Simulated Annealing
因為講師被roychuang嗆所以聽不懂請去找隔壁電研的電神
ROYCHUANG
因為今天講師比較弱,所以如果出事可以看上屆簡報
P
P是什
P是什
Polynomial
P是什
Polynomial
Run time of algorithms
P是什
Polynomial
Run time of algorithms
P是什
Polynomial
Run time of algorithms
a large constant k, is the upperbound for all P algorithms
Time complexity
REVIEW
Binary Search
Binary Search
Binary Search
| 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 14 | 19 | 198 | 1000 | 1234 | 9999 |
|---|
find 1234?
Binary Search
| 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 14 | 19 | 198 | 1000 | 1234 | 9999 |
|---|
find 1234?
Binary Search
| 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 14 | 19 | 198 | 1000 | 1234 | 9999 |
|---|
find 1234?
Binary Search
| 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 14 | 19 | 198 | 1000 | 1234 | 9999 |
|---|
find 1234?
Binary Search
After each operation:
Search space / 2
Binary Search
After each operation:
Search space / 2
Binary Search
After each operation:
Search space / 2
Binary Search
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
random_device rd;
mt19937 rng(rd());
uniform_int_distribution<int> k(1, 114514);
int arr[10];
for (int i=0; i < 10; i++)
arr[i] = k(rng);
int j = *arr;
for (int &x : arr)
cout << x << ' ';
cout << '\n';
sort(arr, arr+10);
for (int &x : arr)
cout << x << ' ';
cout << '\n';
int l = 0, r = 10;
while (l < r)
{
int m = (l + r) / 2;
if (arr[m] > j)
r = m;
else if (arr[m] < j)
l = m+1;
else
{
cout << m;
_exit(0);
}
}
}Selection sort
Selection sort
| 4771 | 8451 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 4771 | 8451 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 4771 | 8451 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 4771 | 8451 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 4771 | 8451 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 4771 | 8451 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 4771 | 8451 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 4771 | 8451 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 4771 | 8451 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 4771 | 8451 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 4771 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 4771 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 4771 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 4771 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 4771 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 4771 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 4771 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 4771 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 4771 | 3010 | 6990 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 3010 | 4771 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 3010 | 4771 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 3010 | 4771 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 3010 | 4771 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 3010 | 4771 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 3010 | 4771 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 3010 | 4771 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 3010 | 4771 | 6020 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 3010 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 4514 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 3010 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 3010 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 3010 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 3010 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 1234 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 3010 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 1234 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 1234 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 1234 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 1234 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 1234 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 1234 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 810 | 11 | 1234 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 1234 | 11 | 810 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 1234 | 11 | 810 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 1234 | 810 | 11 |
|---|
Selection sort
| 8451 | 6990 | 6020 | 4771 | 4514 | 3010 | 1919 | 1234 | 810 | 11 |
|---|
Selection sort
Each element takes
Selection sort
Each element takes
Selection sort
Each element takes
Selection sort
Each element takes
Selection sort
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
random_device rd;
