網頁設計大禮包
Outline
- Sublime Text 4 / Sublime Merge
- HTML
- Javascript
- React
- Express
- Material-UI
Why so important
- 最簡單的方法做出「有介面」的程式
- 每種裝置都可以使用
- 適合部建服務
https://www.sublimetext.com/

優點
- 輕量
- 多功
- 客製化
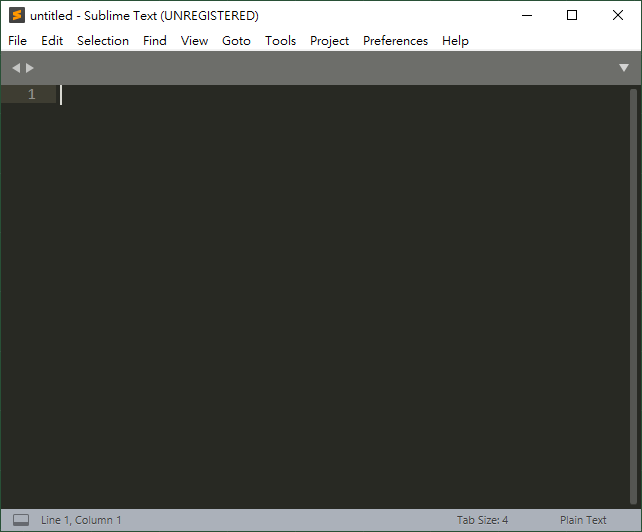
縮排控制
上色語言
| CTRL+F | 搜尋 |
| CTRL+H | 取代 |
| CTRL+Shift+P | 開啟指令介面 |
| Esc | 離開目前功能 |
| CTRL+Click | multiple selection |
插件們
工具們
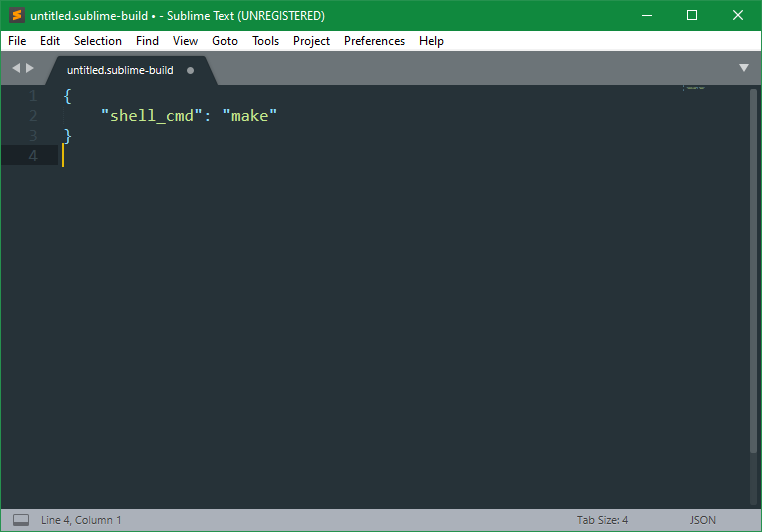
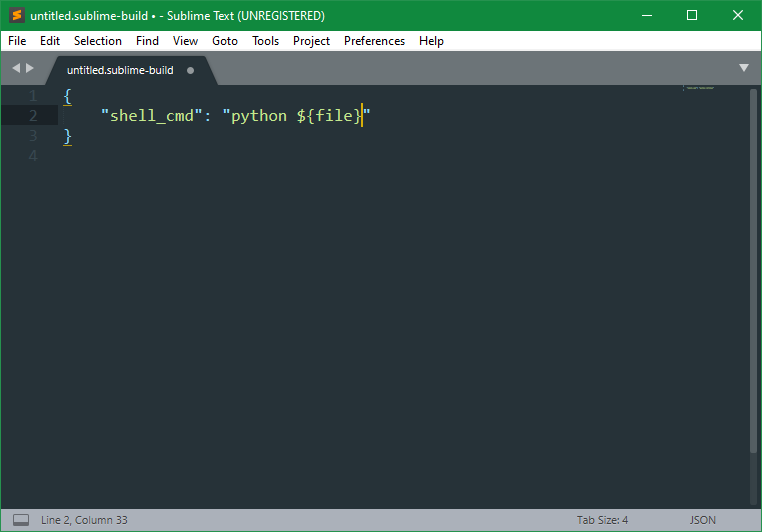
Tools > Build System > New Build System
snippets
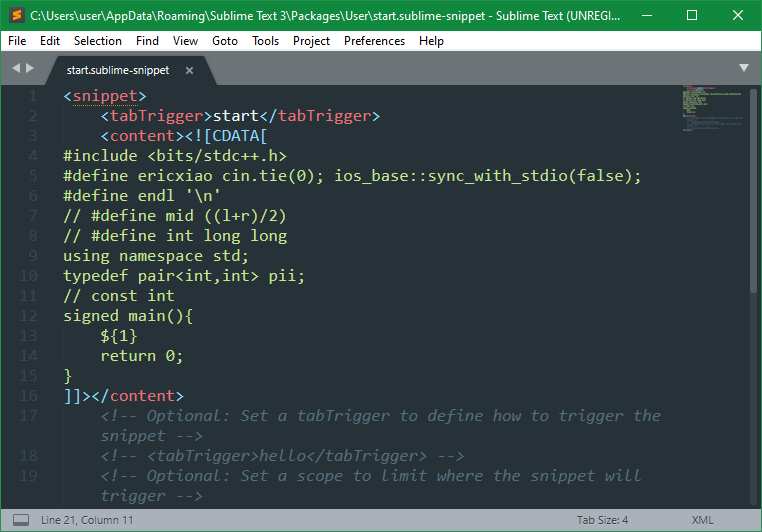
Tools > Developer > New Snippet
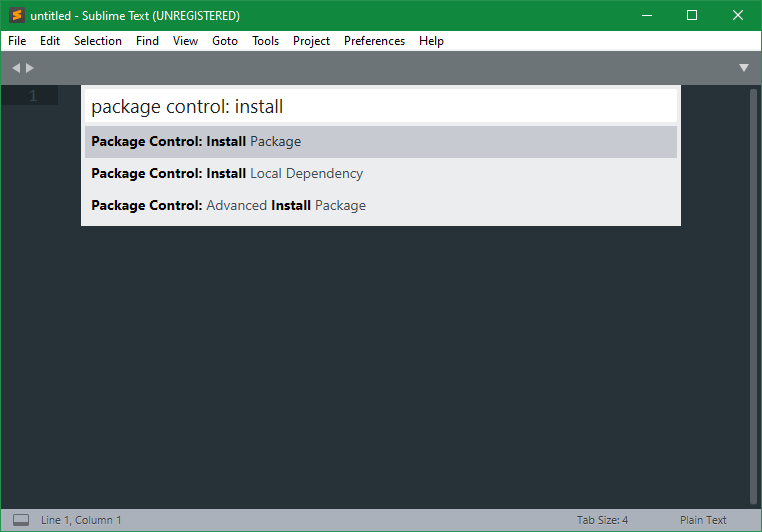
material theme
CTRL+Shift+P >
Package Control: Install Package > material theme
https://www.sublimemerge.com/

mighty git tool
優點
- 美觀
- 視覺化
- 簡單直白
- 操作方便
- 與Sublime Text並用
HyperText Markup Language
超文字
標記
語言

- 標記語言
- 非程式語言
- 宣告物件排版
- 最容易做成介面的方法
基本語法
<TAGNAME>EXAMPLE</TAGNAME>
<html>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph</p>
</body>
</html>基本語法
<TAGNAME>
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/30186107/29488525-f55a69d0-84da-11e7-8a39-5476f663b5eb.png" />
<input />
<br />
<a href="https://www.w3schools.com/html/default.asp" />
<link />
<meta /><!DOCTYPE>
<h1>heading1</h1>
<h2>heading2</h2>
<h3>heading3</h3>
<h4>heading4</h4>
<h5>heading5</h5>
<h6>heading6</h6>
<p>paragraph</p>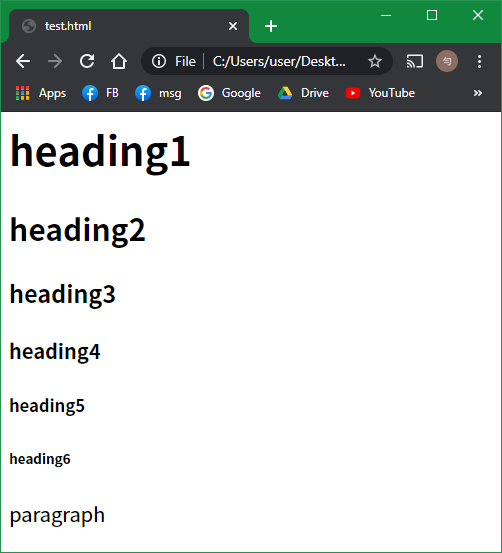
