HTML
Telerik Academy Alpha

Front-End
Table of contents
Web Basics
The Elements of a Web Page
- A Web page consists of
-
HTML markup
-
CSS rules
-
JavaScript code
-
JS libraries
-
-
Images
-
Other resources
-
Fonts, audio, video, Flash, Silverlight, etc...
-
-

Web Application
- Web Application
- Next level web sites
- High interactivity
- High accessibility (Cloud)
- AJAX, Silverlight, Flash, Flex, etc.
- Applications are usually broken into logical chunks called "tiers", where every tier is assigned a role
- Desktop-like application in the web browser
Web Application
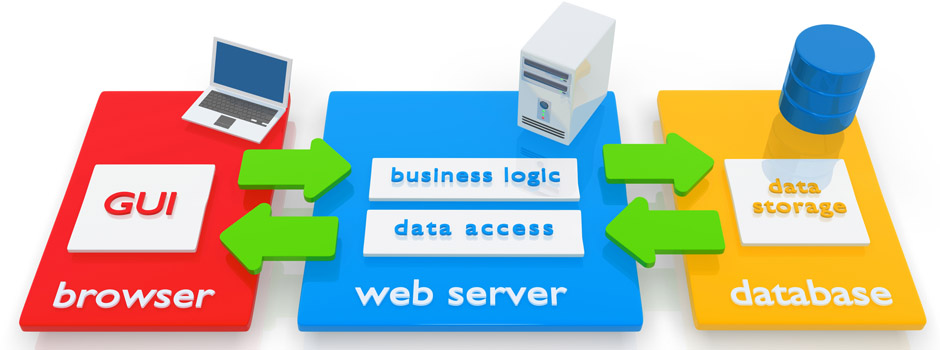
Web Browser
- A Web browser is a program designed to enable users to access, retrieve and view documents and other resources from the Web
- Main responsibilities:
- Bring information resources to the user (issuing requests to the web server and handling any results generated by the request)
- Present web content (render HTML, CSS, JS)
Layout Engines
-
Layout Engines are software components that displays the formatted content on the screen combining:
- Marked up content (such as HTML, XML, image files, etc.)
- Formatting information (such as CSS, XSL, etc.)
- It "paints" on the content area of a window, which is displayed on a monitor or a printer
- Typically embedded in web browsers, e-mail clients, on-line help systems or other applications that require the displaying (and editing) of web content
- The layout engine is the "heart of a browser"
HTML
What is HTML?
- HTML – Hyper Text Markup Language
- A notation for describing
- document structure (semantic markup)
- formatting (presentation markup)
- Looks (looked?) like:
- A Microsoft Word document
- A notation for describing
- The markup tags provide information about the page content structure
- A HTML document consists of many tags
HTML Terminology
- Concepts in HTML
-
Tags
- Opening tag and closing tag
- The smallest piece in HTML
-
Attributes
- Properties of the tag
- Size, color, etc…
-
Elements
- Combination of opening, closing tag and attributes
-
Tags
HTML Demo
HTML
- Tags are the smallest piece in HTML Document
- Start with < and end with >
- Two kinds of tags
-
Opening
- Mark the start of an HTML element
-
Closing
- Mark the end of an HTML element
- Starts with </
-
Opening
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- The place visible to the end user -->
<h1>
Title here
</h1>
<div>
My text here
</div>
</body>
</html>HTML
- Attributes are properties of HTML Elements
- Used to set size, color, border, etc…
- Put directly in the tags
- Has value surrounded by single ' ' or double " " quotes
- The value is always a string
- There are some attributes that are common for every HTML element
- id, class, name, style
- Some attributes are specific
- For example the attribute src of the img element
- Shows the path to the image to be shown
- For example the attribute src of the img element
HTML Document structure
- Some elements are essential to each HTML Document:
html, head, body, doctype
- The html element
- Used to mark the beginning and ending of a HTML document
- All the content of the web page is inside this tag
HTML
- Click F12 in your browser and take a look at the elements of the HTML.
