Classically Pong
1972

History
- First arcade sports game
- Invented in 1972 by [Allan Alcorn] at Atari
- Home game console plugs into TV


Game Design
- Game objects:
- field
- ball
- 2 players/paddles
- Behavior:
- ball bounces on top and bottom of stage
- a player scores when ball hits opponent's goal
- ball bounces on the player's paddle
- Start game:
- SPACE to start ball at the beginning and after each goal
- End game:
- when first player gets 5 points

Intro to JavaScript Object
- The ball has multiple properties: x, y positions and radius
- Solution: use multiple variables to store the properties
- Better solution: define a [JavaScript object] that groups multiple properties into one variable
- Define properties inside curly braces "{ }", separated by a comma ","
- Put a colon ":" in between each property name:value pair
- Access a property by objectName.propertyName (e.g. ball.x, ball.y)
var ballX = 200;
var ballY = 200;
var ballR = 10;
ellipseMode(RADIUS);
ellipse(ballX, ballY, ballR, ballR);var ball = { // one variable "ball" to store multiple properties
x: 100, // colon in between property name and value
y: 200, // comma after each property name:value
r: 10 // no comma after last property
};
ellipseMode(RADIUS);
ellipse(ball.x, ball.y, ball.r, ball.r);Passing Object to Function
- An object can be passed to a function as one argument
- All object properties can be accessed within the function
- Benefits: easier to manage the data, and clearer code
- Learn more about objects at [KhanAcademy, W3schools]
// Use multiple variables
var ballX = 200;
var ballY = 200;
var ballR = 10;
var drawBall = function (x, y, r) {
noStroke();
fill(255,0,0);
ellipseMode(RADIUS);
ellipse(x, y, r, r);
};
// call function with 3 arguments
drawBall(ballX, ballY, ballR);
// Use object with multiple properties
var ball = {
x: 100,
y: 200,
r: 10
};
var drawBall = function (ball) { // ball object
noStroke();
fill(255,0,0);
ellipseMode(RADIUS);
ellipse(ball.x, ball.y, ball.r, ball.r);
};
// pass 1 object argument with 3 properties
drawBall(ball); 0. Define Game Objects
- Game objects: field, ball, player1 and player2
- Define paddle properties common for both players
// --- Define game objects and their properties
var ball = {
x: width/2, // middle of stage width
y: height/2, // middle of stage height
r: 10,
xVelocity: 0,
yVelocity: 0
};
var player1 = { // left paddle
x: 30,
y: height/2,
score: 0
};
var player2 = { // right paddle
x: width-30,
y: height/2,
score: 0
};
var paddle = { // shared by players
h: 30, // paddle height
w: 7, // paddle width
speed: 6
};
1a. DrawPlaying Field
- Define var YELLOW as a global color constant for later use
- Set global draw modes rectMode(RADIUS) & ellipseMode(RADIUS)
- Define functions drawField()
- Define draw() and call drawField() inside it
var YELLOW = color(255,255,0); // global color constant
rectMode(RADIUS); // global draw modes
ellipseMode(RADIUS);
var drawField = function () {
var x = width/2;
var y = height/2;
background(27, 97, 41); // green background
stroke(245, 240, 240); // white color for lines
strokeWeight(4);
line(x, 0, x, height); // vertical midline
noFill();
ellipse(x, y, 20, 20); // small circle
ellipse(x, y, 100, 100); // large circle
rect(x, y, 195, 195); // bounding rectangle
};
var draw = function () { // the Animation "Loop"
drawField();
};
1b. Display Scores
- Define function drawScores() to display the scores
- Call drawScores() inside draw(), after drawField() (why after?)
var YELLOW = color(255,255,0); // global color constant
var drawField = function () { ... };
var drawScores = function() {
var offset = 50;
textAlign(CENTER);
fill(YELLOW); // text color
textSize(30);
text(player1.score, width/2 - offset, offset);
text(player2.score, width/2 + offset, offset);
};
var draw = function () { // the Animation "Loop"
drawField();
drawScores(); // add
};
2. Draw Ball and Paddles
- Define functions drawBall() and drawPaddles()
- Call drawBall() and drawPaddles() inside draw(), after drawField()
var drawBall = function () {
noStroke();
fill(255, 0, 0);
ellipse(ball.__, ball.__, ball.__, ball.__);
};
var drawPaddles = function () {
noStroke();
fill(YELLOW);
rect(player1.__, player1.__, paddle.__, paddle.__, 10);
rect(player2.__, player2.__, paddle.__, paddle.__, 10);
};
// The Animation "Loop"
var draw = function () {
drawField();
drawScores();
drawPaddles(); // add
drawBall(); // add
};
3. Multi-key Keyboard Input
- Type the code below into your program
- Understand how to use it to check for key presses
- It's OK to NOT understand how it works at this time
- For more info, see [keyPress() and keyRelease()]
// --- Define keycode constants
var KEY_W = "W".charCodeAt();
var KEY_S = "S".charCodeAt();
// -------------- Functions -----------------------------------
// Functions to capture multiple key presses at the same time.
// usage example:
// if (keys[UP]) { // arrow keycodes: UP, DOWN, LEFT, RIGHT
// ...
// }
var keys = []; // array of keys pressed
var keyPressed = function () {
keys[keyCode] = true; // set to true when key with keycode is pressed
};
var keyReleased = function () {
keys[keyCode] = false; // set to false when key with keycode is released
};
4. Move Players with Keyboard
- Create movePaddles() to control the paddles w/keyboard inputs
- Call movePaddles() inside draw() and test moving them
var movePaddles = function () {
// W,S keys controls player1
if (keys[KEY_W]) {
player1.y = player1.y - paddle.speed;
}
if (keys[KEY_S]) {
player1.y = player1.y + paddle.speed;
}
// UP, DOWN keys controls player2
if (keys[UP]) {
player2.y = _________ ;
}
if (keys[DOWN]) {
player2.y = _________ ;
}
};
var draw = function () {
drawField();
drawPaddles();
drawBall();
movePaddles(); // add
};5. Keep Paddles inside Field
- Use built-in library functions min() and max() to simplify code
- max(a,b) return a if a > b, else return b
- min(a,b) return a if a < b, else return b
var movePaddles = function () {
// W,S keys controls player1
if (keys[KEY_W]) {
player1.y = max(player1.y - paddle.speed, paddle.h);
}
if (keys[KEY_S]) {
player1.y = min( ______ , _____);
}
// UP, DOWN keys controls player2
if (keys[UP]) {
player2.y = max( ______ , _____);
}
if (keys[DOWN]) {
player2.y = min( ______ , _____);
}
};
var draw = function () {
drawField();
drawPaddles();
drawBall();
movePaddles(); // add
};
6. Game State
- The game can be in one of three states:
- paused - at the start or middle of the game, ball does not move, display help message
- active - ball in motion
- game over - end of game, ball does not move, display winner
- Define global constants and a variable for the game state
// --- Define global game state constants
var GAME_PAUSED = 1;
var GAME_ACTIVE = 2;
var GAME_OVER = 3;
var gameState = GAME_PAUSED; // starting state

