
Aotearoa New Zealand and Te Reo Māori
Quick as History of NZ
The first settlers arrived from Polynesia between 1250 and 1300 AD.
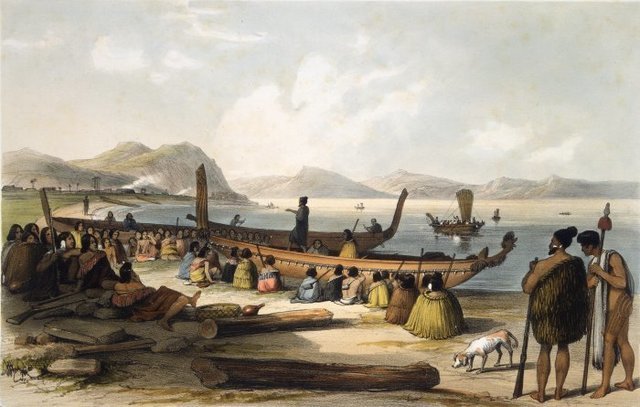
The first European to arrive in New Zealand was the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman in 1642.

Europeans did not revisit New Zealand until 1769 when the British explorer Captain James Cook arrived.

The Treaty of Waitangi is New Zealand’s founding document, signed in 1840 by representatives of the British Crown and Māori chiefs.

Aotearoa is the current Māori name for New Zealand.

