Content Security Policies and you
Content Security Policies you thought you knew
Content Security Policies are actually complicated, OMG why isn't this working :(
What will we cover?
- What is a CSP?
- How do they work?
- Questions
?
What is a CSP?
(and some history)
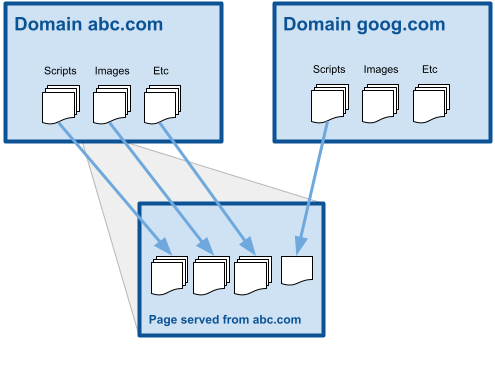
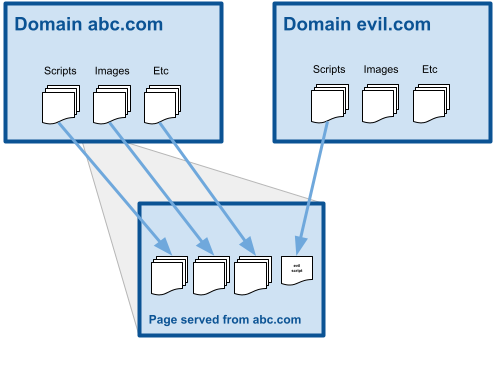
Simply put, they are a standardized set of directives for browsers, used to declare approved content origins for a web page.
- Protection against XSS and other attacks
- Provides control over how a web page can interact with content from other domains
- Reporting mechanism for violations
Before CSP
CSP X


X-CONTENT-SECURITY-POLICY/ X-WEBKIT-CSP (est 2011)
CSP X
X-CONTENT-SECURITY-POLICY/ X-WEBKIT-CSP (est 2011)


- First added in 2011 by Firefox (Gecko 2)
- "Adopted" by other browsers soon after, inconsistent experimental headers with inconsistent features
- Only CSP support available in IE
CSP 1.0
CONTENT-SECURITY-POLICY (est 2013)


CSP 1.0
CONTENT-SECURITY-POLICY (est 2013)


- WC3 published standard in 2012
- Introduced standard CONTENT-SECURITY-POLICY header
-
Currently supported by all major browsers
- Defined initial set of standard policy directives*
*some of which have since changed or have different behavior
CSP 2.0
CONTENT-SECURITY-POLICY (est 2015)


- Introduced several new directives for other types of content, as well as some frame specific ones
- Adds 'nonce' and 'hash/sha256' directive values
- Added reporting capabilities
- Adopted by all major browsers (partially)! (FF, Edge)
a.k.a. Level 2
CSP 3.0
CONTENT-SECURITY-POLICY (est 2017)


