
Transformation:
XPath and XSLT
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
Tiziana Mancinelli
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

Aims of this CLASSES:
- Investigate the structure of a TEI/XML document
- Transform and visualise our TEI/XML
- Learn basic syntax of XSLT and XPATH
- Create a HTML page to visualise our TEI/XML data
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

Transformation

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform" version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="xhtml"
doctype-system="http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"/>
<xsl:template match="/">
<html>
<head>
<title><xsl:value-of select="//title"/>
written by <xsl:value-of select="//author"/></title>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="title">
<h1>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</h1>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="author">
<p><i>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</i></p>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="stanza">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
<br/>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="line">
<div>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</div>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>An example:
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

XSL (eXtensible Stylesheet Language)
is a styling language for XML.
XSLT stands for XSL Transformations.
FROM XML to DIFFERENT OUTPUT
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

XSL (eXtensible Stylesheet Language)
is a styling language for XML.
Transformations
to DIFFERENT OUTPUT
HTML
epub
XML!
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

Transformation

<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

Xpath interrogates and navigateS XML documents
xslt depends on it
oxygen supports both languages

ONLY ONE SLIDE TO BOTHER YOU WITH HTML

The <html> element is the root element of an HTML page
The <head> element contains meta information about the document
The <title> element specifies a title for the document
The <body> element contains the visible page content
The <h1> element defines a large heading
The <p> element defines a paragraph

...ONE MORE THING!

A web page is always made with more than one language.
When you navigate to a web page on the Internet, the browser is doing a lot of work
In general, the main languages are HTML, CSS, and Javascript
First exercise
Let's make our first transformation with default XSLT within oXygen!
- Open your XML file
- Let's create our first SCENARIO
HOW makes "scenarios"

- click on the tool icon
HOW makes "scenarios"

2. Click on the format you would like to choose (HTML/PDF)
HOW makes "scenarios"

3.

what to do to navigate a xml DOCUMENT and transform ITS elements in something ELSE?
we are going to transform our xml into html

Navigate around the tree, selecting nodes by a variety of criteria

<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

What is XPath?
XPath is a major element in the XSLT standard.
XPath can be used to navigate through elements and attributes in an XML document.
A language to describe how to locate a part of an XML document
Used in many XML-based technologies and tools

<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

How XPath works
In XPath, there are seven kinds of nodes: element, attribute, text, namespace, processing-instruction, comment, and document nodes.
XML documents are treated as trees of nodes. The topmost element of the tree is called the root element.

<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| nodename | Selects all nodes with the name "nodename" |
| / | Selects from the root node |
| // | Selects nodes in the document from the current node that match the selection no matter where they are |
| . | Selects the current node |
| .. | Selects the parent of the current node |
| @ | Selects attributes |
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

| Wildcard | Description |
|---|---|
| * | matches any element node |
| @* | matches any attribute node |
| node() | matches any node |
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

A bare-bones path expression is similar to filesystem addressing: if the path starts with a solidus (/ aka forward slash), then it represents a path from the root; if it does not start with a solidus then it represents a path from here
/TEI/teiHeader/fileDesc/titleStmt/title<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

body
div
div
head
head
lg
lg
lg
lg
lg
lg
TEI/XML structure
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

body
div
div
head
head
lg
lg
lg
lg
lg
lg
TEI/XML structure
/body/div/

Toolbar in oXygen
Let's open the file:
Frankenstein-v1c5-transcription.xml

some xpath
/TEI/teiHeader/fileDesc/titleStmt/respStmt/nameEnsure the box is labelled XPath 2.0 (or XPath 3.0). Then type in
/TEI/teiHeader/fileDesc/titleStmt/respStmt/name

//p
//p// Selects nodes in the document from the current node that match the selection no matter where they are

some xpath
//del/@hand
@ Selects attributes

some xpath
//del[@hand='overwritten']
[ ] square brackets are used to create conditions
Take all the 'del' elements with an attribute 'hand' with value 'overwritten'

some xpath
count(//del[@type='overwritten'])
xpath has function
What is a function?
In programming, a named section of a program that performs a specific task

ancestor
ancestor-or-self
attribute
child
descendant
descendant-or-self
following
following-sibling
namespace
parent
preceding
preceding-sibling
self
axes

axis::node
section/child::title
title/parent::section
The node matched is the one at the end of the path
Syntax

examples

xslt
(eXtensible Stylesheet Language Transformations)
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:tei="http://www.tei-c.org/ns/1.0"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
exclude-result-prefixes="xs"
version="2.0">
<xsl:output method="html"/>
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

Transformation
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <poem> <head>Chapter 7th</head> <author></author> <div type="poem"> <l>It was on a dreary night of Novembe</l> </poem> |
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta/> </head> <body> <h1>Untitled</h1> <p>It was on a dreary night of Novembe</p> </body> </html> |
|---|
XML
HTML

| XML | HTML |
|---|---|
| <TEI> ... <body> <text> <body> </body> </text> </body> </TEI> |
<html> <head> <head> <body> </body> </html> |
xslt
XSL (eXtensible Stylesheet Language) is a styling language for XML. XSLT stands for XSL Transformations.

