Neurological phenotypes among
COVID-19 positive cases
Neurological complications can worsen outcome among hospitalized COVID-19 patients, though the prevalence of neurological phenotypes across geographically diverse populations warrants evaluation.
To examine the prevalence of neurological conditions among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in multi-national populations.
Importance and objective
- 35,177 COVID-19 patients
- 348 hospitals
- 6 countries
- 3 continents
- January 2020 - early September 2020
- PHASE 1.1
EHR data of a multi-national, geographically diverse population
Hospitalized patients with positive SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test, both with and without severe COVID-19 disease.
Exposures
Define "severity"
| Severe Illness Category | Clinical Events |
|---|---|
| Diagnoses | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Ventilator-associated pneumonia |
| Procedures | Insertion of endotracheal tube; invasive mechanical ventilation |
| Laboratory results | PaCO2, PaO2 |
| Medications | General anesthetics; benzodiazepine derivatives; muscle relaxants; other hypnotics and sedatives; adrenergic and dopaminergic agents; other cardiac stimulants; other respiratory system products; phosphodiesterase inhibitors; platelet aggregation inhibitors excluding heparin; |
Meet at least one of the clinical events
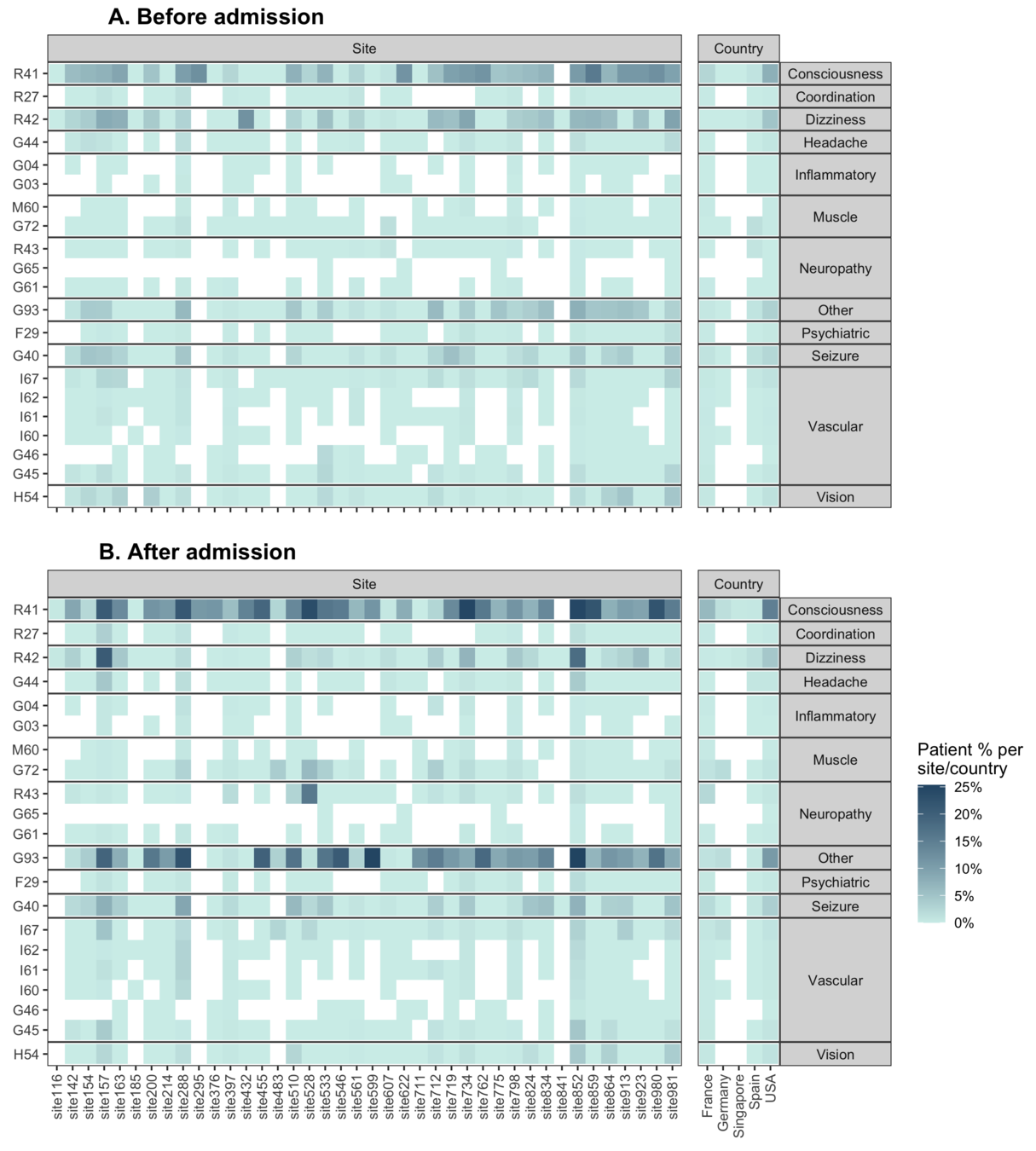
Frequency of each disease category and 3-digit International Classification of Disease (ICD) code of neurological diseases by countries, sites, time before and after admission for COVID-19 related hospitalization, and COVID-19 severity.
