Background
Swissbytes Ltda.
2008
Suiza, Dinamarca, Australia, Bolivia
ATM, BRMS, Web Applications
Un simple problema
Programming Pearls Magazine, 1986
"Leer un archivo de texto, determinar la cantidad de palabras mas usadas, e imprimir una lista ordenada de estas palabras junto con sus frecuencias."Jon Bentley, Programming Pearls, 1986
- Donald Knuth
- Doug McIlroy
Resultado: Knuth
- 10+ páginas de código Pascal detalladamente documentado
- Programa procedimental
- Tomó dos dias terminarlo
Resultado: McIlroy
$> tr -cs A-Za-z '\n' |
tr A-Z a-z |
sort |
uniq -c |
sort -rn |
sed ${1}q
Cuál es la diferencia?
Qué tienes en tu caja de herramientas?
- Lenguajes de programación
- Frameworks y librerías
- Plataformas y protocolos
Qué realmente tienes en tu caja de herramientas?
Programación procedimental
Orientada a objetos
Orientada a aspectos
Funcional
Lógica
Simplicidad
El arte de la programación es el arte de organizar complejidad, de controlar el desorden y evitar el caos de la forma mas efectiva posible.Edsger W. Dijkstra
Simple != Fácil
Por qué nos debería importar?
Los programas complejos tienen mas bugs
Los programas complejos son mas difíciles de cambiar
Los programas complejos son menos legibles
Los programas complejos son menos flexibles
Por qué nos deberia importar?
Nosotros escribimos programas que toman decisiones
Las decisiones se basan en valores o datos
Los datos son percibidos o calculados
Los datos calculados son estables
Nuestros programas deben ser estables
Programación funcional
La programación funcional es un estilo de programación que enfatiza la evaluación de expresiones por encima de la ejecución de comandoscom.lang.functional, 2014
Una función es la relación entre valores donde un valor de entrada retorna exactamente un valor de salida.comp.lang.functional, 2014
Algunas funciones
- Math.sqrt(x)
- Collections.max(x)
- Arrays.asList(x...)
- String.valueOf(x)
Principios de programación funcional
Principios
- Flujo de datos
- Inmutabilidad
- Estilo declarativo
- Datos como datos
Flujo de datos
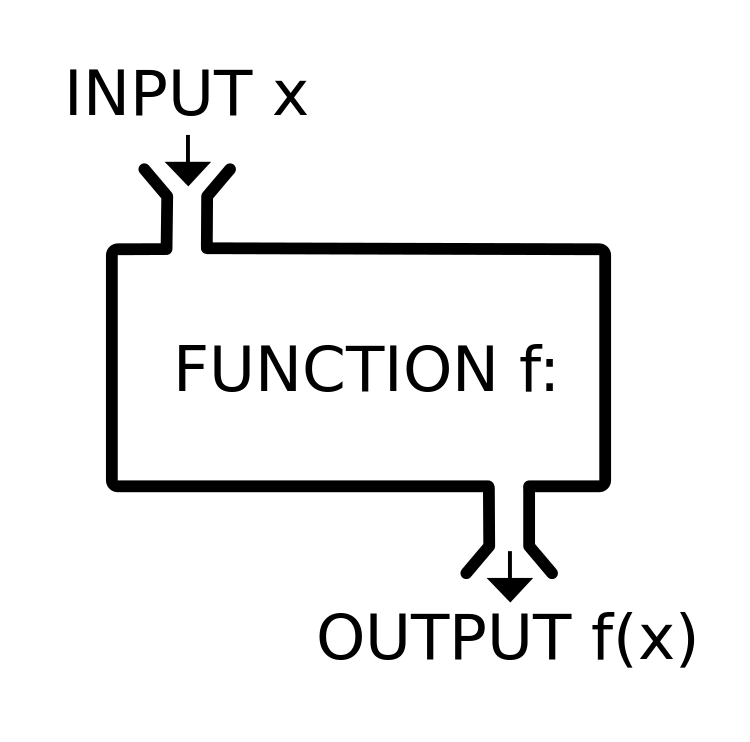
String readAsString(InputStream stream) throw IOException{
val reader = new InputStreamReader(stream);
return CharStreams.toString(reader);
}
List<String> readAsLines(InputStream stream) throw IOException{
return IOUtils.readLines(stream);
}
void main(){
val input = new FileInputStream("myfile.txt");
println("content: " + readAsString(input));
println("lines: " + readAsLines(input));
}
Exception!!!!