Make a new file: File >
XML declaration

namespace


XML Namespaces provide a method to avoid element name conflicts.
XML standard way to use two or more XML vocabularies
In XSLT there are at least two vocabularies (can be more):
XSLT
HTML
Namespaces

tei Namespace


<xsl:output/>
<xsl:output method=" HTML ">
The <xsl:output> element defines the format of the output document.

<xsl:template>
The <xsl:template> element is used to build templates.
The match attribute is used to associate a template with an XML element. The match attribute can also be used to define a template for the entire XML document. The value of the match attribute is an XPath expression (i.e. match="/" defines the whole document).

<xsl:template match="node">
[materials to include before node's content]
<xsl:apply-templates/>
[materials to include after node's content]
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="node">
[materials to include before node's content]
<xsl:apply-templates/>
[materials to include after node's content]
</xsl:template> <xsl:template>

<xsl:apply-templates>
- Indicates where to put the node matched by the template
- In
process the node an allits content (other nodes included!)

1 instruction:
Transform the element root <TEI> into <html>
EXERCISE

Add to your xslt the template that matches with your root element:
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>

Add some more instructions:
The element XML <head> into the element HTML <h2>
<xsl:template match="//tei:head">
<h2>
<ins><xsl:apply-templates/></ins>
</h2>
</xsl:template>
HTML tags
The <h1> to <h6> tags are used to define HTML headings.
<ins>...</ins> underline the text:

Add some more instructions:
The element XML <p> into the element HTML <p>
<xsl:template match="//tei:p">
<p><xsl:apply-templates/></p>
</xsl:template>
HTML
The <p> in TEI is the same in HTML <p> > paragraph
You can also use <br/> stands for line break in HTML

Create a scenario with your XSLT!


Create a scenario with your XSLT!


