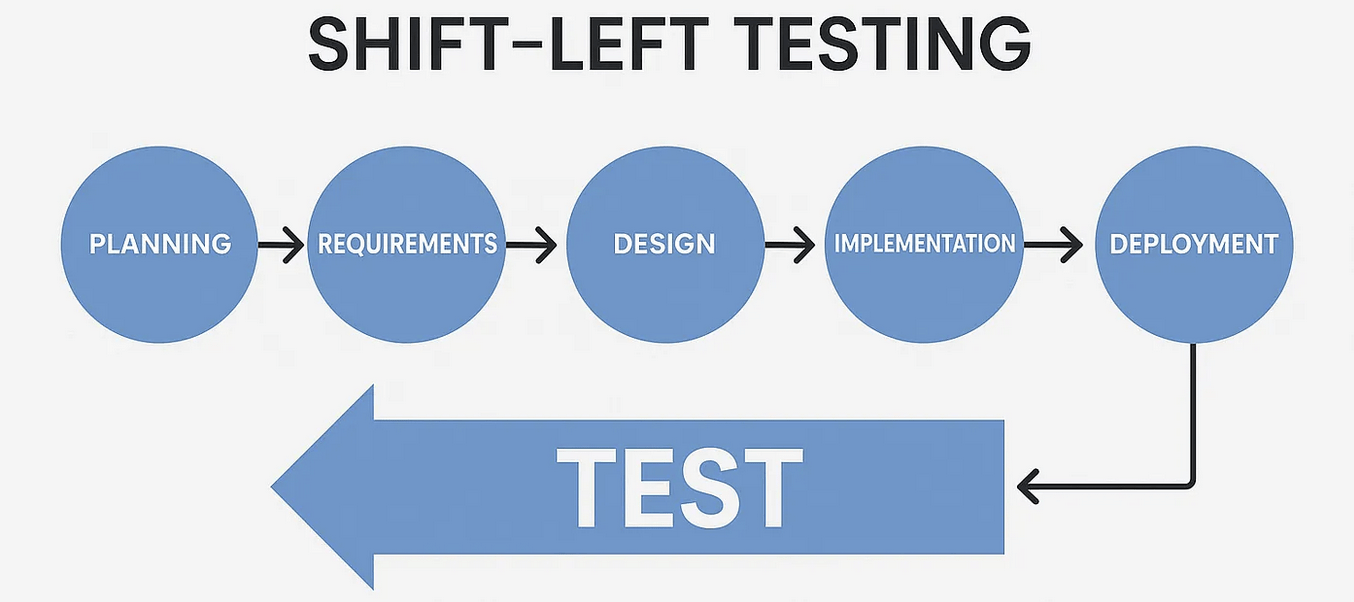
Shift-Left Testing
Quality Assurance

-
What is shift-left testing
-
Core principles
-
Key benefits
-
How to implement
-
Conclusion
AGENDA
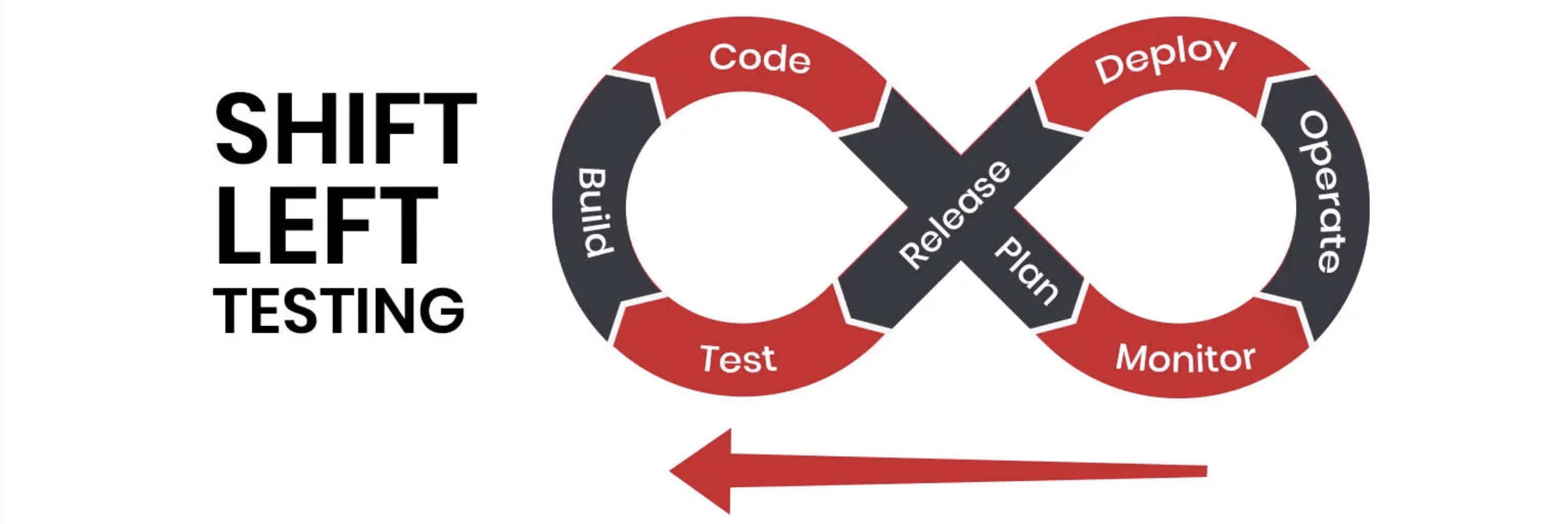
WHAT IS SHIFT-LEFT TESTING
Shift-Left Testing is a paradigm shift in software development and quality assurance. Instead of confining testing to the later stages of the software development lifecycle (SDLC), it advocates for integrating testing activities as early and continuously as possible – literally "shifting" them to the "left" on the project timeline.
The core idea is to find and prevent defects at their source, rather than discovering them much later when they are more costly and complex to fix.
CORE PRINCIPLES
Early and continuous testing: Testing begins from the moment requirements are defined and continues throughout every phase of development.
Prevention over detection: The primary goal is to prevent defects from being introduced, rather than just finding them after they've been created.
Collaboration: Developers, testers, business analysts, and operations teams work together from the outset.
Automation first: Automating tests (unit, integration, API, UI) at every possible layer to enable rapid and repeatable feedback.
Fast feedback loops: Providing immediate feedback to developers on code quality and functionality.
Quality is everyone's responsibility: Moving away from the idea that quality is solely the QA team's job.
Key Benefits
Reduced Costs
-
Lower defect remediation costs (fixing bugs early is cheaper).
-
Less rework and fewer delays.
Faster Release
-
Streamlined development and testing cycles.
-
Reduced bottlenecks at the end of the SDLC.
-
Fewer critical defects reach production.
-
More stable and reliable applications.
Improved software quality
Enhanced Team Collaboration
-
Breaks down silos between development and QA.
-
Fosters a shared understanding of quality.

-
Integrate Testing Early
-
Automate Everything Possible
-
Enable Continuous Feedback
How To Implement

Requirements gathering phase
- Review functional and non-functional requirements
- Analyse and forecast QA risks
- Collaborating with product managers to define testable acceptance criteria for each requirement or user story.
- Beginning to map requirements to potential test cases, ensuring every requirement can be verified.

QA's involvement here is purely preventative, focusing on ensuring that the foundation of the project – the requirements – is solid, clear and testable.
Design phase
- Review testability of the application design
