Terraform: An Overview & Introduction (GCP)
David Chou

What is Infrastructure as Code?
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
The Process of Managing and Provisioning Computer Data Centers Through Machine-Readable Definition Files





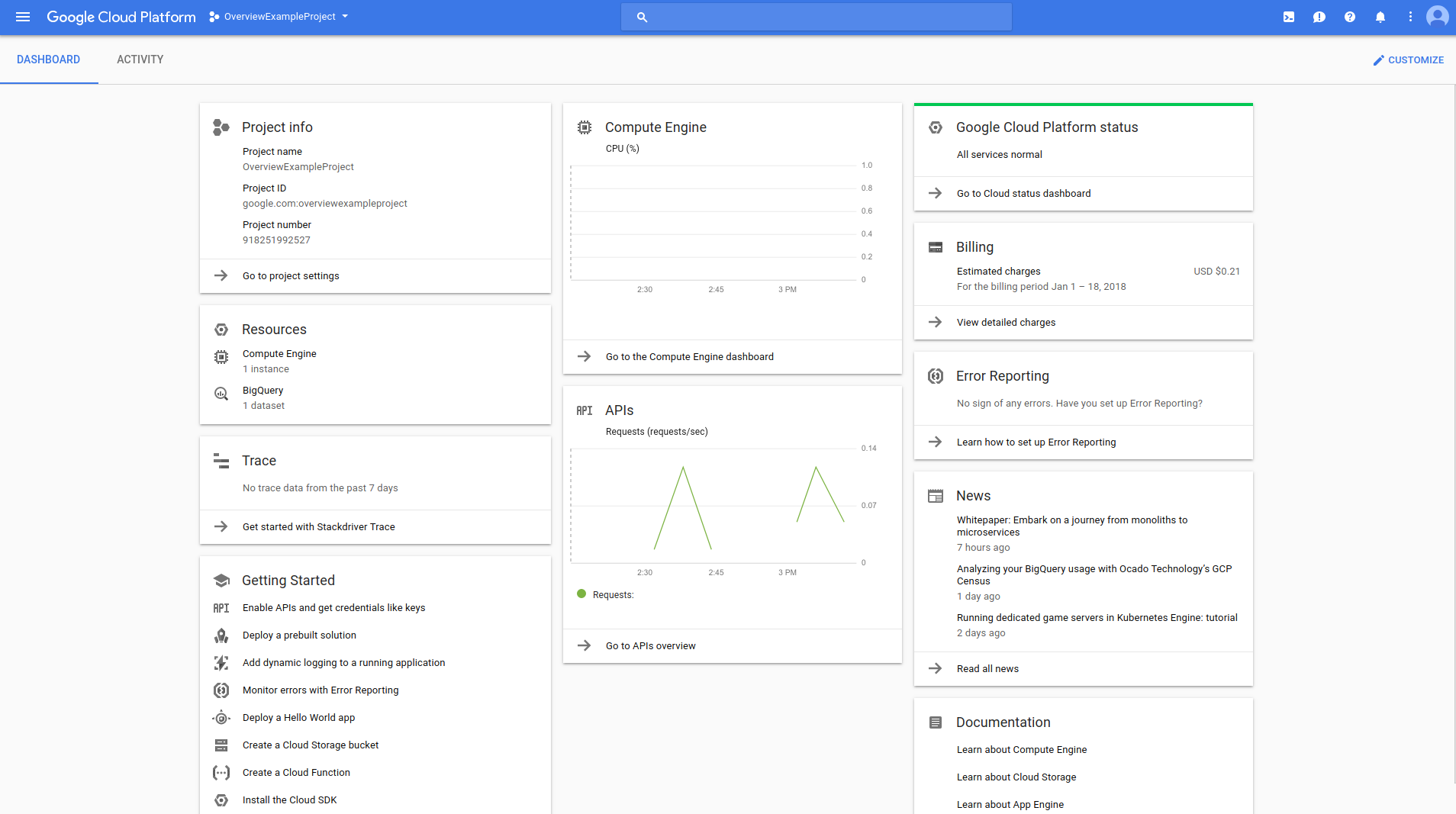

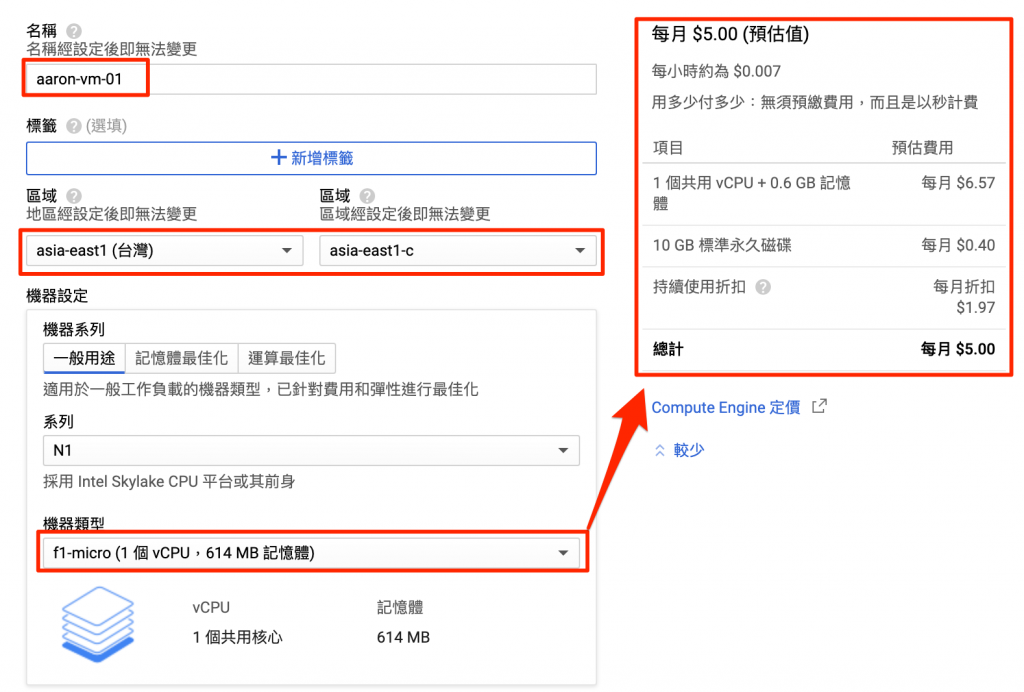
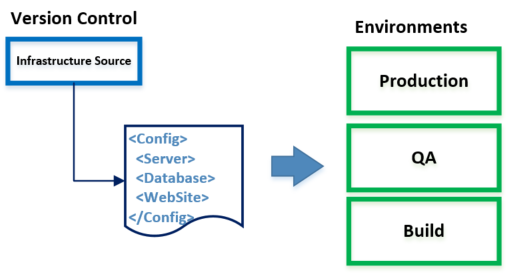
Record cloud resource with IaC tool & source code, not document !
What is Terraform?