7. Reset Ball & Game State
- Define resetBall() to reset ball position and velocity, player positions, and set gameState to GAME_PAUSED
- Call resetBall() outside of the draw() function
// initialize ball and player positions, and game state
var resetBall = function () {
ball.x = 200;
ball.y = 200;
ball.xVelocity = 1.5 + random(0,1); // random initial velocity
ball.yVelocity = 2 + random(0,1);
player1.y = 200;
player2.y = 200;
gameState = GAME_PAUSED; // pause game
};
var draw = function () { ... };
resetBall(); // initialize outside draw()8. Move Ball & Check Boundaries
- Move ball by changing the ball's x by xVelocity and y by yVelocity
- Check for goal and increase score for the appropriate player
- Reset ball and pause game after each score
- Check against top and bottom boundaries
var moveBallAndCheckBoundaries = function () {
// move ball
ball.x += _________;
ball.y += _________;
// Check for Goal
if (ball.x < ball.r) { // left boundary
_______.score += 1;
resetBall();
} else if (ball.x > width - ______) { // right boundary
_______.score += 1;
resetBall();
}
// Bounce the ball against the top and bottom boundaries (Y coordinates)
if (ball.y < ______ || ball.y > _______ ) {
ball.yVelocity = _____________; // reverse Y direction
}
};
9. Move Ball if Game is Active
- Define showMessage() to display a help message or a winner's message depending on the game state
var showMessage = function () {
textSize(22);
fill(YELLOW); // text color
if (gameState === GAME_PAUSED) {
text("W, A UP, DOWN", 200, 300);
text("left paddle right paddle", 200, 330);
text("SPACE to start!", 200, 370);
} else if (gameState === GAME_OVER) {
if (player1.score > player2.score) {
text("Player 1 Wins!", 100, 80);
} else {
text("Player 2 wins!", 300, 80);
}
text("SPACE to restart!", 200, 350);
}
};- In draw(), call moveBalland-CheckBoundaries() if game is active, else call showMessage()
var draw = function() {
...
if (gameState === GAME_ACTIVE) {
moveBallAndCheckBoundaries();
} else {
showMessage();
}
};

