Linked Lists

A journey into data structures
What is a Linked List?
A Linked List is a data structure we create contains a list of nodes that are linked with code we write to link them
node: A node is an object that holds at most 2 pieces of information.
- A data value
- The next node it points to in the list
Vocabulary
- node - an object in memory
- head - the first object in the list
- tail - the last object in the list
//What does a node look like
//A node that does NOT link to another node
{
data: "Turkey Sandwich",
next: null
}
//A node that DOES link to another node
{
data: "Turkey Sandwich",
next: {
data: "Meatballs",
next: null
} // this is really a reference to an object in memory
}In code a single node can "look" 2 ways:
In memory an un-linked list looks like this:
Memory

They are simply JUST objects in memory
Note: There is no such thing as an un-linked list
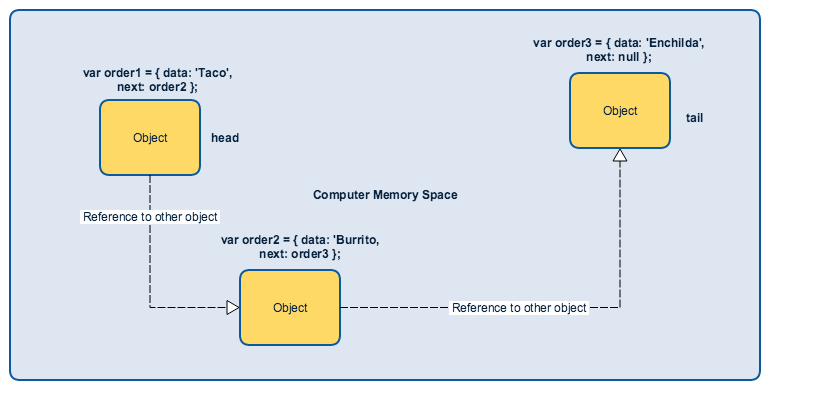
In memory a linked list looks like this:
Memory
One object holds a reference to another object
Or: One node holds a pointer to the next node in order
Why Use A Linked List?
We use linked lists in situations where we don't know the exact size but anticipate that the list could potentially grow to large sizes
We still need to preserve order AND anticipate that order will change over time
Why not an Array or Nested Object?
Arrays and Objects take their own physical "chunk" of memory and grow that space as they get larger
- This doesn't let the operating system best allocate/distribute chunks of available memory
- Changing the structure of large single data structures in memory is "expensive"
Linked Lists are just small simple objects in memory that can be stored anywhere and simply "point" to other objects in other places/addresses in memory
Changing the structure of a large linked list is much faster than changing the structure of a large array
What happens when we add NEW data?

Array or Nested Object:
myArray.push(1);
Linked List:
myLinkedList.add(obj);
Performance
Adding something to a Linked List is very fast since we just create an object and point to it.
Finding something in a Linked List can be slow since we always have to search from the beginning.
Finding something in a Single Linked List can only search from the beginning of the list.
A Single Linked List Implementation:
A Linked List is a rather simple implementation
It is generally comprised of:
- A linked list object
- A head node
- A tail node
- A method to add a node
- A method to insert a node
- A method to find a node
- A method to remove a node
In a Single Linked List, each node knows about the next node but not the previous
To Add A Node:
- Add a new node to the current tail
- Update the current tail's next to the new node
- Update your linked list to point tail to the new node
To Insert A Node:
- Find the position/node in your linked list where you want to insert your new node after
- Update the next property of the new node to point to the node that the target node currently points to
- Update the next property of the node you want to insert after to point to the new node
To Find A Node:
- Start at the head node of your linked list
- Check if value matches what you're searching for, if found return that node
- If not found, move to the next node via current node's .next property
- Repeat until .next is null (tail / end of list)
To Delete A Node:
- Find the node you are searching for and keep track of previous node
- When found, update previous node's next to point to the next node referenced by node to be deleted
- Delete found node from memory
Other Types of Linked Lists:
Double Linked List - same as a Single Linked List with the exception that each node also points to the previous node as well as the next node
Circular Linked List - same as a Double Linked List with the exception that there is no concept of a head or tail. All nodes point to the next/previous in a circular fashion. No true start to the list.