Terraform is an open source tool for managing Infrastructure as Code
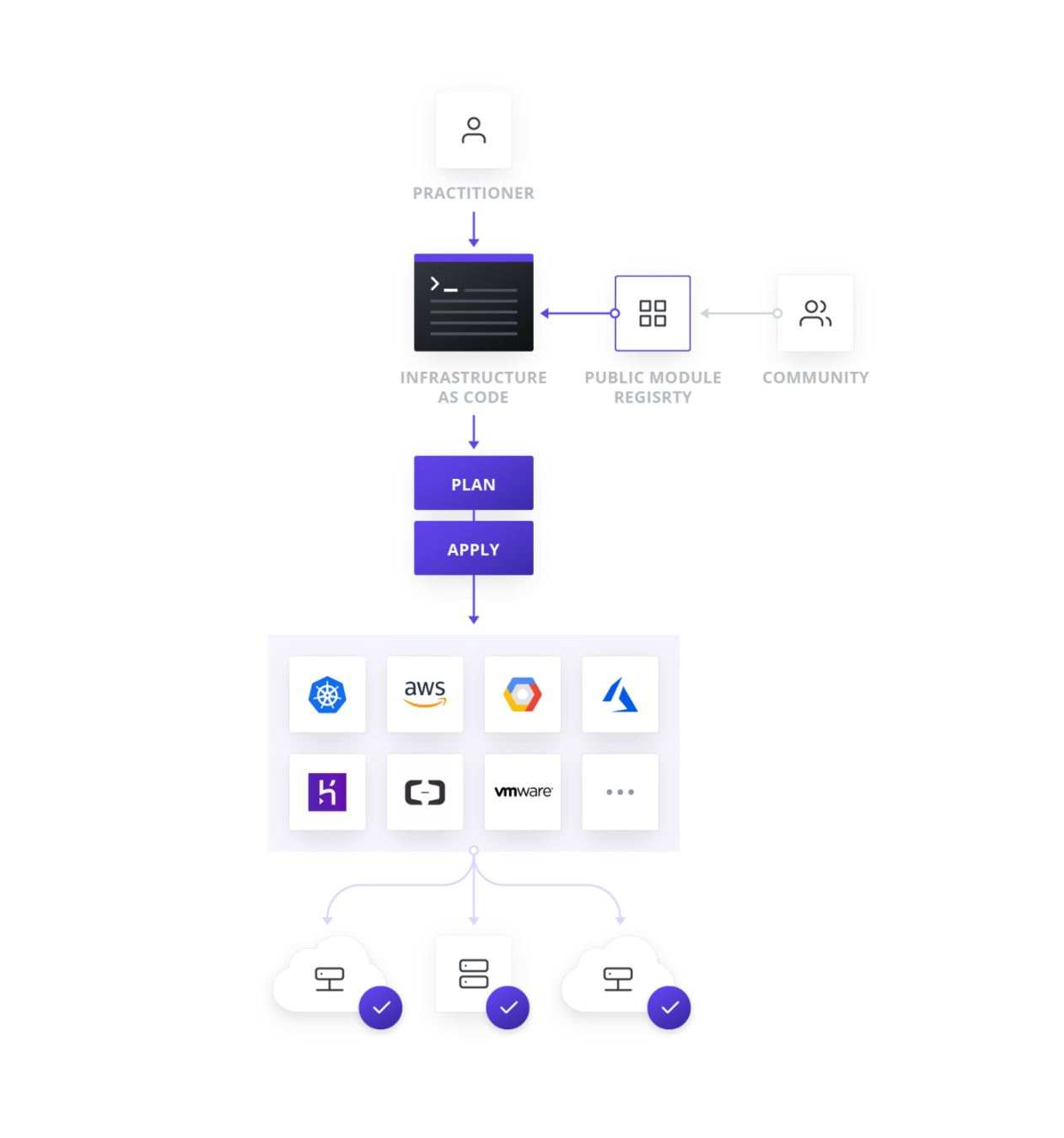
Terraform facts
- Developed by HashiCorp
- Opensource
- Golang
- HCL syntax
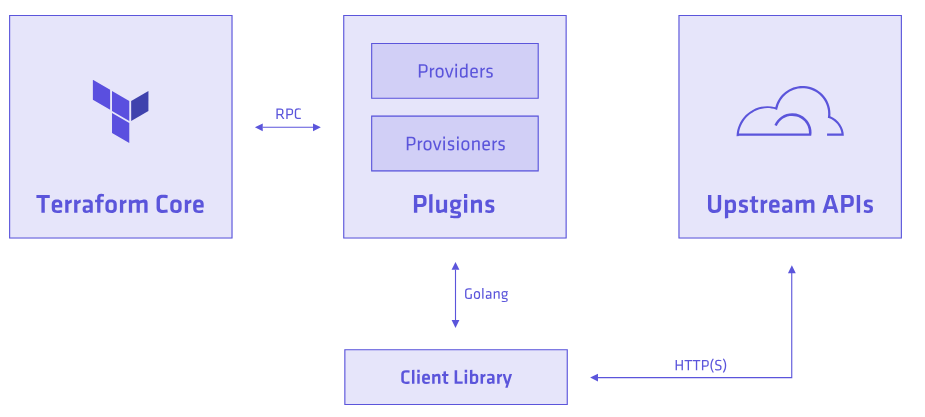
Core & Plugins

and more...


