Recording and editing podcasts: An introduction
July 14, 2021
Duane Woods
Audio Video Design Specialist, CEE
In this session:
Participants will
- Be introduced to podcasting projects
- Discover SFU audio resources and community
- Be able to set up for audio recording
- Demo the basics of editing audio
- Share audio content on a variety of platforms.
Theory & Practice:
Why Podcasting?
- Can listen to anywhere and anytime
- Adds a different form of learning
- High bandwidth not required to listen
- Sparks the imagination
- Great way to share conversations
Theory & Practice:
Best uses
- Interviews or a conversations with an expert or guest
- Where it can spark the imagination with voice rather than visuals
- Where you want to concentrate on the auditory nature (ie. park, farm, factory)
- Share music or other sounds
Theory & Practice:
Remember to...
-
Plan it out
-
Get a quality recording
-
Speak clearly
-
Incorporate other audio
-
Keep it interesting
-
Length can vary
Theory & Practice:
Remember...
-
Don't record a 2-3 hours in one file
-
Try not to read notes/text verbatim
-
Don't speak in a flat, monotone voice
-
Add inflection
Theory & Practice:
1. Write out your dialogue or interview questions
2. Plan out all the gear that will be needed – hardware and software
3. Find a quiet location – be mindful of your environment
4. Get close to the microphone – 4-12 inches away
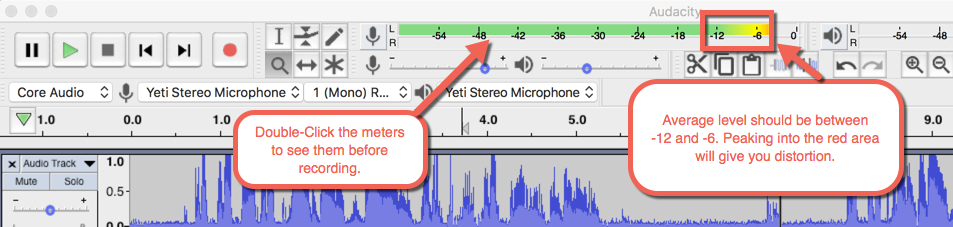
5. Set a proper level on your recording device – record at an average of -12db to -6db and has absolute peaks at -6db. Don't go into the RED.
6. Don’t try to capture “The One” – record important parts more than once when possible
Theory & Practice:
1. Write out your dialogue or interview questions
2. Find a quiet location – be mindful of your environment
3. Get close to the microphone – 4-12 inches away