<!DOCTYPE>
<h1 style="color: red;">heading1</h1>
<h2 style="color: orange;">heading2</h2>
<h3 style="color: yellow;">heading3</h3>
<h4 style="color: green;">heading4</h4>
<h5 style="color: blue;">heading5</h5>
<h6 style="color: purple;">heading6</h6>
<p style="color: #808080;">paragraph</p>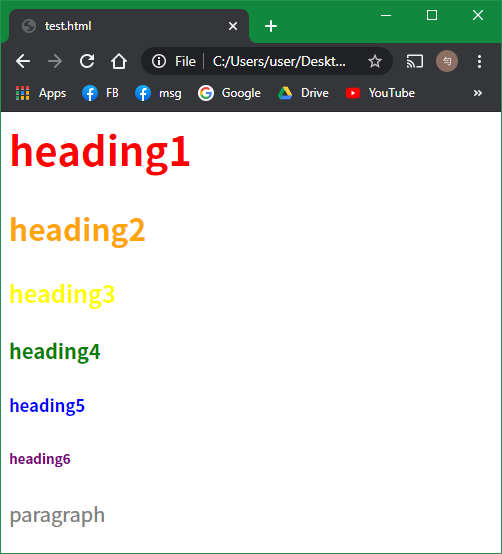
基本語法
<TAGNAME ATTRIBUTE="VALUE"></TAGNAME><!DOCTYPE>
<h1 style="color: red;text-align: center;border-style: solid;">heading1</h1>
<h2 style="color: orange;text-align: center;border-style: solid;">heading2</h2>
<h3 style="color: yellow;text-align: center;border-style: solid;">heading3</h3>
<h4 style="color: green;text-align: center;border-style: solid;">heading4</h4>
<h5 style="color: blue;text-align: center;border-style: solid;">heading5</h5>
<h6 style="color: purple;text-align: center;border-style: solid;">heading6</h6>
<p style="color: gray;text-align: center;border-style: solid;">paragraph</p>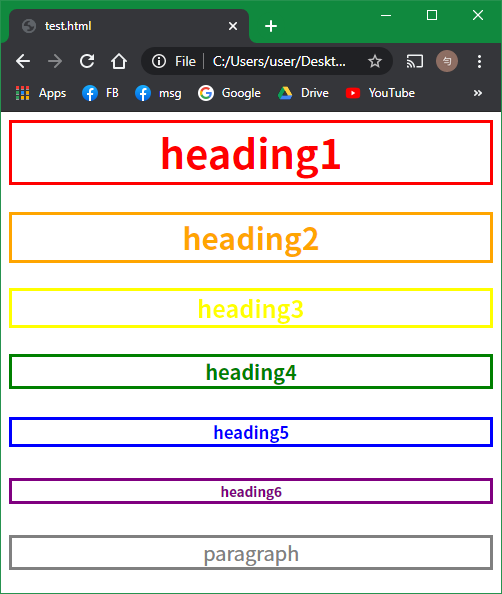
<!DOCTYPE>
<style>
.text{
text-align: center;
border-style: solid;
}
.round{
border-radius: 100px;
}
</style>
<h1 class="text round" style="color: red;">heading1</h1>
<h2 class="text" style="color: orange;">heading2</h2>
<h3 class="text round" style="color: yellow;">heading3</h3>
<h4 class="text" style="color: green;">heading4</h4>
<h5 class="text round" style="color: blue;">heading5</h5>