HCL
A structured configuration language that is both human and machine friendly, and specifically targeted towards DevOps tools, etc.
resource "google_compute_instance" "vm_instance" {
name = "terraform-instance"
machine_type = "f1-micro"
boot_disk {
initialize_params {
image = "debian-cloud/debian-9"
}
}
network_interface {
# A default network is created for all GCP projects
network = "default"
access_config {
}
}
}Terraform command
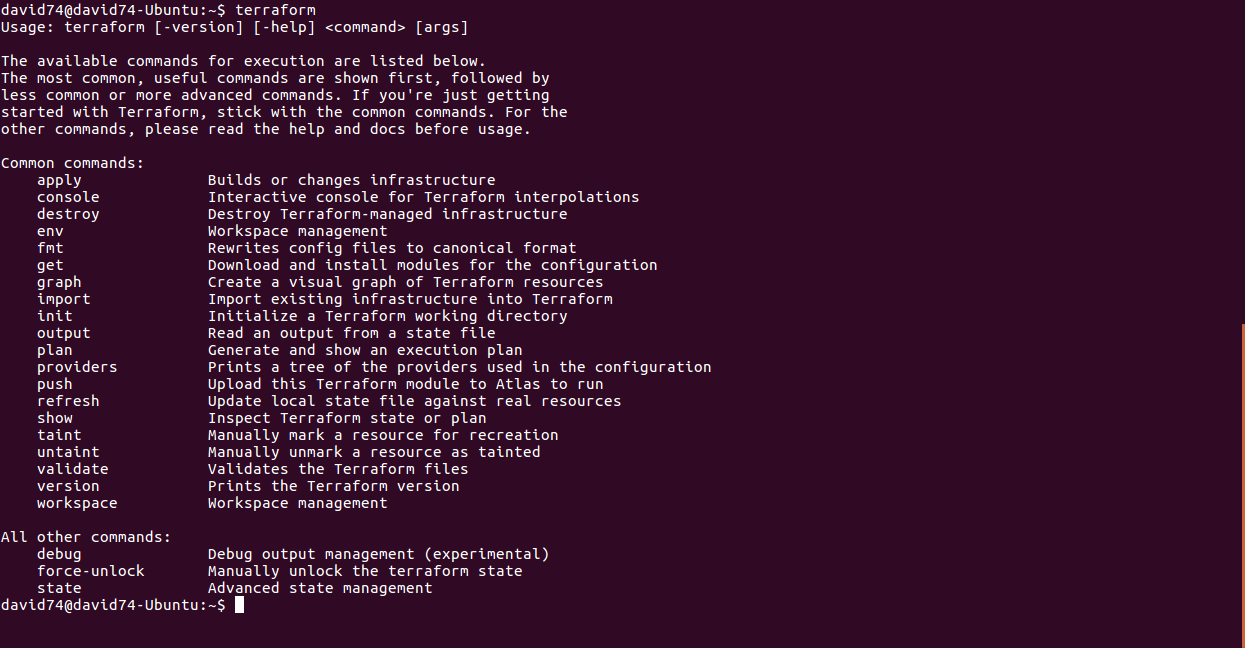
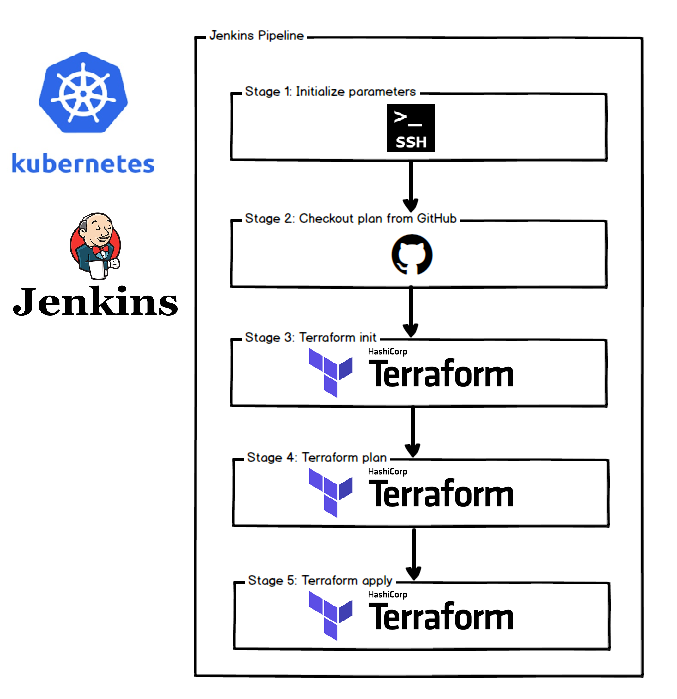
Terraform flow
$ terraform init
To initialize a working directory containing Terraform configuration files
