Queues
Tarun Luthra




Agenda

What you will learn?
-
Basics of Queues
-
Implementation
-
Examples


Queues
The Queue in data structure is an ordered, linear sequence of items. It is a FIFO (First In First Out) data structure, which means that we can insert an item to the rear end of the queue and remove from the front of the queue only. A Queue is a sequential data type, unlike an array, in an array, we can access any of its elements using indexing, but we can only access the element at the front of the queue at a time.

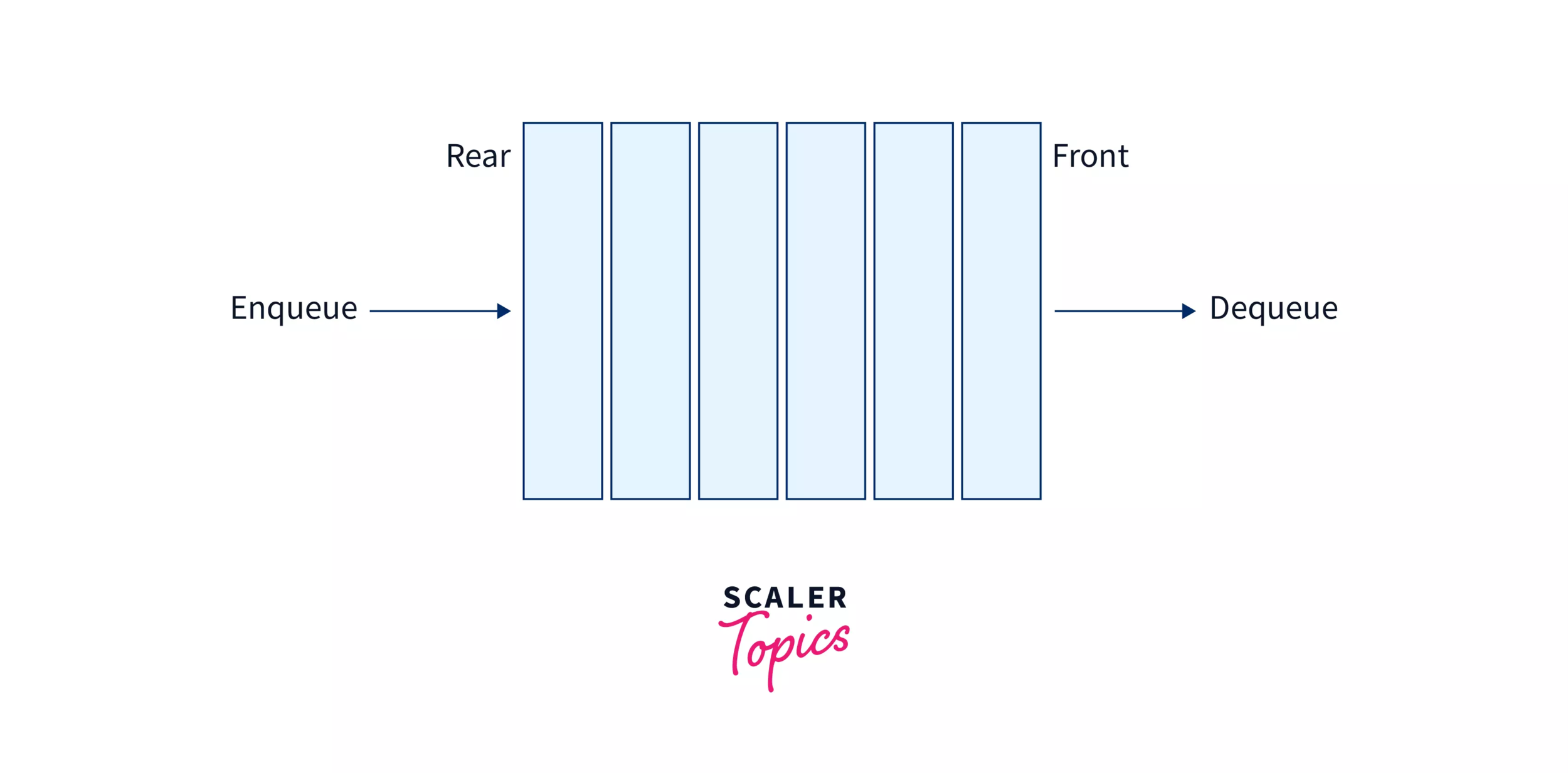




Operations on Queues


- push(x)

Operations on Queues


- push(x)
: insert x at the rear

Operations on Queues


- push(x)
- pop()
: insert x at the rear

Operations on Queues


- push(x)
- pop()
: insert x at the rear
: delete the front element

Operations on Queues


- push(x)
- pop()
- front()
: insert x at the rear
: delete the front element

Operations on Queues


- push(x)
- pop()
- front()
: insert x at the rear
: delete the front element
: return the front element
Operations on Queues



- push(x)
- pop()
- front()
- rear()
: insert x at the rear
: delete the front element
: return the front element
Operations on Queues



- push(x)
- pop()
- front()
- rear()
: insert x at the rear
: delete the front element
: return the front element
Operations on Queues

: return the rear/back element


- push(x)
- pop()
- front()
- rear()
- size()
: insert x at the rear
: delete the front element
: return the front element
Operations on Queues

: return the rear/back element


- push(x)
- pop()
- front()
- rear()
- size()
: insert x at the rear
: delete the front element
: return the front element
Operations on Queues

: return the rear/back element
: return no of elements


- enqueue(x) / push(x)
- dequeue() / pop()
- front()
- rear()
- size()
: insert x at the rear
: delete the front element
: return the front element
Operations on Queues

: return the rear/back element
: return no of elements


Can we iterate over a queue ? 🧐


Not without removing the data.
Can we iterate over a queue ? 🧐


Queue Libraries
There are ready-made implementations of Queue in most language's libraries/modules. You can find them here :
-
Queues in C -
https://www.scaler.com/topics/c/implementation-of-queue-using-linked-list/ -
Queues in Java -
https://www.scaler.com/topics/java/stack-and-queue-in-java/ - Queues in Python -
https://www.scaler.com/topics/queue-in-python/


Visualisers
- Queue Visualiser - Array Implementation -https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/QueueArray.html
- Queue Visualiser - Linked List Implementation -
https://visualgo.net/en/list?slide=1-1


Codes
- Java LL Implementation :
https://ide.codingminutes.com/?id=aat - Python LL Implementation :
https://ide.codingminutes.com/?id=aac

