = a
self.y = b
def main():
n1 = Node(50, 20)
n2 = Node(-20, 10)
main()


Can we have an object reference as a property ? 🧐


The 'next' property
class Node:
data = 0
next = None

The 'next' property
class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None


The 'next' property
class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
main()


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
main()
data
next


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
main()
data
next
10
null


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
main()
data
next
10
null
t1


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
t1.next = Node(20)
main()
data
next
10
null
t1


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
t1.next = Node(20)
main()
data
next
10
null
t1
data
next
20
null


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
t1.next = Node(20)
main()
data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
t1.next = Node(20)
t2 = t1.next
main()
data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
t1.next = Node(20)
t2 = t1.next
main()
data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null
t2


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
t1.next = Node(20)
t2 = t1.next
t2.next = Node(30)
main()
data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null
t2
data
next
30


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
t1.next = Node(20)
t2 = t1.next
t2.next = Node(30)
t2 = t2.next
print(t2.data)
main()
data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null
t2
data
next
30


class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None
def main():
t1 = Node(10)
t1.next = Node(20)
t2 = t1.next
t2.next = Node(30)
t2 = t2.next
print(t2.data) # 30
main()
data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null
t2
data
next
30


data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null
t2
data
next
30


data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null
t2
data
next
30
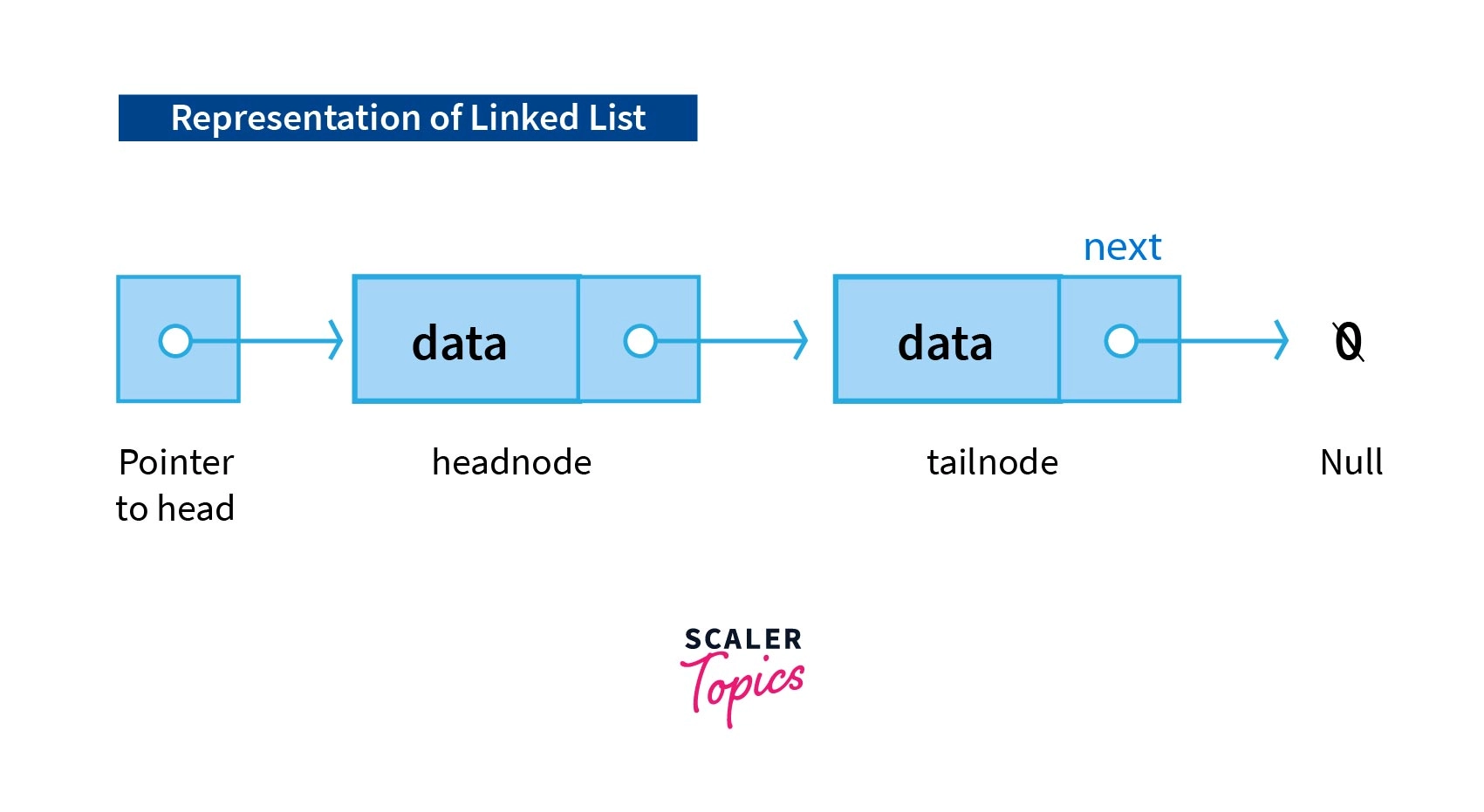
We only need head Node address to access entire chain of data.



