暑假資讀[1]
謝一
講師介紹
- 209
- thanksone、四維大蛤蠣(?
- 資讀最弱的
- 建青美編
- FB : 謝一
競賽們
學科能力競賽
- 校內賽(取11個)
- 北市賽(取10個)
- 全國賽(取10個)
資奧
- 海選
- 初選(過了海選或是APCS實作三級分以上可以參加)
- TOI1!(10人全國賽保送,20人初選)
- TOI2!(12人)
- APIO(TOI2!可以參加)
- IOI(4人) (URL by pi_tw)
APCS認證
- 觀念
- 實作
團體賽
- NPSC
- YTP
- ISSC
個人賽
- HP Codewars
OJ們
- TIOJ(有些題序很奇怪)
- OJDL(magic mirror)
- ZeroJudge(難度參差不齊)
- CSES(很多模板題)
- AtCoder(題序精簡,定期比賽)
- Codeforces(題序複雜,定期比賽)
- UVA(最古老的OJ?)
- OIchecklist(收錄各國OI)
what you eat?
- AC(你超電)
- WA(滾回去底爸)
- TLE(換個複雜度、壓常(X)
- MLE(換個複雜度、壓常、叫你的扣不要亂存記憶體)
- RE(你陣列開太小、除以0、main沒有return 0)
- CE(自己回去編譯好啦)
條件判斷
判斷式
判斷式回傳bool, 也就使true或false
| 符號 | 意義 |
|---|---|
| == | 等於 |
| != | 不等於 |
| < | 小於 |
| > | 大於 |
| <= | 小於等於 |
| >= | 大於等於 |
| && | 和 |
| || | 或 |
範例
a == b
a 是否等於b
a, b可能為變數、固定值、算式
if, else, else if
if
if(條件){ //條件成立
做事;
}else
if(條件){ //條件成立
做事;
}else{ //上面的條件不成立
做事;
}else if
if(條件){ //條件成立
做事;
}else if(條件){ //上面的條件不成立但自己的條件成立
做事;
}else{ //上面的條件都不成立
做事;
}範例
int score;
cin >> score;
if(score >= 90){
cout << "A";
}else if(score >= 80){
cout << "B";
}else if(score >= 70){
cout << "C";
}else if(score >= 60){
cout << "D";
}else{
cout << "F";
}switch case
switch(變數/式子){
case 可能1: //符合可能1
做事;
break;
case 可能2: //符合可能2
做事;
break;
default: //上面的可能都沒符合
做事;
break;
}範例
int score;
cin >> score;
switch(score / 10){
case 10:
cout << "A";
break;
case 9:
cout << "A";
break;
case 8:
cout << "B";
break;
case 7:
cout << "C";
break;
case 6:
cout << "D";
break;
default:
cout << "F";
break;
}三元運算子
條件 ? 做事(成立) : 做事(不成立);範例
int score;
cin >> score;
cout << (score >= 60? "YA" : "FAILURE");題目們
給定一個包含三個數字的序列,求此序列為等比、等差、兩者都是或兩者都不是。
給定三條線段的長度,詢問這三條線斷是否能構成三角形。
(先不要管多筆輸入怎麼辦,那個後面會教)
Hints : 注意值域
題解
假設三個數分別為a, b, c。如果要同時滿足等比、等差三數必須相等。滿足等比數列則a * c = b * b。滿足等差時a + c = b + b。最後要注意等比數列中不能出現0。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
signed main(){
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if(a == b && b == c && a * b * c != 0) cout << "both";
else if(a * c == b * b && a * b * c != 0) cout << "geometric";
else if(a + c == b + b) cout << "arithmetic";
else cout << "normal";
return 0;
}
根據國中數學,三角形的最長邊必定小於另外兩邊之和。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
signed main(){
long long a, b, c, mx;
while(cin >> a >> b >> c){
mx = a > b? a : b;
mx = mx > c? mx : c;
if(a + b + c - mx > mx) cout << "SAFE\n";
else cout << "BYE\n";
}
return 0;
}
迴圈
for
for(起始; 判斷條件; 更新){
做事;
}範例
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
cout << i << " ";
}輸出
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
套娃
for(int i = 1; i < 10; i++){
for(int j = 1; j < 10; j++){
cout << i * j << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}輸出 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27
4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45
6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54
7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63
8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 72
9 18 27 36 45 54 63 72 81
while
while(條件){ //條件成立
做事;
}
while = if?

NO!
範例
int i = 5;
while(i > 0){
cout << i << " ";
i--;
}輸出 :
5 4 3 2 1
無限迴圈
while(true){
做事;
}do-while
do{
做事;
}while(條件);範例
int i = 5;
do{
cout << i << " ";
i--;
}while(i > 0);輸出
5 4 3 2 1
while = do-while?
yes but actually no
while : 先奏後斬
do-while : 先斬後奏
想讓迴圈停下來怎麼辦?
break!
while(true){
做事;
if(想停下來的條件){
break;
}
做事;
}想跳過一些怎麼辦?
continue!