Outcomes
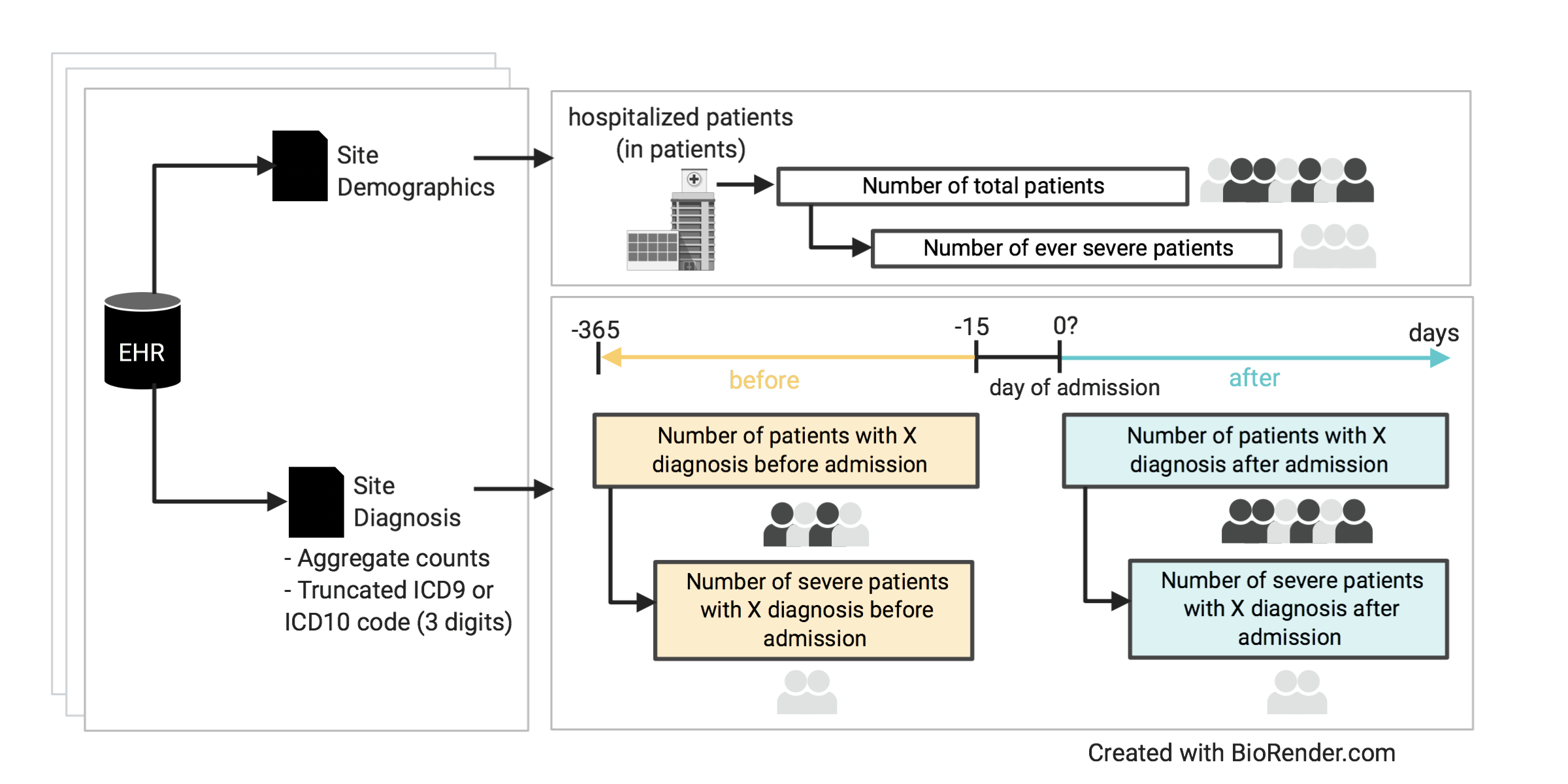
Workflow
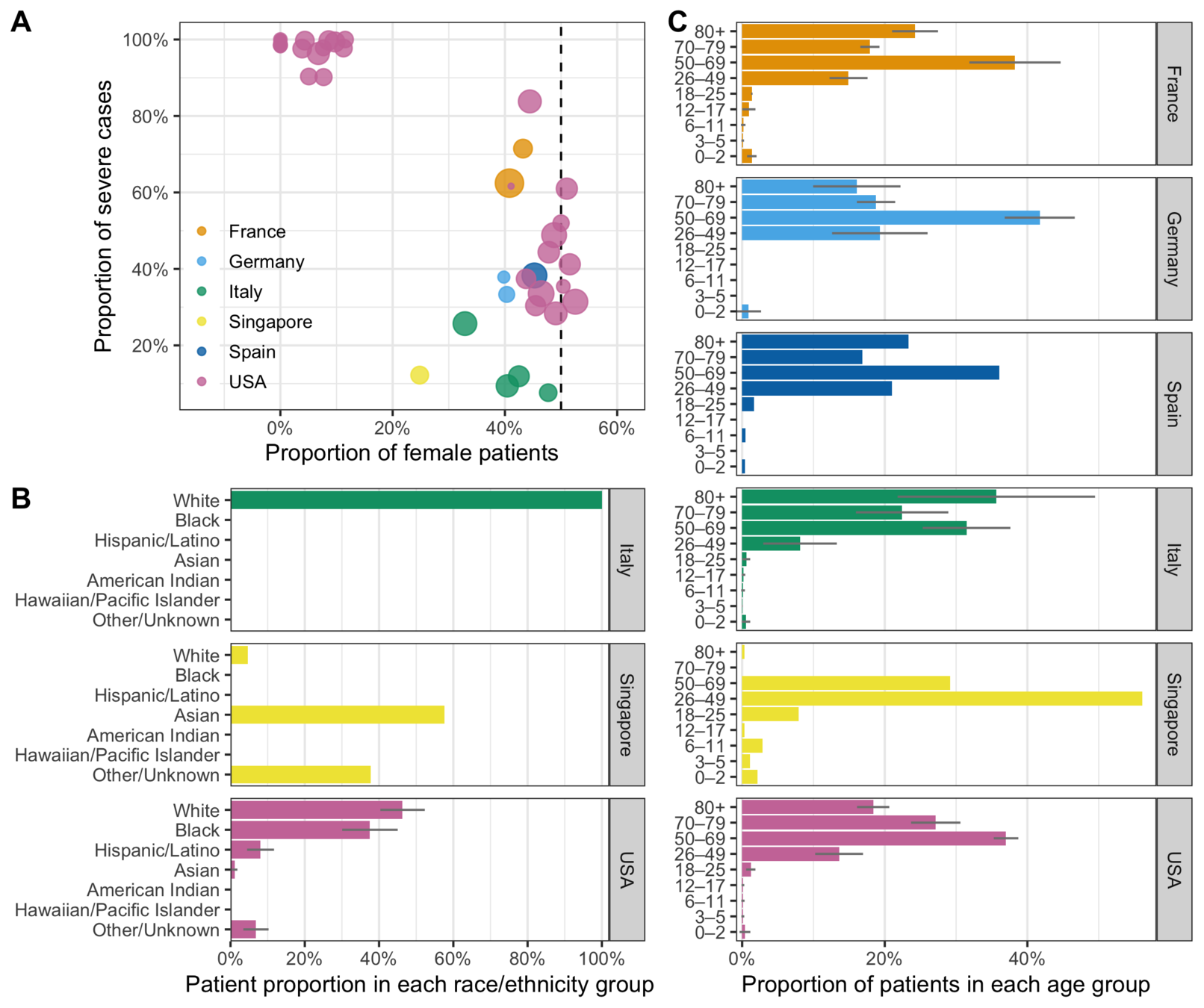
34,647 patient characteristics
Is there a difference in prevalence of ICD-10 codes between before and after admission?