mt19937 rng(rd());
uniform_int_distribution<int> k(1, 114514);
int arr[10];
for (int i=0; i < 10; i++)
arr[i] = k(rng);
for (int &x : arr)
cout << x << ' ';
cout << '\n';
for (int i=0, k=0; i < 10; k = ++i)
{
for (int j=i+1; j < 10; j++)
k = (arr[j] > arr[k]? j : k);
swap(arr[i], arr[k]);
}
for (int &x : arr)
cout << x << ' ';
}NP
NP是什
NP是什
non-deterministic polynomial
NP是什
non-deterministic polynomial
Chessboard & Queen
Chessboard & Queen
Chessboard & Queen
講師自覺虧欠無法模擬請看code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector <vector <char>> saves(8, vector <char> (8));
unordered_map <int, int> pieces;
int ans = 0;
bool check_valid(int y, int x) {
if(saves[y][x] != '*') {
for (int i=0; i < y; i++) {
if (pieces[i] - x == i - y)
return false;
if (pieces[i] == x)
return false;
if (pieces[i] + i == x + y)
return false;
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
void solution(int row) {
if (row == 8) {
ans++;
return;
}
for (int i=0; i < 8; i++) {
if (!check_valid(row, i))
continue;
pieces[row] = i;
solution(row + 1);
pieces.erase(row);
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
for (int i=0; i < 8; i++)
for (auto &x : saves[i])
cin >> x;
solution(0);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}Knight's tour
Knight's tour
講師自覺虧欠無法模擬請看code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
static int dy[8] = {1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1};
static int dx[8] = {-2, -1, 1, 2, -2, -1, 1, 2};
static int grid[8][8];
bool notoutofbound(int i, int j)
{
return i >= 0 && i < 8 && j >= 0 && j < 8;
}
int degree(int i, int j)
{
int cnt = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 8; ++k)
{
int row = i + dy[k], col = j + dx[k];
if (notoutofbound(row, col) && grid[row][col] == 0)
++cnt;
}
return cnt;
}
void backtrack(int i, int j, int cnt)
{
if (cnt == 64)
{
for (int i=0; i < 8; ++i)
for (int j=0; j < 8; ++j)
cout << grid[i][j] << " \n"[j == 7];
exit(0);
}
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> candidate;
for (int v=0; v < 8; ++v)
{
int row = i + dy[v], col = j + dx[v];
if (notoutofbound(row, col) && grid[row][col] == 0)
candidate.emplace_back(degree(row, col), row, col);
}
sort(candidate.begin(), candidate.end());
++cnt;
for (auto &[c, a, b] : candidate)
{
grid[a][b] = cnt;
backtrack(a, b, cnt);
grid[a][b] = 0;
}
}
int main()
{
int y, x; cin >> y >> x;
grid[--x][--y] = 1;
backtrack(x, y, 1);
}如果不理解上面code
你該來聽枚舉演算法小社課
如果不理解上面code
你該來聽枚舉演算法小社課
sun-tzu
Preserve Framework
Preserve Framework
constant_search(arr, n, k)
j = choice()
if (k == arr[j])
return j
else
return 0
P & NP
P & NP
P
NP
P & NP
1.NP - verification in P
2.P - problems solvable in polynomial time
P
NP
Monte Carlo Algorithms
Monte Carlo Algorithms是什
Monte Carlo Algorithms是什
Fixed runtime
Might not produce correct answer
Monte Carlo Algorithms是什
Simulated Annealing
Genetic Algorithm
Monte Carlo Algorithms是什
補充: Las Vegas algorithms
Monte Carlo Algorithms是什
補充: Las Vegas algorithms是什
produce correct answers, runtime varies
Monte Carlo Algorithms是什
補充: Las Vegas algorithms是什
produce correct answers, runtime varies
like quicksort
Simulated Annealing
Simulated Annealing
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
when exact methods are impractical
==唬爛
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
greedy (constructive)
hill climbing (local search)
2-opt swap (local search)
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
Meta是什
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
Meta是什
facebook
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
Meta是什
-high level idea
-utilize heuristics
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
Meta是什
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
Meta是什
要解決什問題
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
Meta是什
要解決什問題
-when search space is complex or large
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Heuristic是什
Meta是什
要解決什問題
Simulated Annealing
Meta heuristic
Simulated Annealing
IDEA
Simulated Annealing
IDEA
Simulated Annealing
IDEA
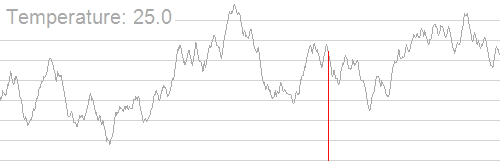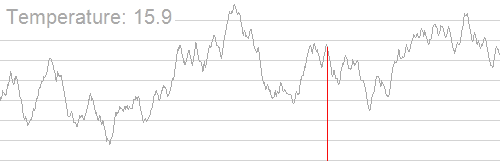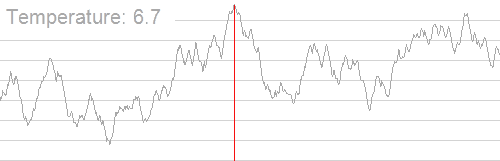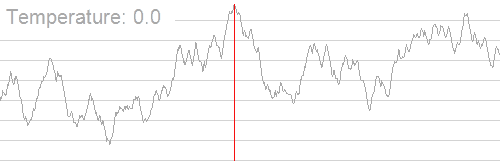
Simulated Annealing
STEPS
Simulated Annealing
STEPS
1. Set Temp, cooling rate
Simulated Annealing
STEPS
1. Set Temp, cooling rate
2. Start the cooling process
Simulated Annealing
STEPS
1. Set Temp, cooling rate
2. Start the cooling process
3. Accept Probability decrease
Simulated Annealing
STEPS
1. Set Temp, cooling rate
2. Start the cooling process
3. Accept Probability decrease
4. => stop the search
Simulated Annealing