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ //重複n次
作事;
if(想跳過的條件) continue;
作事;
}break vs continue


題目們
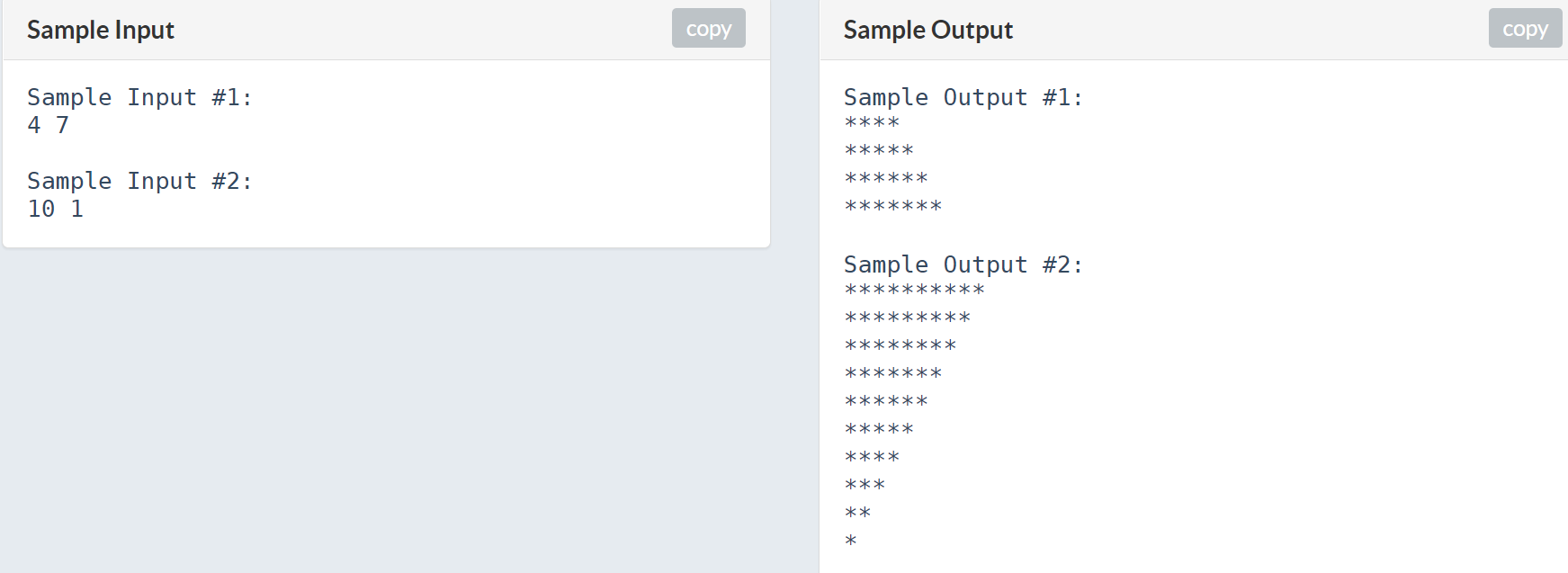
印星星(參考範測)
因數分解
範例 : 12 = 2^2 * 3
題解
以題目給的兩個數字分別為上底和下底用星星畫梯形
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
signed main(){
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
for(int i = a; i != b; i += (b - a) / abs(b - a)){
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++){
cout << "*";
}
cout << "\n";
}
for(int j = 0; j < b; j++) cout << "*";
return 0;
}
對每個根號以下的數字嘗試,剩下來的一定是質數
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
signed main(){
int n, cnt;
bool first = 1;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 2; i * i <= n; i++){
cnt = 0;
while(n % i == 0){
n /= i;
cnt++;
}
if(cnt > 0){
if(cnt == 1){
cout << (first == 0? " * " : "") << i;
}else{
cout << (first == 0? " * " : "") << i << "^" << cnt;
}
if(first == 1) first = 0;
}
}
if(n > 1) cout << (first == 0? " * " : "") << n;
return 0;
}
陣列
紀錄5個值
好像還行(?
int num1, num2, num3, num4, num5;紀錄500個值
int num1, num2, num3, num4, ..., num500; 好像有點糟(?
你看,這樣很麻煩吧,所以我們可以用陣列
陣列能幹嘛?