(X, Y)

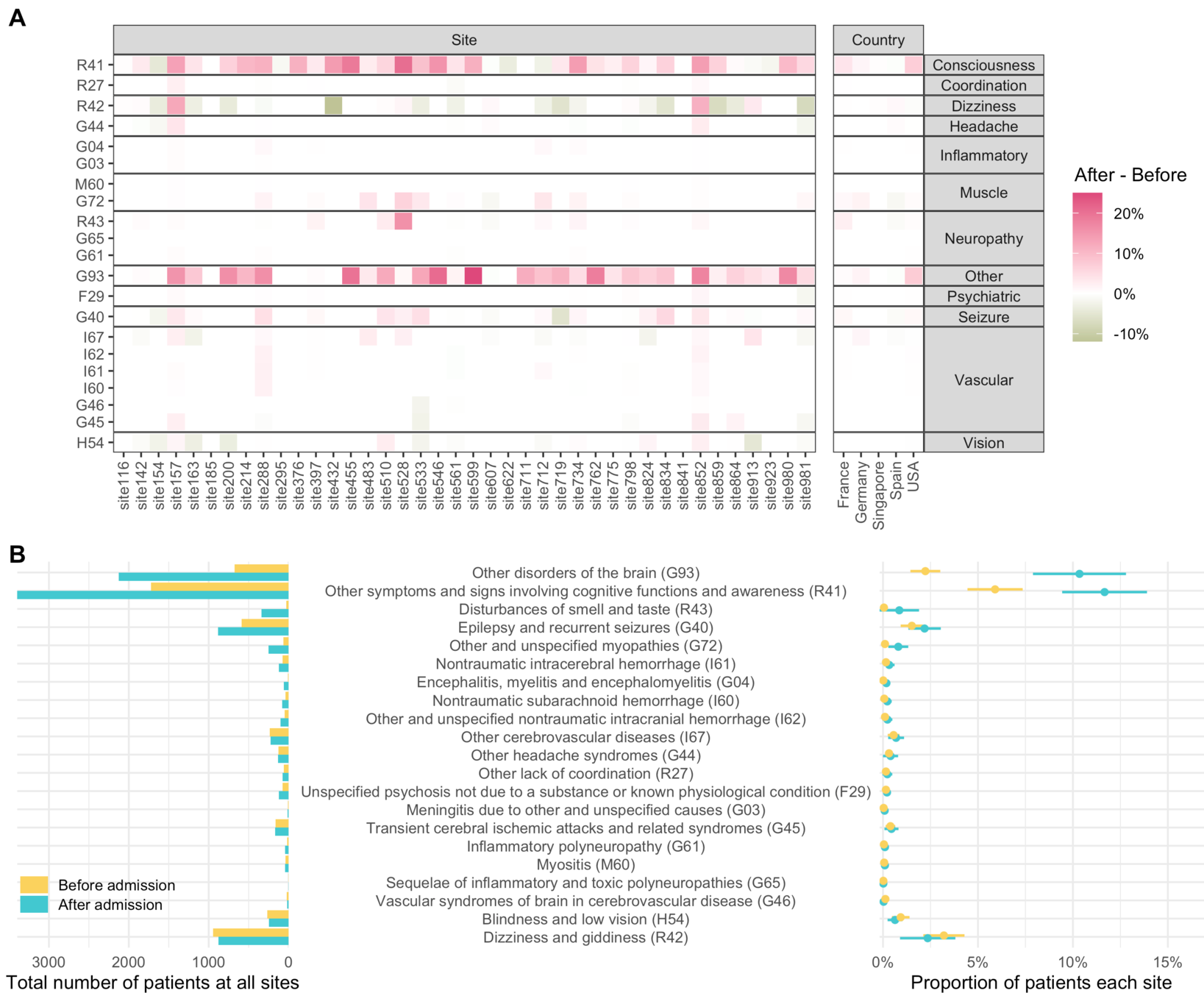
Do sites that report more neurological code X
report more severe cases or more never severe cases?