String readAsString(InputStream stream) throw IOException{
val reader = new InputStreamReader(cloneOf(stream));
return Streams.toString(reader);
}
List<String> readAsLines(InputStream stream) throw IOException{
return IOUtils.readLines(cloneOf(stream));
}
InputStream cloneOf(InputStream input){
val cloned ....
return cloned;
}
No tocar el estado global
No modificar datos de entrada
No interrumpir el flujo de ejecución
No usar NULL
Alcance local
Determinístico
Baja complejidad
No interrumpe el flujo de ejecución
Inmutabilidad

El problema que tenemos es que por años hemos enseñado efectivamente a generaciones de programadores que el estado mutable nos permite trabajar de la mejor forma. Ahora estamos en una carrera para enseñar que no todo eso es ciertoAnders Hejlsberg, SEI-Radio, 2008
Valores < - > Tiempo
Git / Mercurial / Fossil
Acoplamiento temporal
Request req = new Request("http://juanbandafanpage.com"); req.method(Request.POST); request.body("fanId=chichico"); request.fetch();Request req = new Request("http://juanbandafanpage.com"); // req.method(Request.POST); request.body("fanId=chichico"); request.fetch(); //NPE!!!
Acoplamiento temporal
Request req = new Request("http://juanbandafanpage.com"); req = req.body("fanId=chichico"); req = req.post(); req.fetch();Request req = new Request("http://juanbandafanpage.com"); req.body("fanId=chichico").post().fetch();
- java.lang.String
- java.util.Date
- com.google.guava
Todo valor es inmutable por defecto
Todo valor modificado, genera un nuevo valor
Los estados mutables son privados/locales
Los valores no cambian, generan nuevos valores
Los valores no necesitan thread-safety
No existen efectos secundarios
Identidad!!!
Estilo declarativo
Diga lo que hace, haga lo que dice
int countBugs(String filePath){
Path path = Paths.get(filePath);
int count = 0;
try(FileReader reader = new FileReader(
Files.newInputStream(path))
){
String line = null;
while( (line = reader.readLine()) != null )
if(line.contains(“BUG”))
count++;
}catch(IOException e){
printErr(e);
}
}
int countBugs(String filePath){
return Files.readAllLines(Paths.get(filePath))
.stream()
.filter(line -> line.contains(“BUG”))
.count();
}
Mas ejemplos?
List<Deposit> deposits= …;
// give me the big transfers
long allBigTransfers = deposits.stream()
.filter(d -> d.amount > 10000L)
.mapToLong(d -> t.amount)
.sum();
// give me the smallest transfer
Optional<> minTransfer = deposits.stream()
.min((d1, d2) -> d1 > d2);
Enfocarse en el qué, no en el cómo
Abstraer infraestructura
Generar expresiones, y no órdenes
Código expresivo/legible
Enfoque en el fondo, no la forma
Simplicidad inherente
Evaluación optimizable
Datos como datos
HttpServletRequest
getAsyncContext,getAttribute, getAttributeNames,
getCharacterEncoding,getLength,getContentLength,
getType,getContentType,getDispatcherType,getLocalName,
getLocalAddr,getLocale,getLocales,getLocalName,
getLocalPort,getParameterNames,getParameterValues,
getProtocol,getReader,getRealPath,getRemoteAddr,
getRemoteHost,getRemotePort,getRequestDispatcher,
getScheme,getServerName,getServerPort,isSecure,
removeAttribute,setAttribute,setCharacterEncoding,
startAsync,getHeader,getHeaderNames,getIntHeader,
getResponseStream,
...
[
"remote-addr": "127.0.0.1",
"scheme": "http",
"form-params": [],
"query-string": "fanId=chichico",
"request-method": "GET",
"content-type": "text/csv",
"server-name": "localhost",
"params": ["key": "value"],
"server-port": 8080,
"headers": [
"accept-encoding" : "gzip, deflate",
"connection": "close",
"content-length": 0,
...
]
]
class CustomerId{
private int id;
private String value;
//.....
}
class InValue{
private int id;
private String value;
private int type;
//...
}
class OutValue{
//...
}
class InValueContainer{
//...
}
class OutValueContainer{
//...
}
Efectos
Inconsistencia
Duplicidad
Acoplamiento
La especificidad esta sobre-valorada
Primitives
Lists
Sets
Dictionary
Usar primitivos hasta donde se pueda
Usar estructuras hasta donde se pueda
Evitar los objetos anémicos
Evitar estructuras hereditarias
Datos expresivos y claros
Uniformidad y simplicidad de código
Re-utilización
JSON...
Finalmente
La simplicidad es la característica mas devaluada de los sistemas de software.Yo, hace 10 segs