<h6 class="text" style="color: purple;">heading6</h6>
<p class="text round" style="color: gray;">paragraph</p>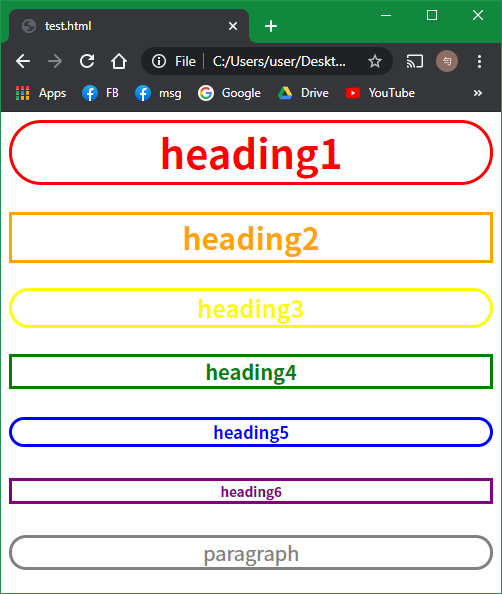
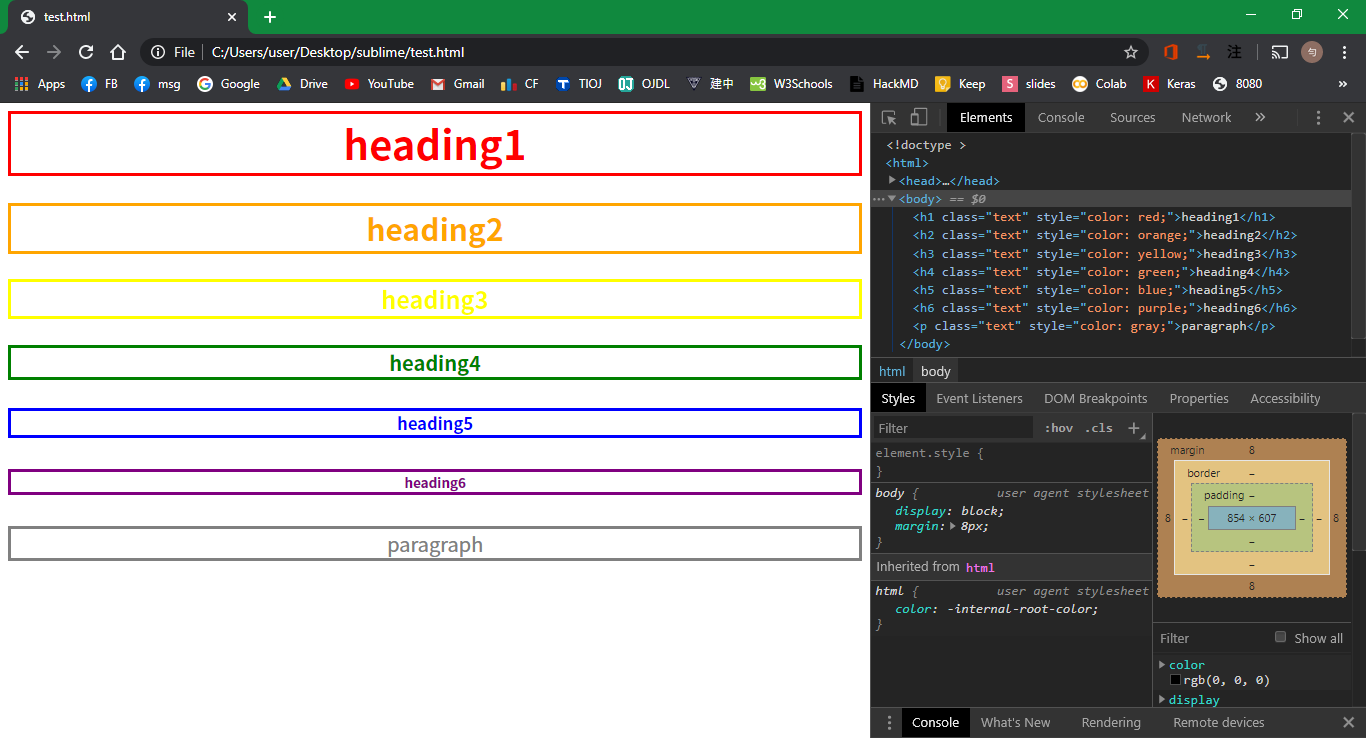
最熟悉的工具—Chrome

F12
Cascading Style Sheets

- 設定每個元素、類別的style
- 將style與html分離
- 類似「呈現與內容分離」的理念
- 讓排版變漂亮
selector 語法
/* select by element name */
h1 {font-weight: 1000;}
/* select by class */
.center {text-align: center;}
/* select by id */
#box {background-color: red;}
/* select all */
* {font-family: 'Noto Sans TC';}
- 讓物件動起來
- 邏輯處理
- 是程式語言
基本語法 跟C++很像
- 宣告變數用 \(\texttt{const}\) / \(\texttt{let}\)
- 弱型別
- \(\texttt{String}\)
- \(\texttt{Number}\)
- \(\texttt{Array}\)
- \(\texttt{Object}\)
-
print用console.log
-
任何東西都是Object
-
函式宣告用function NAME(ARGS){}
-
簡化版function宣告(類似lambda function)
-
const func = in => out;
-
const square = x => x * x;
Arrow function
const func = (a, b, c) => {
a += b;
return a + c;
}function func(a, b, c){
a += b;
return a + c;
}
HTML DOM
- 更改HTML網頁的內容
- 處理網頁發生事件
document.getElementById
document.getElementsByTag
document.getElementsByClassName
<h1 id="test">Testing Page</h1>
<script>
let ele = document.getElementById('test');
ele.innerHTML = `
<span style="color: red">
RED TEXT
</span>
`;
</script>
<button onclick="add()">Add</button>
<ol id="list"></ol>
<script>
function add(){
const ele = document.getElementById('list');
ele.innerHTML += `<li>item</li>`;
}