$ terraform plan
Terraform performs a refresh, then determines what actions are necessary to achieve the desired state specified in the configuration files.
$ terraform apply
Apply the changes required to reach the desired state of the configuration
Hello Terraform
Let's provision a GCS bucket
main.tf
#Configure aws with a default region
provider "google" {
credentials = file("~/.gcp/david74-service-account.json")
project = "gcp-playground-332207"
}
/*Create a demo GCS bucket*/
resource "google_storage_bucket" "auto-expire" {
name = "david74-auto-expiring-bucket"
location = "asia-east1"
lifecycle_rule {
condition {
age = 3
}
action {
type = "Delete"
}
}
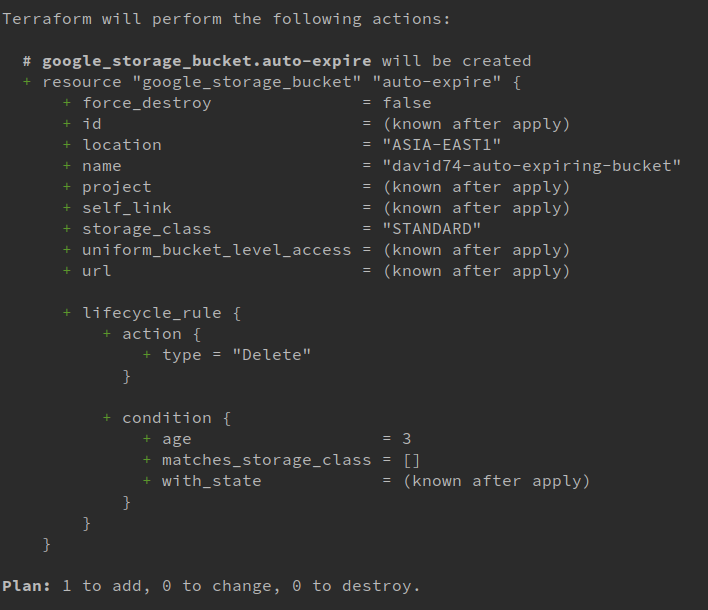
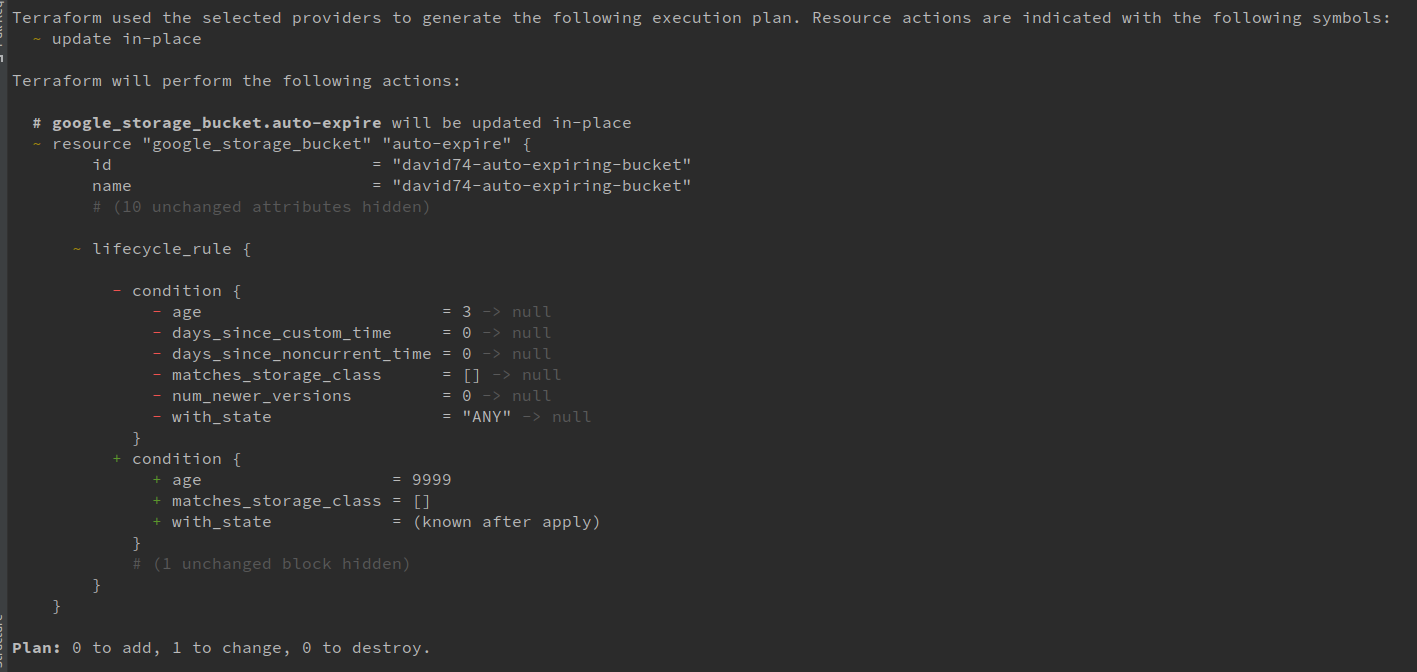
}Terraform plan
Terraform apply
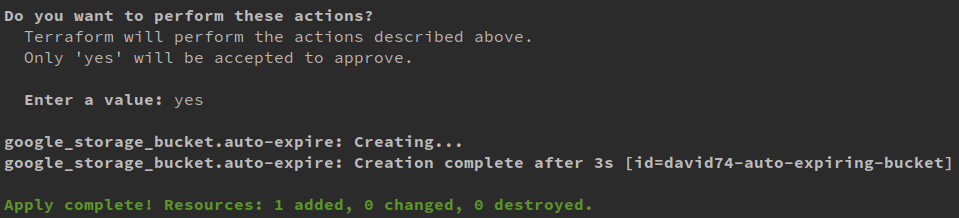
Terraform apply
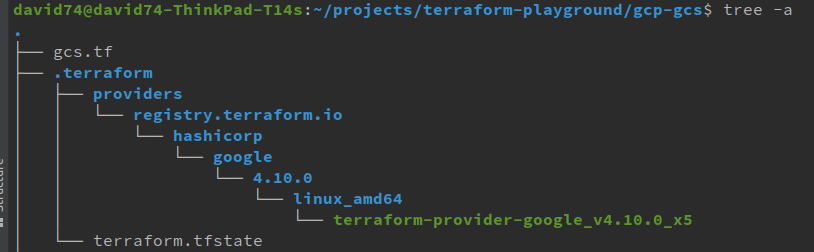
- terraform-provider-google provider plugin
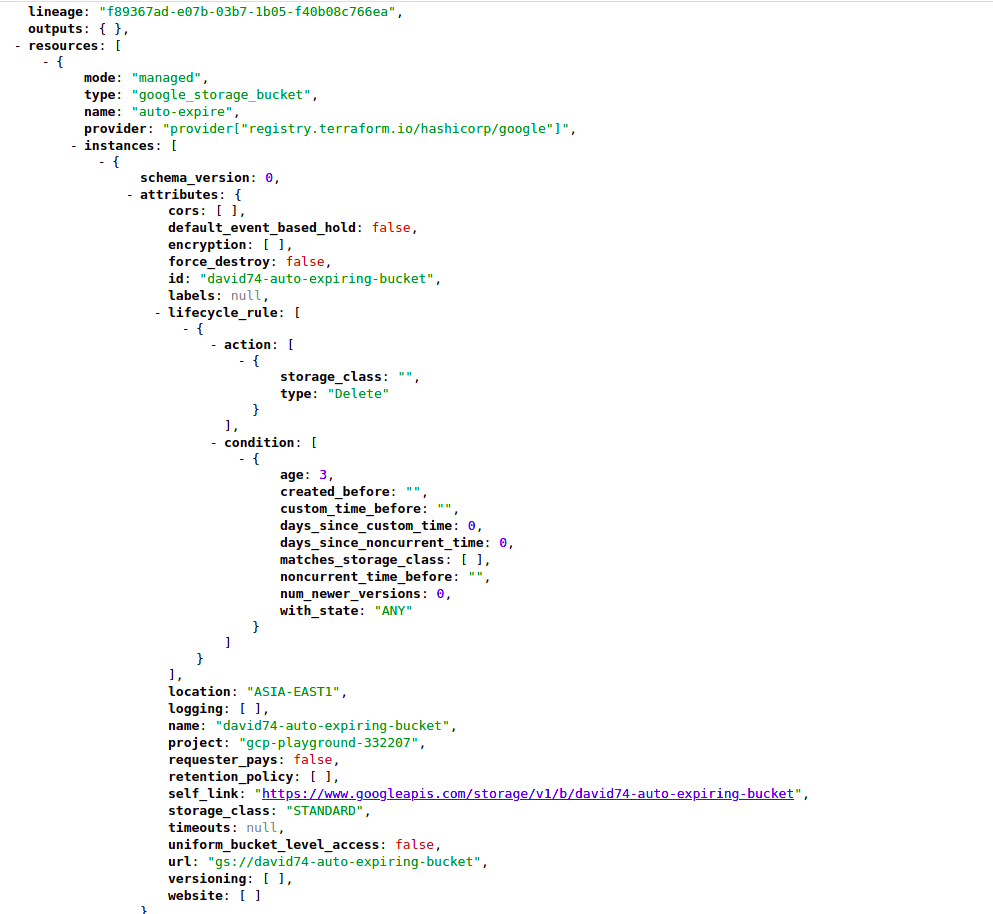
- terraform.tfstate
terraform.tfstate
What if I want to change the settings?
#Configure aws with a default region
provider "google" {
credentials = file("~/.gcp/david74-service-account.json")
project = "gcp-playground-332207"
}
/*Create a demo GCS bucket*/
resource "google_storage_bucket" "auto-expire" {
name = "david74-auto-expiring-bucket"
location = "asia-east1"
lifecycle_rule {
condition {
age = 9999
}
action {
type = "Delete"
}
}
}
variables.tf
main.tf
resource "google_storage_bucket" "auto-expire" {
name = "david74-auto-expiring-bucket-${var.env}"
location = "asia-east1"
lifecycle_rule {
condition {
age = var.bucket_age
}
action {
type = "Delete"
}
}
}variable "env" {
default = "local"
}
variable "bucket_age" {
default = 1
}
What if I want different settings for different env?
