JSON
WEB
TOKENS
By Tommy Marshall
What is JWT
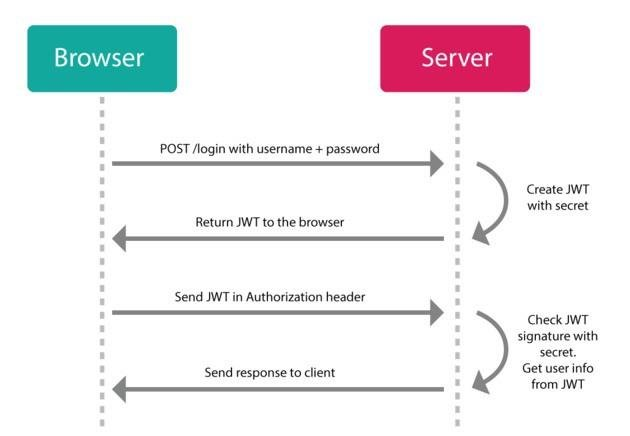
JSON Web Token (JWT) is an open standard (RFC 7519) that defines a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. This information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed. JWTs can be signed using a secret (with the HMAC algorithm) or a public/private key pair using RSA or ECDSA.
(jwt.io)
A standard for signing, sending and receiving tokens to validate something.
(me)

Using Sessions
Using Tokens
What makes up a JSON WEB TOKEN
- Header
- Payload
- Signature
header.payload.signature
xxxxxx.yyyyyy.zzzzzz

HEADER
Consists of two parts: the type of the token, which is JWT, and the signing algorithm being used, such as HMAC SHA256 or RSA.

PAYLOAD
Contains the data which is to be serialized and checked against.

SIGNATURE
A hash which is a serialized string consisting base64 encoded of the previous two parts of the token (headers and payload) and a secret that lives on the server.
DEMO
BENEFITS
- Stateless – No session to manage
- Portable – Same token used across services
- Performance – No extra lookups, just validate the signature
- Decoupled/Decentralized – Auth server to sign tokens, other app/resource servers don't need to auth. Shared sessions across servers is hard!
Drawbacks
- Tokens live forever – Must expire tokens, enforce algorithm.
- Refresh Tokens – Store refresh tokens in DB, delete when used to log in.
- Security – Storing in localStorage, secure XSS. Storing as Cookies, secure CSRF and use httpOnly cookies.
- Security – You have to protect your secret at all costs... or regenerate a new one.
HUGE Drawbacks
- Banned Users – They still have valid tokens!
You're going to need a Database call anyways in case a user's role/permission changes.
Then why?
Using them for services that connect multiple 3rd party services can be useful!
Could we do this?