</script><button id="add">Add</button>
<ol id="list"></ol>
<script>
function add(){
const ele = document.getElementById('list');
ele.innerHTML += `<li>item</li>`;
}
document.getElementById('add')
.addEventListener('click', add);
</script>
設計網頁時建議選擇一種
framework / library下手
- 結構明確
- 物件導向
- 開發方便
- 額外工具
- JS library
- single-page application
- 「非常」方便的開發工具
- OOP (components)
- 用狀態(states)控制元素
- 提供JSX語法擴充
- 邏輯和呈現綁在一起
React
- Install node.js https://nodejs.org/en/download/
-
npx create-react-app my-app
-
cd my-app -
npm start - 可以看到預設的react頁面
Get Started
檔案架構
| node_modules/ | 套件安裝的目的(不會動到) |
| public/ | meta data(不會動到) |
| src/ | 網頁主體 |
| package.json | 管理套件的檔案 |
src/App.js
- 一個js檔就是一個component
- 一個component是一個function
- JSX:把html元素寫在js裡
function App() {
return (
<>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph</p>
</>
);
}
export default App;嵌入變數
function App() {
const name = 'INFOR';
return (
<>
<h1>Hello {name}</h1>
</>
);
}
export default App;變數也可以是元素
function App() {
const greeting = <h1>Hello INFOR</h1>;
return (
<>
<ol>
<li>{greeting}</li>
</ol>
</>
);
}
export default App;變數也可以是陣列
function App() {
const people = [
<li>thomaswang</li>,
<li>casperwang</li>,
<li>ericxiao</li>,
];
return (
<>
<ol>
{people}
</ol>
</>
);
}
export default App;變數也可以是陣列
function App() {
const people = [
'thomaswang',
'casperwang',
'ericxiao',
];
return (
<>
<ol>