- You can even manipulate the html there and see the immediate result
- This result is temporary and visible only to you
- This result is temporary and visible only to you
- You can even manipulate the html there and see the immediate result
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML
HTML Tags
- Text formatting tags
| Tag | Meaning |
|---|---|
| <b></b> | bold |
| <i></i> | italiazed |
| <u></u> | underlined |
| <sup></sup> | superscript |
| <sub></sub> | subscript |
| <strong></strong> | strong (same result as bold but different meaning to the browser) |
| <em></em> | emphasized (same as italized but different meaning to the browser) |
| <pre></pre> | preformatted text |
HTML Tags
- Hyperlink Tags
<a href="https://telerikacademy.com/" title="Telerik">Link to Telerik Web site</a>- Image Tags
<img src="logo.gif" alt="logo" />- Text formatting tags
This text is <em>emphasized.</em>
<br />new line<br />
This one is <strong>more emphasized.</strong>HTML Tags
HTML Forms
HTML Forms
- The primary method for gathering data from site visitors
- HTML Forms can contain
- Text fields for the user to type
- Buttons for interactions like "Register", "Login", "Search"
- Menus, Sliders, etc…
- Check Google, Facebook
- Google search field is a simple Text field
HTML Forms
- How to Create a HTML Form?
- Create a form block with
- <form></form>
- Create a form block with
<form name="myForm" method="post" action="path/to/some-file">
...
</form>- The "action" attribute tells where the form data should be sent
- The "method" attribute tells how the form data should be sent – via GET or POST request
Forms - text fields
- Single-line text input fields
<input type="text" name="FirstName" value="This is a text field" />- Multi-line text input fields (textarea)
<textarea name="Comments">
This is a multi-line text field
</textarea>- Password input – a text field which masks the entered text with * signs
<input type="password" name="pass" />Forms - buttons
- Reset button – brings the form to its initial state
<input type="reset" name="resetBtn" value="Reset the form" />- Submit button
<input type="submit" name="submitBtn" value="Submit" /><input type="button" value="Apply Now" />- Ordinary button – no default action, used with JS
Forms - checkbox and radio buttons
- Checkboxes
<input type="checkbox" name="fruit" value="apple" />- Radio buttons
<input type="radio" name="title" value="Mr." />Forms - select fields
- Dropdown menus
<select name="gender">
<option value="Value 1"
selected="selected">Male</option>
<option value="Value 2">Female</option>
<option value="Value 3">Other</option>
</select>- Multiple-choice menus
<select name="products" multiple="multiple">
<option value="Value 1"
selected="selected">keyboard</option>
<option value="Value 2">mouse</option>
</select>Forms - input with validation
- Email, Url, Telephone or custom
<input type="email" required="true" />
<input type="url" required="true" />
<input type="tel" required="true" />
<input required="true" pattern="[^ @]*@[^ @].[^ @]"/>iframes
- Inline frames provide a way to show one website inside another website:
<iframe
width="1280"
height="720"
src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/kJQP7kiw5Fk"
frameborder="0"
allowfullscreen>
</iframe>Semantic HTML
Semantic HTML
- Semantic HTML is:
- The use of HTML markup to reinforce the semantics of the information in Web pages
- Make the content understandable for computers
- Rather than merely to define its presentation
- A kind of metadata about the HTML content
- The use of HTML markup to reinforce the semantics of the information in Web pages
- Semantic HTML is processed by regular Web browsers and other user agents
- CSS is used to suggest its presentation to human users
Semantic HTML
- Semantic HTML is:
- Easier to read by developers, parsers, bots, machines, AIs
- A way to show the search engines the correct content
Semantic HTML
- Just follow some guidelines when creating a Web site
- Use HTML5 semantic tags
- <header>, <nav>, <section>, <article>, <aside>, <footer>
- Use Headings when you need to structure the content into sub-headings
- In increasing order, staring with <h1>
- Do not use empty tags
- Like a clearing <div>
- Use HTML5 semantic tags
Semantic HTML
- HTML5 introduces semantic structure tags
- Imagine the following site:
- This is a common Web page structure
- Used in 90% of the web sites