Create a scenario with your XSLT!
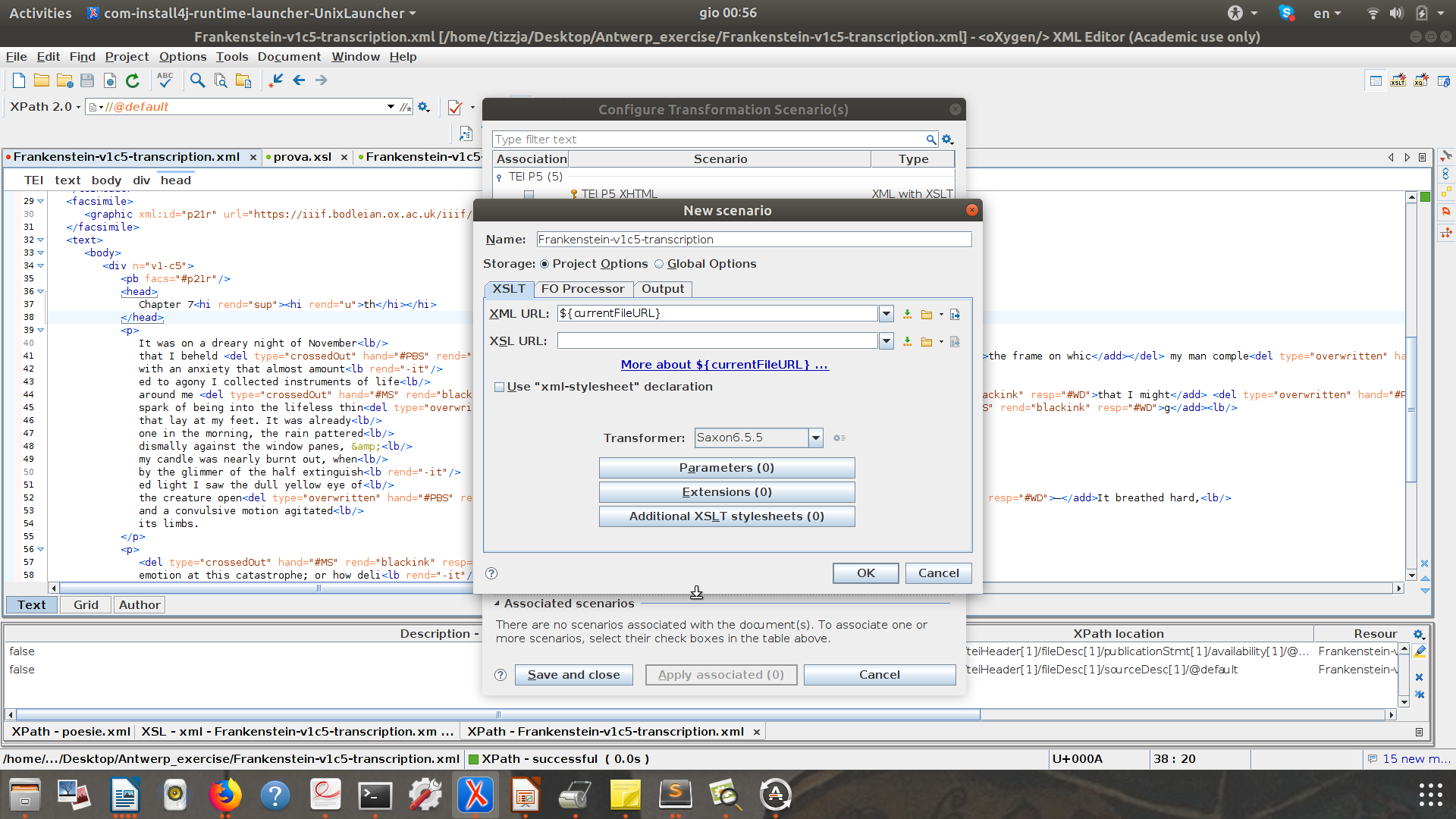

Create a scenario with your XSLT!


Create a scenario with your XSLT!
file XML
file XSLT
SAXON VERSION 9
(software)

Create a scenario with your XSLT!


Create a scenario with your XSLT!


Add some more instructions:
The element XML <lb> into the element HTML <br/>
<xsl:template match="//tei:lb">
<xsl:apply-templates/><br/>
</xsl:template>

Add some more instructions:
The element XML <del> into the element HTML <s>
<xsl:template match="tei:del">
<s><xsl:apply-templates/></s>
</xsl:template>

Add some more instructions:
The element XML <add> into the element HTML <sup/>
<xsl:template match="tei:add">
<sup><xsl:apply-templates/></sup>
</xsl:template>
Add some more instructions:
The element XML <hi> into the element HTML <sup>
<xsl:template match="tei:hi[@rend='sup']">
<sup><xsl:apply-templates/></sup>
</xsl:template>
Add some more instructions:
The element XML <u> into the element HTML <br/>
<xsl:template match="tei:hi[@rend='u']">
<ins><xsl:apply-templates/></ins>
</xsl:template>
add 'Bootstrap' css
- Divide the page in two.
- We are going to use the Bootstrap framework (https://getbootstrap.com/ )
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.3/css/bootstrap.min.css"/>

add 'Bootstrap' css
<xsl:template match="tei:TEI">
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.3/css/bootstrap.min.css"/>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
[....]
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
Handling attributes in XSLT
Attributes in the source (XML)
Attributes in the output (HTML)
Attributes in both source and output

Handling attributes in XSLT
<facsimile>
<graphic url="myImg.gif">myImg.gif</graphic>
</facsimile>
<img>
<xsl:attribute name="src">
<xsl:value-of select=“figure"/>
</xsl:attribute>
</img> HTML
The <img> tag defines an image in an HTML page.
src URL Specifies the URL of an image

<xsl:attribute>
The <xsl:attribute> element replaces existing attributes with equivalent names.
<xsl:attribute name=“ATTRIBUTE”>VALUE
</xsl:attribute>
<img>
<xsl:attribute name=“src”>
<xsl:value-of select=“image”/>
</xsl:attribute>
</img>
<xsl:value-of select="node"/>
The <xsl:value-of> element can be used to extract the value of an XML element and add it to the output stream of the transformation:
<img width="600" height="600">
<xsl:attribute name="src">
<xsl:value-of select="//tei:facsimile/tei:graphic/@url"/>
</xsl:attribute>
</img>
DARIAH tutorial to learn Xpath and Xslt:
https://teach.dariah.eu/course/view.php?id=32§ion=6
W3SCHOOLS
Resources:

Many thanks!
Contacts: @tizmancinelli
tiziana.mancinelli2@unibolo.it