{people.map(name => <li key={name}>{name}</li>)}
</ol>
</>
);
}
export default App;Key
- 識別「相同的元素」
- 效能考量
without key
with key
1,2,3 \(\longrightarrow\) 2,3,4
- delete 1
- delete 2
- delete 3
- insert 2
- insert 3
- insert 4
- delete 1
- insert 4
styling
function App() {
const people = [
'thomaswang',
'casperwang',
'ericxiao',
];
return (
<>
<ol style={{ color: 'red' }}>
{people.map(name => <li>{name}</li>)}
</ol>
</>
);
}
export default App;HTML
<div style="color: #fff; font-size: 20px;">React
<div style={{ color: '#fff', fontSize: '20px' }}>-
flex-direction -
text-align
-
flexDirection -
textAlign
使用自定義component
function Button() {
return (
<button>click me</button>
);
}
function App() {
return (
<>
<Button />
<Button />
</>
);
}
export default App;傳入properties
function Button({ name }) {
return (
<button>{name}: click me</button>
);
}
function App() {
return (
<>
<Button name="A" />
<Button name="B" />
</>
);
}
export default App;特殊property——children
function Button({ children }) {
return (
<button>{children}</button>
);
}
function App() {
return (
<>
<Button>A</Button>
<Button>B</Button>
</>
);
}
export default App;特殊property——onClick
function Button({ children }) {
return (
<button onClick={() => console.log(children)}>{children}</button>
);
}
function App() {
return (
<>
<Button>A</Button>
<Button>B</Button>
</>
);
}
export default App;目前為止我們做到了什麼?創造自己的tag
寫程式的精神:減少重複!