Te Reo Māori
Te Reo Māori is the indigenous language of Aotearoa, New Zealand.
The Māori alphabet is made up of ten consonants and five vowels
Consonants
h, k, m, n, ng, p, r, t, w, wh
r is very short and slightly rolled
wh is pronounced as f
ng is pronounced as the ng in singer
a, e, i, o, u
The lines above vowels (macrons) indicate the way a vowel is pronounced: short or long.
Short sound: A/a (as in up); E/e (as in pen); I/i (as in eat); O/o (as in fork); U/u (as in you)
Long sound: Ā/ā (as in far); Ē/ē (as in peel); Ī/ī (as in heel); Ō/ō (as in your); Ū/ū (as in roof)
Vowels
Greetings (Mihi)
| Kia ora | Hello / Thank you |
| Kei te pēhea koe? | How are you? |
| Tēnā koe | Formal greeting to one person |
| Tēnā kōrua | Formal greeting to two people |
| Tēnā koutou | Formal greeting to many people |
| Mōrena / Ata mārie | Good morning |
Endings
| E noho rā | Goodbye (from a person leaving) |
| Haere rā | Goodbye (from a person staying) |
| Nāku noa, nā | Yours sincerely (one signatory) |
| Ngā mihi | Regards |
| Kia ora rawa atu | Many thanks |
| Ka kite anō | See you again |
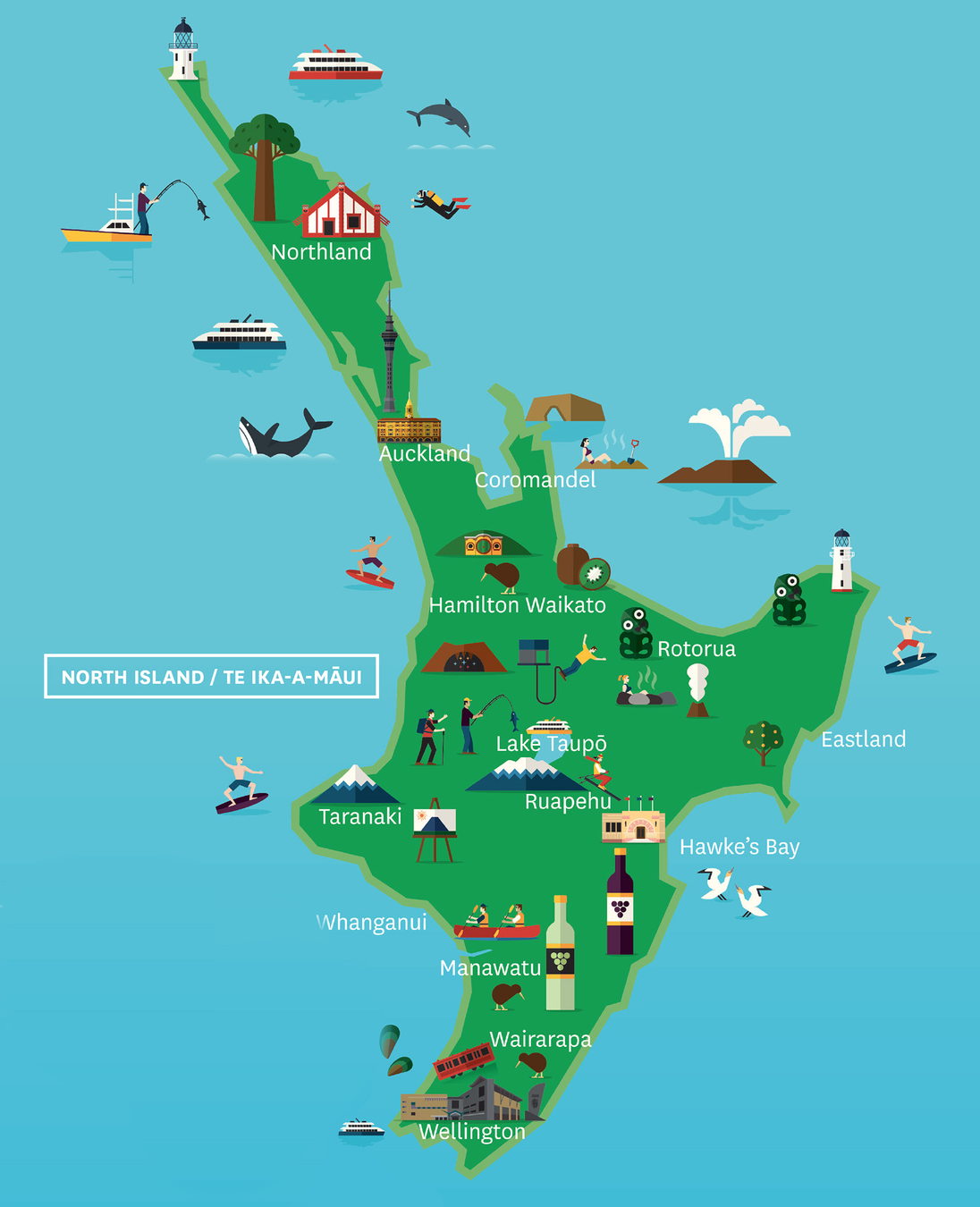
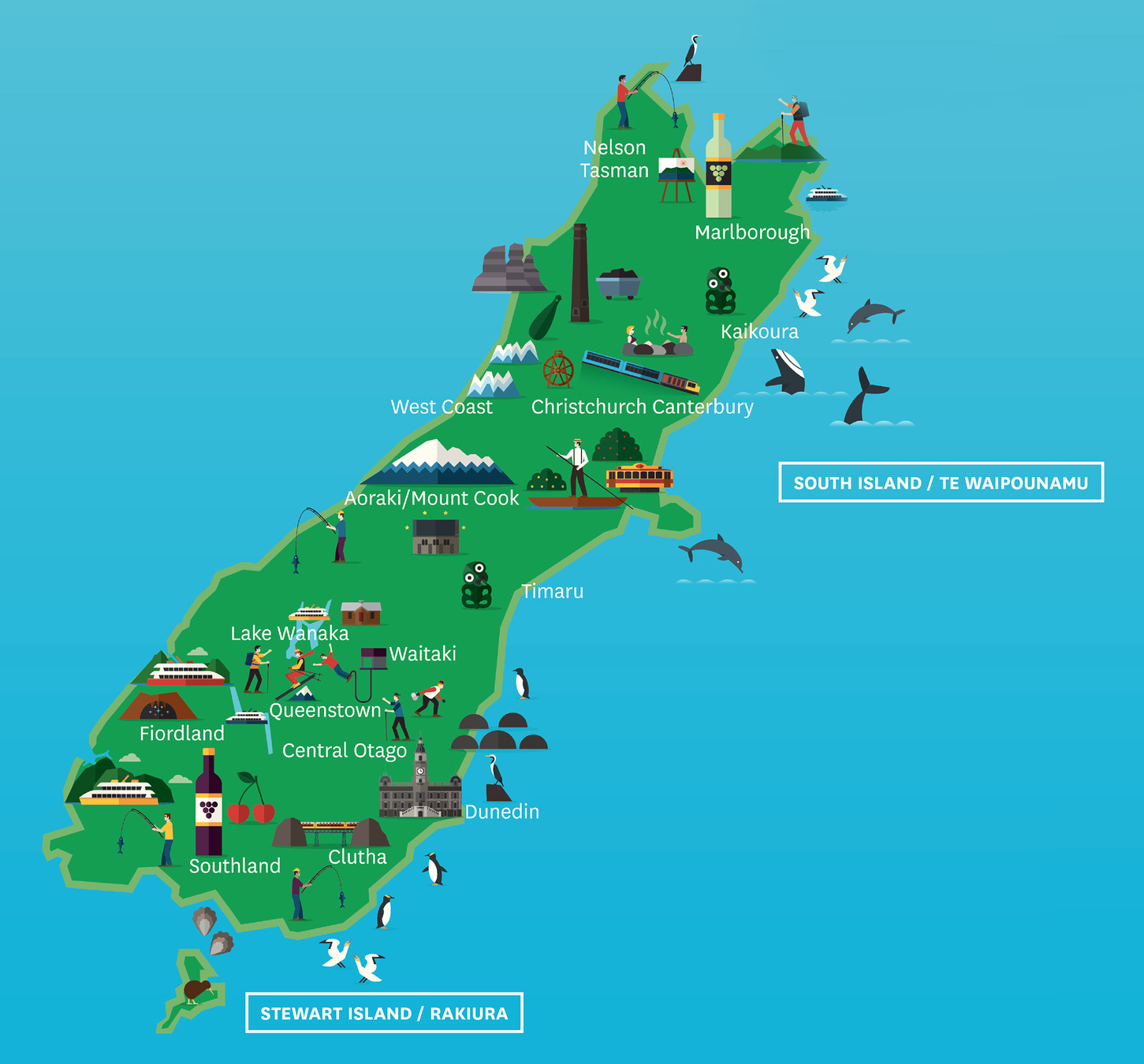
Place Names
| Kaikoura | Taupō |
| Manawatū | Tauranga |
| Rakiura (Stewart Island) | Waikato |
| Rotorua | Wairarapa |
| Ruapehu | Whakatāne |
| Tairāwhiti | Whanganui |
| Taranaki | Whangārei |
Resources
Māori Dictionary
https://maoridictionary.co.nz/
NZ Tourism
https://www.newzealand.com/nz/