4. Set a proper level on your recording device – record at an average of -12db to -6db and has absolute peaks at -6db. Don't go into the RED.
5. Don’t try to capture “The One” – record important parts more than once when possible
POdcast Production:
Recording gear - at home
-
External Microphone (eg. Yeti) or Headset Mic
-
Headphones
-
Quiet Space
Recording gear - in the field
-
smartphone with a recording app
-
Headphones
-
possible external microphone
POdcast Production:
Recording Methods:
-
Audacity (Open Source, Free)
-
Audition (Adobe, SFU-supported in labs)
-
Zoom/ Skype (*note that students do NOT have recording ability)
-
smartphones
POdcast Production:
Editing Software
-
Audacity (Open Source)
-
Audition (Adobe, SFU-supported)
Audacity
Audacity
File Types:
- WAV, AIFF, MP3, M4A files
- phones and Zoom records with M4A files
- WAV's and AIFF's are uncompressed, high quality and large files
- MP3's are compressed, lower quality and small, but still acceptable
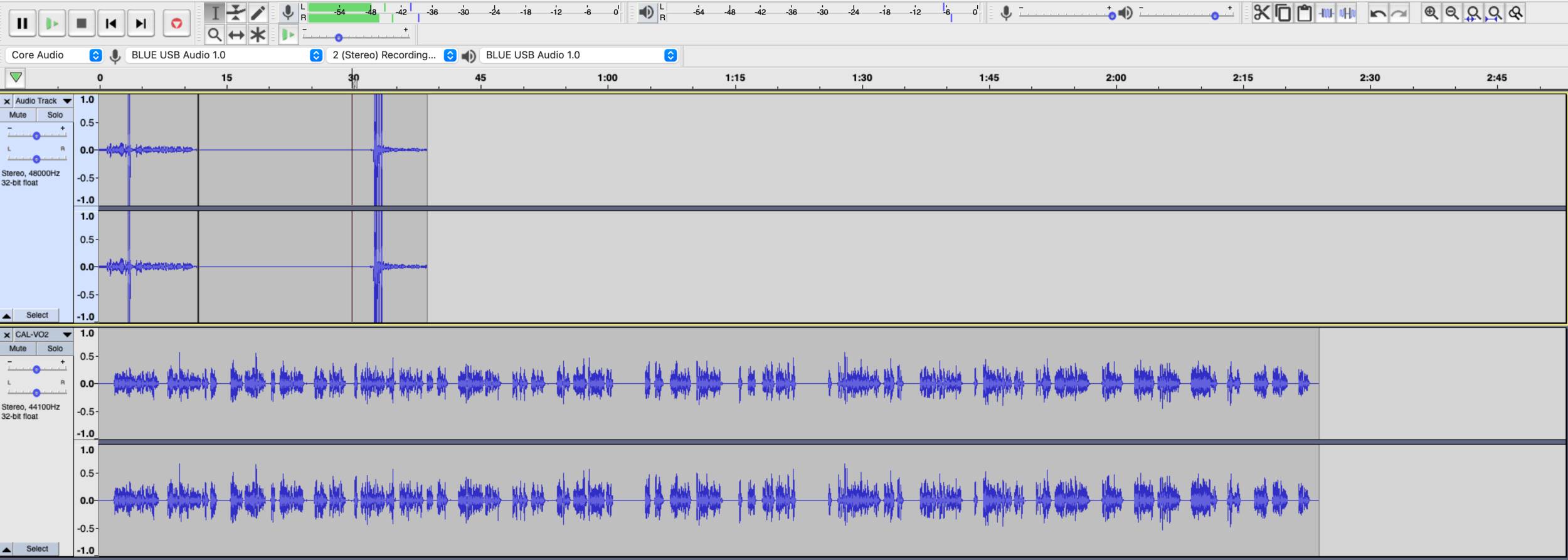
Interface
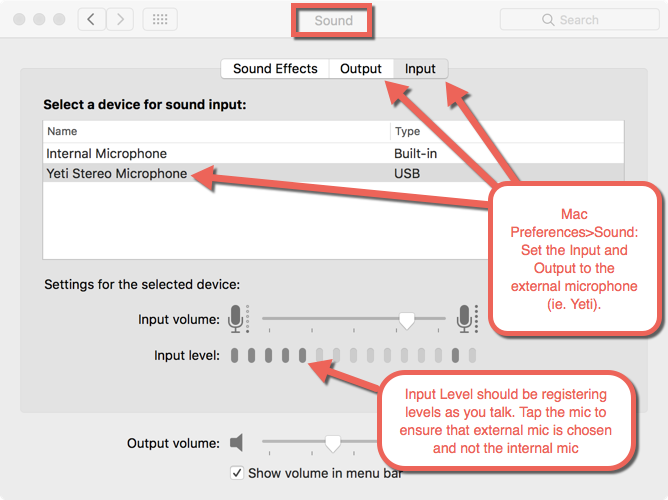
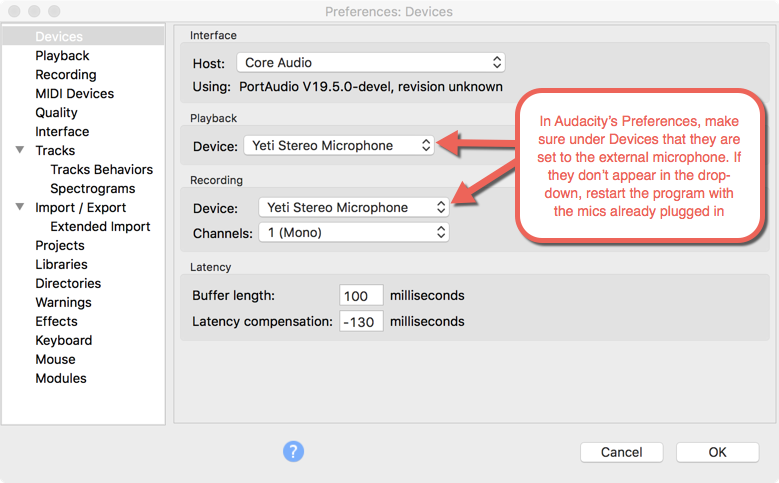
MICROPHONE SET UP
audacity prefs
meters and sound levels
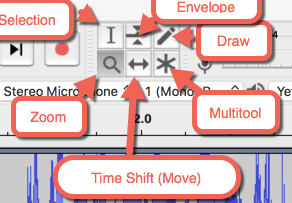
Tools

Tools
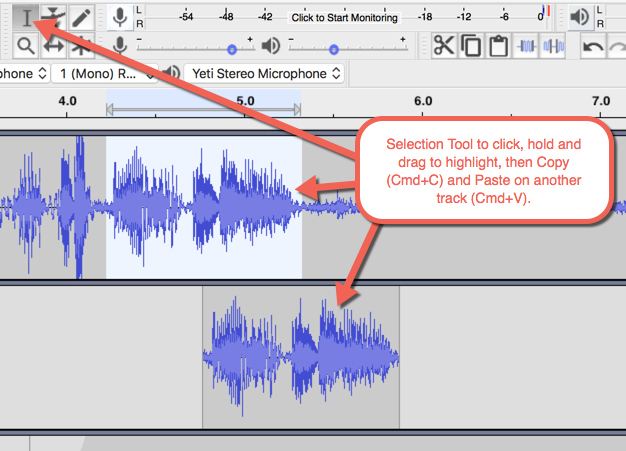
selection tool
Tools
time shift tool (move)
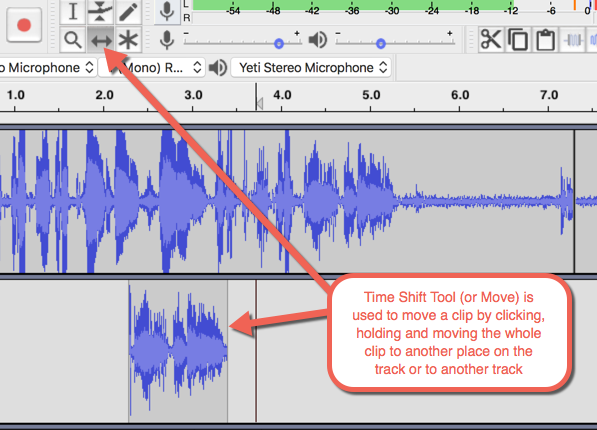
Tools
envelope tool
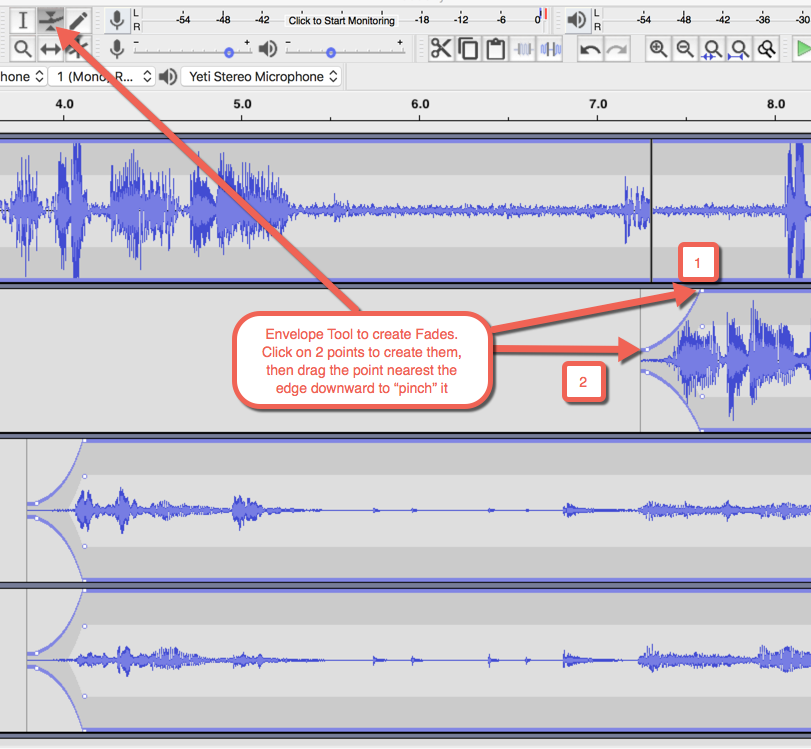
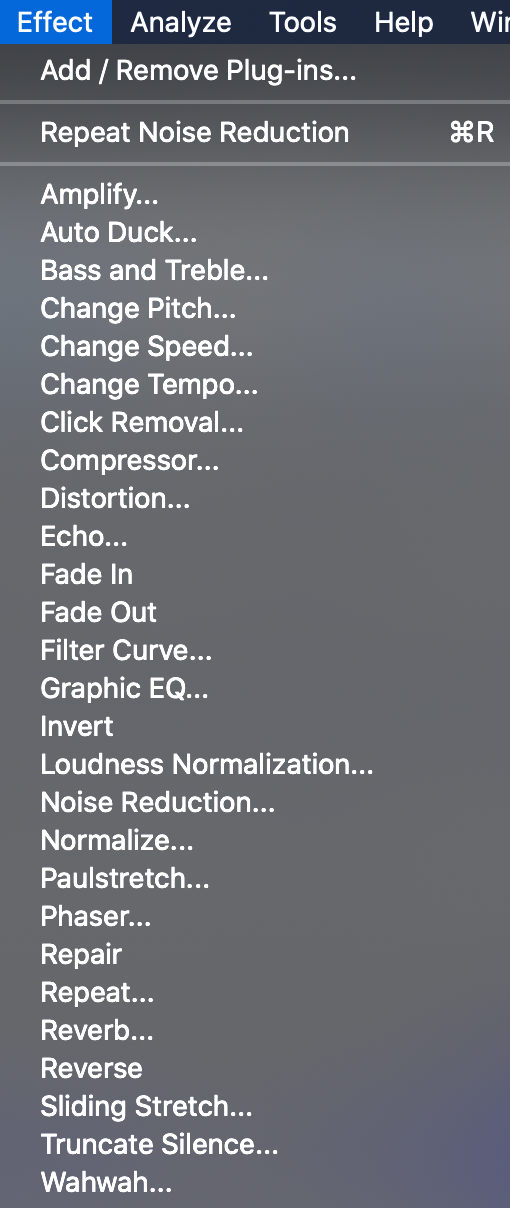
Important EFFECTS
- Amplify
- Fade In
- Fade Out
- Normalize
- Noise Reduction
Important Shortcuts
- Select a clip (double-click with Selection tool)
- Split (COMMAND + I)
- Cut (COMMAND + X)
- Paste (COMMAND + V)
Track controls
- Mute (mutes only that track)
- Solo (mutes every other track)
- Gain (audio level)
- Pan (left and right channels)