function Button({ children }) {
return (
<button style={{
background: 'red',
cursor: 'pointer',
}} onClick={() => console.log(children)}>
{children}
</button>
);
}
function App() {
const btns = [
'btn-1',
'btn-2',
'btn-3',
'btn-4',
'btn-5',
'btn-6',
'btn-7',
'btn-8',
]
return (
<>
{btns.map(x => <Button key={x}>{x}</Button>)}
</>
);
}
export default App;<button
style="background: red;cursor: pointer;"
onclick="console.log('btn-1')">
btn-1
</button>
<button
style="background: red;cursor: pointer;"
onclick="console.log('btn-2')">
btn-2
</button>
<button
style="background: red;cursor: pointer;"
onclick="console.log('btn-3')">
btn-3
</button>
<button
style="background: red;cursor: pointer;"
onclick="console.log('btn-4')">
btn-4
</button>
<button
style="background: red;cursor: pointer;"
onclick="console.log('btn-5')">
btn-5
</button>
<button
style="background: red;cursor: pointer;"
onclick="console.log('btn-6')">
btn-6
</button>
<button
style="background: red;cursor: pointer;"
onclick="console.log('btn-7')">
btn-7
</button>
<button
style="background: red;cursor: pointer;"
onclick="console.log('btn-8')">
btn-8
</button>以上,我們簡化了排版部分
state
- react的design pattern
- 相同的state對應到相同的畫面狀態
- state = 畫面背後記錄的資料
Example:計數器
plain JavaScript
<h1 id="counter">0</h1>
<button onclick="add()">++</button>
<script>
let cnt = 0;
function add(){
cnt++;
document.getElementById('counter').innerText = cnt;
}
</script>-
cnt其實就是state
-
缺點:state改變後要手動改變畫面(line 7)
React
import { useState } from 'react';
function App() {
const [cnt, setCnt] = useState(0);
function add(){
setCnt(cnt + 1);
}
return (
<>
<h1>{cnt}</h1>
<button onClick={add}>++</button>
</>
);
}
export default App;-
cnt真的就是state
-
state改變後會直接反應在畫面上
- 每次state改變,react就會重新計算一次畫面的元素
- react做好了各式各樣的優化
- 只有跟變動的state有關的部分才會重算
Simple Design, High Efficiency
我們做到了什麼?使用state設計程式邏輯
more to learn
-
useEffect // making change to non-state things
-
useMemo // states computed from other states
-
useCallback // specialized useMemo for function
-
react-router-dom // handle route (url) change
-
context // global state
build
-
npm start開的是開發伺服器(development server)
-
開發伺服器並不適合做為產品
-
事實上我們做的都是靜態網頁,而靜態網頁不需要伺服器
-
要將所有react設計編譯、最佳化成靜態檔案
npm run buildfront-end / back-end
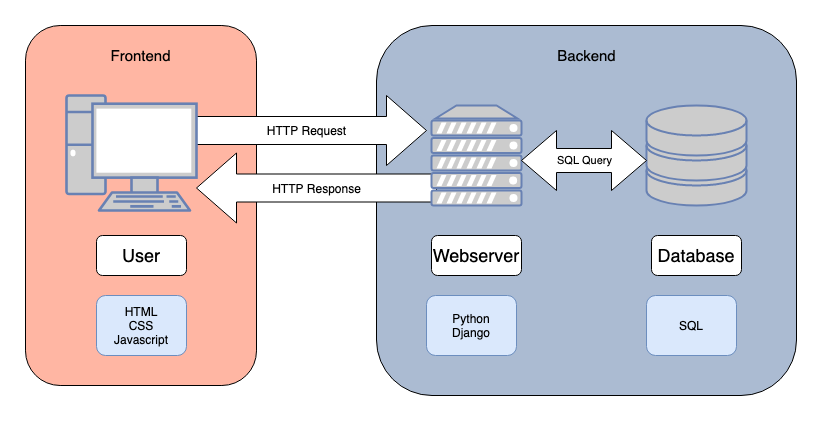
node.js 後端套件
JS async/await
- 「岔開來做某件事」
- 一般程式都是一行一行執行
- 「同步」
- 若要「等待」某些東西跑完再繼續計算
- JS使用Promise來實現
- async / await 為 Promise 的簡化版
- 某些函式是非同步的(需要等待時間)
- 例如 HTTP request、計算hash、檔案讀取
- 通常使用外部資源的函式都是非同步的
- 要使用非同步函式就必須搭配async/await
function resolveAfter2Seconds() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('resolved');
}, 2000);
});
}
async function asyncCall() {
console.log('calling');
const result = await resolveAfter2Seconds();
console.log(result);
}
console.log('before');
asyncCall();
console.log('after?');async function asyncCall() {
console.log('calling');
let res = await fetch('http://localhost:5000');
res = await res.text();
console.log(`localhost:5000 says: ${res}`);