10. Continue or End Game
- Check key input for SPACE, set game state to active is game is paused; if game is over, set to active and reset scores to 0
- Game is over when the first player scores 3 points
var draw = function() {
...
if (gameState === GAME_ACTIVE) {
moveBallAndCheckBoundaries();
} else {
showMessage();
}
if (keys[32]) { // keycode=32 for SPACE
if (gameState === GAME_PAUSED) {
gameState = GAME_ACTIVE;
} else if (gameState === GAME_OVER) {
gameState = GAME_ACTIVE;
player1.score = 0; // clear scores
player2.score = 0;
}
}
// Check scores for end of game
if (player1.score === 3 || player2.score === 3) {
gameState = GAME_OVER;
}
};

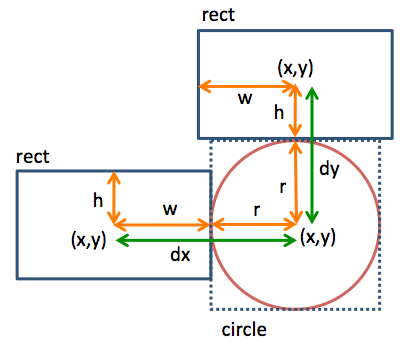
11. Detect Collision: Player & Ball
- Define
playerHitsBall(player, ball) to detect collision between a player and the ball; returns true if they collide, else return false
- Recall that rectMode(RADIUS) & ellipseMode(RADIUS) are in use
- Built-in function abs(number) returns the absolute value of number
- dx = absolute value of the distance between the x coordinates of the 2 objects
- dy = absolute value of the distance between the y coordinates of the 2 objects
- Objects collide when dx < paddle.w + ball.r and dy < paddle.h + ball.r
var playerHitsBall = function (player, ball) {
var dx = abs(ball.x - player.x);
var dy = abs(ball.y - player.y);
return dx < (paddle.w + ball.r) &&
dy < (paddle.h + ball.r) ;
};
Type in the code and proceed.
Review later if you do not understand
12. Bounce on Paddles
- Define bounceOnPaddles() to check collision between the ball and each of the two paddles
- If collide, reverse direction
- Call bounceOnPaddles() inside draw()
var bounceOnPaddles = function () {
// check for collision with player1
if (playerHitsBall(player1, ball)) {
ball._______ = -(ball.________); // reverse direction
}
// check for collision with player2
if (playerHitsBall(player2, ball)) {
ball._______ = -(ball.________); // reverse direction
}
};
var draw = function() {
...
movePaddles();
bounceOnPaddles(); // add
...
};
Please enter Classically Pong for Exercise Name