- Still technically in Working Draft but mostly complete
- Partially adopted by all current evergreen browsers
- Not yet supported in Safari (only in canary)
- Adds 'strict-dynamic' directive value
a.k.a. Level 3
Parts of a CSP
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self' https://goog.com;
{ }{ }{ }Header name
Directive
Directive values
- Only one CSP header is allowed per request
- All directives are defined in that header, delimited with semicolons
- First directive parsed for a type is used, duplicates are ignored (i.e. script-src https://host1.com; script-src https://host2.com )
- Only keywords can have quotes (i.e. 'none', 'self', etc)
Directives
Content
img-src style-src font-src script-src
object-src media-src plugin-types prefetch-src
URI
frame-src connect-src
child-src frame-ancestors base-uri form-action
worker-src manifest-src
Behavior
default-src report-uri sandbox
report-to navigate-to
Directive Values
Keywords
'none' 'self' 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval'
'nonce-' 'sha256-'
'strict-dynamic' 'unsafe-hashes'
Scheme source
http: https: data: blob: filesystem:
Host source
http://*.goog.com mail.goog.com:443 https://goog.com *.goog.com *
Reporting
-
There is also a Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only header that can be used for reporting instead of blocking violations
-
The 'report-uri' and 'report-to'* directives allow the inclusion of an endpoint to POST violations to
*'report-to' is used in conjunction with the 'Reporting-Endpoints' header, which can define endpoints as variables to be used in other headers
// example report
{
"csp-report": {
"document-uri": "http://example.org/page.html",
"referrer": "http://evil.example.com/",
"blocked-uri": "http://evil.example.com/evil.js",
"violated-directive": "script-src 'self' https://apis.google.com",
"original-policy": "script-src 'self' https://apis.google.com; report-uri http://example.org/my_amazing_csp_report_parser"
}
}Reporting allows you to monitor and adjust your CSP based on actual user experience
Fun facts!
-
The CSP can also be set as a meta tag
-
You can use CONTENT-SECURITY-POLICY-REPORT-ONLY header in tandem to test new directives without breaking your site!
-
Most directives* use a fallback strategy, ultimately falling back to 'default-src' directive values
*excluding base-uri, form-action, frame-ancestors, plugin-types, report-uri, sandbox - be sure to set these explicitly!
-
Obviously new directive values not recognized by agents using previous versions, but some old values are ignored when certain new values are present. (more on that later)
How do they work?


Page is served with CSP header and begins parsing HTML including bad script
Page is served with CSP header and begins parsing HTML including bad script


Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'none'; script-src 'self' *.goog.com; img-src 'self'; style-src 'self';CSP is parsed by user agent at page load
Refused to load the script 'evil-script.js' because it violates the following Content Security Policy directive: "script-src".
If script origin is not included in approved hosts, loading is blocked, and an error is thrown
The core concept is pretty simple!
for simple cases...
Complications arise with third parties...


ADOOBEEEEE!!!
How can we safely allow 'unsafe-inline'?
- Don't do it?
- Use a 'nonce'
- Use a hash 'sha256'
- Use 'strict-dynamic'
- Get a job at Adobe, work your way onto the analytics team. Fix the offending script that requires 'unsafe-inline' from the inside, ship it, then immediately quit because it's Adobe
What is a Nonce?
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'nonce-r@nd0m' 'self' *.goog.com;<script nonce="r@nd0m">
doWhatever();
</script>A nonce is a randomly generated value used by the browser to authenticate elements (not limited to script tags) before parsing
- Generated server-side, must be added to any element of the directive type
- All or nothing, nonce attribute must be present or it will be refused
What is a Hash?
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'sha256-RFWPLDbv2BY+rCkDzsE+0fr8ylGr2R2faWMhq4lfEQc=' 'self' *.goog.com;<script>
doWhatever();
</script>A hash is a value generated using the element contents and is used by the browser to authenticate specific elements (not limited to script tags) before parsing
- Generated server-side must include a hash for any inline content for it to work
- Not very flexible, hard to account for unknown entities
What is Strict Dynamic?
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'nonce-r@nd0m' 'strict-dynamic' 'self' *.goog.com;// trusted-script.js
var s = document.createElement('script');
s.text = "doSomething();";
document.body.appendChild(s);Strict Dynamic is a level 3 directive value that permits scripts that have been safely loaded to perform or load inline scripts
- Not widely supported yet, only in Chrome and FF
- Still requires a nonce for initial third party script loading
<script src="https://goog.com/trusted-script.js" nonce="r@nd0m"></script>Remember the bit about ignoring directive values?
- When `strict-dynamic` is present, ‘unsafe-inline’, ‘unsafe-eval’, and ‘self’ are ignored, as well as http: and https: host based source lists.
- When `nonce-{random}` is present, ‘unsafe-inline’ and ‘unsafe-eval’ are ignored by browsers with Level 2 support
- This actually can be leveraged to create backwards compatible directives (albeit in a complicated manner)
Questions?
CSP Links and resources will be included with the recording email