data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null
t2
data
next
30
This type of data structure is called a


data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null
t2
data
next
30
This type of data structure is called a
Linked List


data
next
10
t1
data
next
20
null
data
next
30
Linked List
A Linked List is a linear data structure consisting of connected nodes where each node has corresponding data and a pointer to the address of the next node.
The first node of a linked list is called the Head, and it acts as an access point.
Time to try!
Let's begin!





Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.


Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
null
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
i = 2
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
i = 2
data
next
2
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
i = 2
data
next
2
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
i = 3
data
next
2
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
i = 3
data
next
2
data
next
3
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
i = 3
data
next
2
data
next
3
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
i = 4
data
next
2
data
next
3
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
i = 4
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
i = 4
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Given N > 0, create a linked list which contains data from 1 to N.
n = 4
data
next
1
head
temp
null
return head
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
def generateLL(n):
head = Node(1)
temp = head
for i in range(2, n + 1):
temp.next = Node(i)
temp = temp.next
return head

Size of a Linked List 👨💻


Given the head of a linked list, return its size


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return count

Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
temp
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
int size(Node head) {
Node temp = head;
int count = 0;
while (temp != null) {
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return count;
}def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
temp
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
count = 0


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
temp
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
count = 1


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
temp
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
count = 1


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
temp
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
count = 2


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
temp
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
count = 2


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
temp
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
count = 3


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
temp
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
count = 4


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
temp
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
count = 4


Given the head of a linked list, return its size
def size(head):
temp = head
count = 0
while temp != None:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
return countdata
next
1
head
temp
null
data
next
2
data
next
3
data
next
4
return count
count = 4


Insertion


Given the head node of a linked list, insert a new node at kth index (0 based indexing)


Given the head node of a linked list, insert a new node at kth index (0 based indexing)
def insert(head, pos, data):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
temp = head
newNode = Node(data)
if pos == 0:
newNode.next = head
return newNode
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
newNode.next = temp.next
temp.next = newNode
return head

Deletion


Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.


Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3


Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
temp
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
temp
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
temp
Loop will run only one iteration
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
temp
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return headLoop will run only one iteration


Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
temp
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
temp
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
temp
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
30
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
temp
This node is not referred by any reference. It will be cleaned by the garbage collector.
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
40
0
1
2
3
pos = 2
temp
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
40
0
1
2
pos = 2
temp
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Given the head of a linked list, delete the kth node.
data
next
10
head
null
data
next
20
data
next
40
0
1
2
pos = 2
temp
def remove(head, pos):
if pos < 0 or pos > size(head):
return head
if pos == 0:
return head.next
temp = head
for i in range(pos - 1):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
return head

Codes 👨💻
Python -
https://ide.codingminutes.com/?id=aik


Problems to Practice 👨💻