存一大串東西
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| value | 2 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 4 |
宣告
int a[5];
SS //宣告一個有5格空間的int陣列a
array<int, 5> a;注意 : 使用array之前要先#include <array>,而且要C++11以上以上
高階大氣上檔次的宣告
int a[5] = {2, 1, 4, 7, 4};
SS
array<int, 5> a = {2, 1, 4, 7, 4};a[i] = a陣列中第i個
a[i]的所有操作都跟變數一樣
好用的技巧
int A[size] or array<int, size> A;
for(int a : A){
做事;
}題目們
給定一個字串,求出現最多次的字母,若有多個則按照字母排序輸出
給定n,詢問1~n中間有哪些質數
題解
對字母開一個陣列,當字串中出現a就把第0個元素 +1, 出現b時把第1個元素+1,以此類推
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
signed main(){
int n, k, mx;
char c;
array<int, 26> cnt;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> k;
mx = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < 26; j++){
cnt[j] = 0;
}
for(int j = 0; j < k; j++){
cin >> c;
cnt[c - 'a']++;
mx = max(mx, cnt[c - 'a']);
}
for(int j = 0; j < 26; j++){
if(cnt[j] == mx) cout << (char)(j + 'a');
}
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
對於每個數字用所有比自己小的數除除看以判別是否為質數並利用陣列紀錄。
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
signed main(){
int n;
array<bool, 5004> prime;
for(int i = 2; i <= 5000; i++){
prime[i] = 1;
for(int j = 2; j < i; j++){
if(i % j == 0){
prime[i] = 0;
break;
}
}
}
while(cin >> n){
cout << "primes between 1 ~ " << n << ": ";
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
if(prime[i]) cout << i << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
時間複雜度
Bubble Sort
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
|---|
從小排到大
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
|---|
比較第1、第2個
(交換)
| 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
|---|
| 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
|---|
比較第2、第3個
(交換)
比較第3、第4個
(交換)
重複直到序列被排序好
Worst Case : 原序列遞減
第1次 : 做n - 1次
第2次 : 做n - 2次
.
.
.
第n - 1次 : 做1次
複雜度 :
複雜度
Merge Sort
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
|---|
| 4 | 1 |
|---|
| 3 | 2 |
|---|
| 4 |
|---|
| 1 |
|---|
| 3 |
|---|
| 2 |
|---|
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
|---|
| 4 | 1 |
|---|
| 3 | 2 |
|---|
| 4 |
|---|
| 1 |
|---|
| 3 |
|---|
| 2 |
|---|
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
|---|
| 4 | 1 |
|---|
| 3 | 2 |
|---|
| 4 |
|---|
| 1 |
|---|
| 3 |
|---|
| 2 |
|---|
| 4 |
|---|
| 1 |
|---|
| 3 |
|---|
| 2 |
|---|
| 1 | 4 |
|---|
| 2 | 3 |
|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|
複雜度
層數 * 每層時間
每層時間 = 合併時間 =
有幾層呢?
設有 層,每次砍半 =>
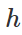
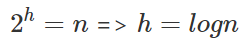
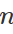
複雜度 :
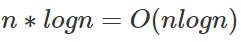
那麼電腦跑多快呢
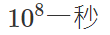
| n | 可能的複雜度 |
|---|---|
| 100 | |
| 1000 | |
| 10000 | |
| 100000 | |
| 1000000 | |
| 10000000 |

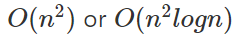
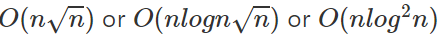
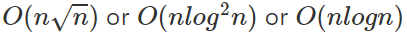
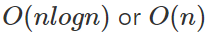
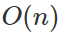
Quick Sort
從陣列中隨機選一個數字,比較小的通通丟到左邊,大的通通丟到右邊的排序演算法。
Worst Case
Best Case
每次都挑到最小/最大的
每次都挑到中位數
第1次 : 看n - 1個
第2次 : 看n - 2個
.
.
.
第n - 1次 : 看1個
每次都切半
=> logn 層
每層看約 n 個
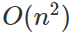
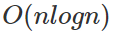
Average?
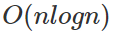
by 芾棠
更多題目
題解們
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
signed main(){
long long n, x, sum, mx;
while(cin >> n){
sum = mx = 0;
for(long long i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> x;
sum += x;
mx = max(mx, x);
}
if(2 * mx < sum) cout << "YES\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
signed main(){
int n, alive, i = 0;
cin >> n;
alive = n;
bool vis[n], ok = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) vis[i] = 1;
while(alive > 1){
if(vis[i % n]){
if(!ok){
vis[i % n] = 0;
alive--;
ok = 1;
}else ok = 0;
}
i++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(vis[i]){
cout << i + 1;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
signed main(){
int n, sum = 0;
string s;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> s;
if(s[2] == s[3] && s[3] == s[4] && s[4] == s[5]) sum += 2000;
else if(s[2] == s[3] && s[4] == s[5]) sum += 1500;
else sum += 1000;
}
cout << sum << '\n';
return 0;
}#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
signed main() {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int rec[a][b];
int down[b][a];
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b; j++) {
cin >> rec[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a; j++) {
down[i][j] = rec[j][i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a; j++) {
cout << down[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}