- While detailed test cases are typically written during the development phase, the design phase is used to brainstorm and identify high-level test scenarios and critical test cases

The goal here is to identify and mitigate potential quality issues inherent in the design itself, ensuring that the system is designed for quality, testability, and maintainability. This helps avoid costly rework later in the development cycle.
Development phase
- Developers write and execute unit tests
- QA's prepare main test scenarios and test cases based on the design
- QA's prepare automated tests based on test cases before the code

The goal is to identify and prevent defects as the code is being written, rather than waiting for a separate testing phase.
Testing phase
- Running designed test cases (manual and automated) designed and developed in previous phases
- Logging, tracking, prioritizing, and managing defects identified during testing. This includes communicating with developers, retesting fixes and ensuring defects are resolved

In a Shift-Left environment, this phase is transformed: it's no longer the first time major testing occurs, but rather a validation and verification stage that builds upon the quality already embedded earlier. The goal in a Shift-Left context is for this phase to be more efficient, less bug-ridden, and focused on broader system validation rather than basic defect discovery.
Deployment on pre-prod and prod
- Ensure that the software has been successfully deployed to the target (typically pre-production) environment without critical errors
- After deployment on production should monitoring production logs, user feedback and performance metrics for any issues that may arise after release

The goal is fundamentally transformed from a traditional approach. It's no longer about finding major bugs, but rather about confirming and sustaining the quality that has been built in during earlier stages.
Maintenance
- Performing regression tests whenever bug fixes, enhancements, or new features are deployed to the live system.
- Investigating and analyzing defects reported from the production environment.

The goal is continuously improving the product and processes based on live system feedback. This involves bug fixes, performance improvements and other enhancements.
Summary
Shift-Left Testing is not just a trend; it's a fundamental evolution in how we approach software quality. By embedding quality activities throughout the entire development lifecycle, we can build more robust, reliable and cost-effective software. It's about building quality in from the start, rather than trying to test it in at the end.