}
console.log('before');
asyncCall();
console.log('after?');express
-
npm install express
-
node index.js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 5000;
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World!');
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`listening on port ${port}`);
});basics
app.get('/:name', (req, res) => {
res.send(`Hello ${req.params.name}!`);
});URL with parameters
cnt = {};
app.get('/:name', (req, res) => {
const name = req.params.name;
if(cnt[name] === undefined)
cnt[name] = 0;
res.send(cnt[name].toString());
});more functionality
cnt = {};
app.get('/:name', (req, res) => {
const { name } = req.params;
if(!(name in cnt))
cnt[name] = 0;
res.send(`${cnt[name]}`);
});more functionality
app.post('/add', (req, res) => {
const { name } = req.body;
cnt[name]++;
res.send(cnt[name].toString());
});POST with extra data
app.post('/add', (req, res) => {
const { name } = req.body;
if(!(name in cnt))
return res.sendStatus(400);
cnt[name]++;
res.send(cnt[name].toString());
});POST with extra data
work with React
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
const [cnt, setCnt] = useState(false);
const [name, setName] = useState("");
const [value, setValue] = useState("");
async function add(){
let res = await fetch(`http://localhost:5000/add`, {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({ name: name }),
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
}
});
res = await res.text();
setCnt(Number(res));
}
function change(event){
setValue(event.target.value);
}
useEffect(() => {
if(name.length === 0) return;
(async () => {
let res = await fetch(`http://localhost:5000/${name}`);
res = await res.text();
setCnt(Number(res));
})();
}, [name]);
return (
<>
<input type="text" value={value} onChange={change}/>
<button onClick={() => setName(value)}>OK</button>
<p>
{cnt !== false ?
<>
{cnt}<button onClick={add}>++</button>
</> : ""}
</p>
</>
);
}
export default App;even cooler
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
const [cnt, setCnt] = useState(false);
const [value, setValue] = useState("");
async function add(){
let res = await fetch(`http://localhost:5000/add`, {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({ name: value }),
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
}
});
res = await res.text();
setCnt(Number(res));
}
function change(event){
setValue(event.target.value);
setCnt(false);
}
useEffect(() => {
if(value.length === 0){
setCnt(false);
return;
}
const id = setTimeout(async () => {
let res = await fetch(`http://localhost:5000/${value}`);
res = await res.text();
setCnt(Number(res));
}, 500);
return () => clearTimeout(id);
}, [value]);
return (
<>
<input type="text" value={value} onChange={change}/>
<p>
{cnt !== false ?
<>
{cnt}<button onClick={add}>++</button>
</> : ""}
</p>
</>
);
}
export default App;more to learn
-
npm install fs // access file system
- firebase authentication