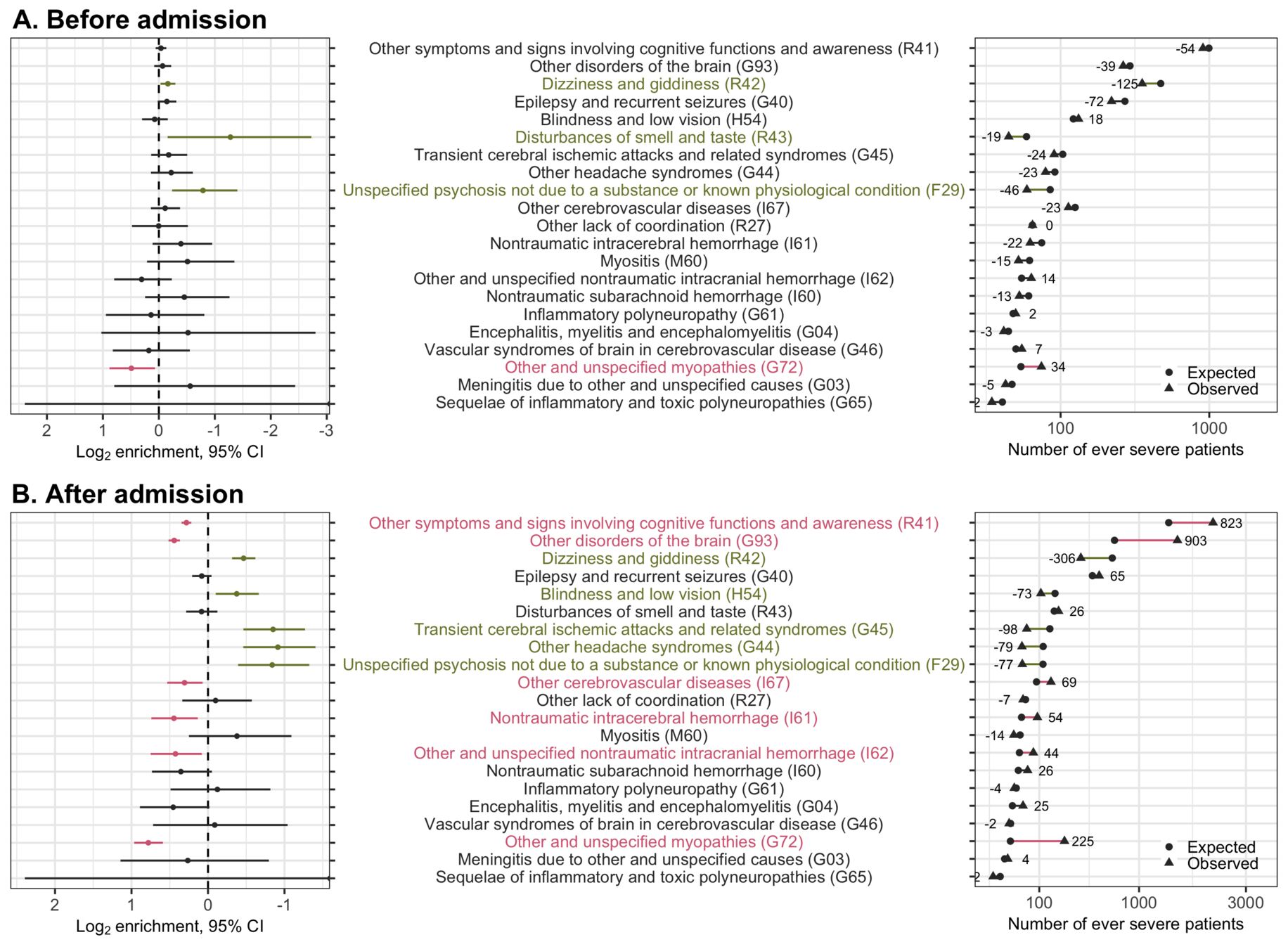
During COVID-19-related hospitalization, severe patients had more neurological diagnoses than those without severe disease.
- 1.22 times more disorders of consciousness (95% CI: 1.16-1.27)
- 1.24 times more other cerebrovascular diseases (95% CI: 1.05-1.45)
- 1.36 times more nontraumatic intracerebral / intracranial hemorrhage (95% CI: 1.10-1.67)
- 1.72 times more myopathy (95% CI: 1.51-1.95)
Key findings
to paper