- staging: 7d lifecycle
- production: 365d lifecycle
terraform workspace
- Create different workspace with differen tfvars for different envs
- Each workspace has its on tfstate file
variables.tf
main.tf
resource "google_storage_bucket" "auto-expire" {
name = "david74-auto-expiring-bucket-${var.env}"
location = "asia-east1"
lifecycle_rule {
condition {
age = var.bucket_age
}
action {
type = "Delete"
}
}
}variable "env" {
default = "local"
}
variable "bucket_age" {
default = 1
}
staging.tfvars
env = "staging"
bucket_age = 3
production.tfvars
env = "production"
bucket_age = 365
$ terraform workspace new staging
$ terraform apply -var-file=staging.tfvars
$ terraform workspace new production
$ terraform apply -var-file=production.tfvars
Teamwork on Terraform?
Terraform Remote Backend
- By default, .tfstate file stores on local disk
- Save .tfstate file to a remote backend
- Easier for state sharing and team work
- CI/CD
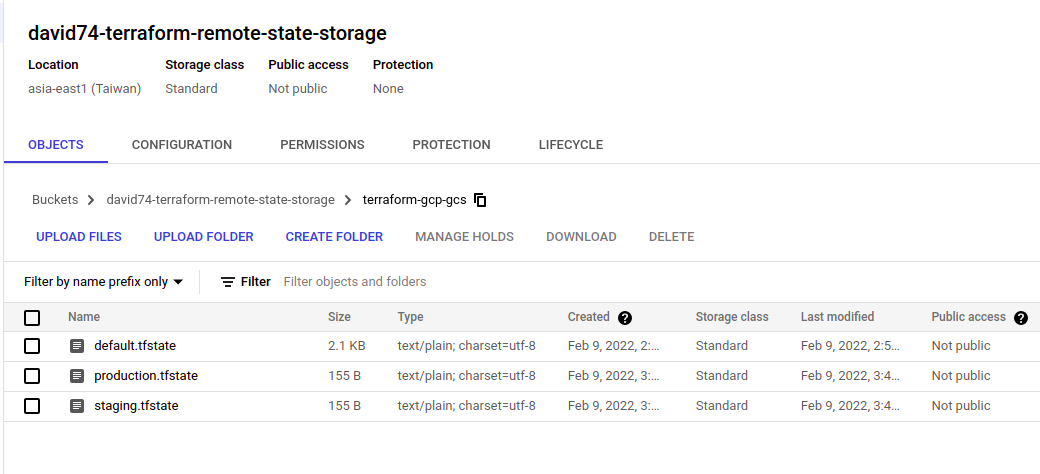
GCS Remote Backend
terraform {
backend "gcs" {
credentials = "~/.gcp/david74-service-account.json"
bucket = "david74-terraform-remote-state-storage"
prefix = "terraform-gcp-gcs"
}
}
GCS Remote Backend
terraform {
backend "gcs" {
bucket = "cresclab-terraform-remote-state-storage"
impersonate_service_account = "terraform@cresclab.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
prefix = "line-workshop-go"
}
}Advanced topics
Terraform module
- Code re-usability
- Self-contained module
- Terraform Registry
provider "aws" { region = "${var.requester_region}" profile = "${var.requester_aws_profile}" } module "vpc_peering" { source = "./vpc-peering" allow_remote_vpc_dns_resolution = "${var.allow_remote_vpc_dns_resolution}" # Requester Data requester_vpc_id = "${var.requester_vpc_id}" # Accepter Data accepter_aws_profile = "${var.accepter_aws_profile}" accepter_region = "${var.accepter_region}" accepter_vpc_id = "${var.accepter_vpc_id}" }
Terraform import
- Bring existing resources under terraform management
resource "google_compute_instance" "vm" {
/* ... */
}$ terraform import google_compute_instance.vm {name}
Terraform State Mircomanagement
Terraform State Mircomanagement
$ terraform state show ADDRESS
$ terraform state mv SRC DEST
$ terraform state rm ADDRESS
Everything as Code,
but how to test?

Terratest is a Go library that makes it easier to write automated tests for your infrastructure code.
Recap