Rice
Simulated Annealing
Rice

Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
在講什
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
在講什
A salesman is traveling around
He wants to visit all cities exactly once
He returns to his starting city
There is a cost from one city to another
find minimum cost
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
簡單來說就是
Given a weighted, complete, undirected graph
Find a minimum cost hamiltonian cycle
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
Time complexity
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
Time complexity
Bruteforce
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
Time complexity
Bruteforce
DP
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
Time complexity
n > 20 卡常
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
Time complexity
SA
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
| DIST | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| C | 7 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
| DIST | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| C | 7 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
A
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
| DIST | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| C | 7 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
A
B
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
| DIST | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| C | 7 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
A
B
C
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
| DIST | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| C | 7 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
A
B
C
D
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
| DIST | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| C | 7 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
A
B
C
D
E
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
| DIST | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| C | 7 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
A
B
C
D
E
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
| DIST | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| C | 7 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
A
B
C
D
E
3 + 9 + 2 + 7 + 2 = 23
Optimal?
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
| DIST | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| C | 7 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
A
B
C
D
E
idk
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
| DIST | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| C | 7 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| E | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
A
B
C
D
E
退火試試
Simulated Annealing
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> grid;
vector<int> min_tour;
int minc = 1e9 + 114514 + 1919810;
int cost(vector<int> &tour, int a, int b)
{
return grid[tour[a]][tour[b]];
}
void sa(vector<vector<int>> g, int n, double temp, double rate)
{
random_device rd;
mt19937 rng(rd());
uniform_int_distribution<int> picknode(0, n-1);
vector<int> prev;
for (int i=0; i < n; i++)
prev.push_back(i);
shuffle(prev.begin(), prev.end(), rng);
int prevc = g[prev.back()][prev[0]];
for (int i=1; i < prev.size(); i++)
prevc += g[prev[i-1]][prev[i]];
while ( (temp *= rate )> 1.919810)
{
int i = picknode(rng), j = picknode(rng);
if (abs(i-j) < 3) continue;
if (i > j) swap(i, j);
int curc = prevc;
// ~ a i b ~ c j d ~
int a = (i-1+n)%n, b = (i+1+n)%n, c = (j-1+n)%n, d = (j+1+n)%n;
curc -= (cost(prev, a, i) + cost(prev, i, b) + cost(prev, c, j) + cost(prev, j, d));
curc += (cost(prev, a, j) + cost(prev, j, b) + cost(prev, c, i) + cost(prev, i, d));
int delta = curc - prevc;
if (delta <= 0 || exp((double)-delta/temp) > uniform_real_distribution<double>(0, 1)(rng))
swap(prev[i], prev[j]), prevc = curc;
if (prevc < minc)
min_tour = prev, minc = prevc;
}
}
int main()
{
double temp = 1e3;
double rate = 0.80632090761 * 1.234;
int n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
grid.resize(n);
for (auto &x : grid)
x.resize(n);
random_device rs;
mt19937 rg(rs());
uniform_int_distribution<int> gr(1,234);
for (int i=0; i < n; i++)
for (int j=0; j < n; j++)
grid[i][j] = (i == j? 0 : gr(rg));
for (int i=0; i < n; i++)
for (int j=0; j < n; j++)
cerr << grid[i][j] << " \n"[j == n-1];
cout << "------------------------------------------\n";
while (q--)
{
cout << q+1 << "th query\n" << "============================" << '\n';
sa(grid, n, temp, rate);
cout << minc << '\n';
for (int &x : min_tour)
cout << x << " \n"[x == min_tour.back()];
}
}