(Async) Stack Traces
What should you know about


True Story
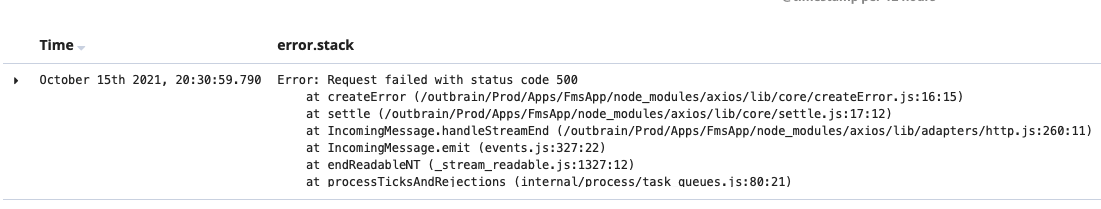

What is Stack Trace?
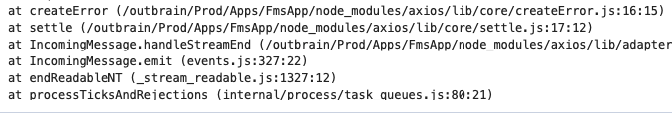

How to print a Stack Trace?
//option 1
console.log(new Error().stack);
//option 2
try {
throw new Error();
} catch (e) {
console.log(e.stack)
}
//option 3
console.trace();
try {
//don't do it!
throw 'error!'
} catch (e) {
console.log(e.stack);
}
//don't do it!
try {
throw 'error!'
} catch (e) {
console.log(e.stack);
}

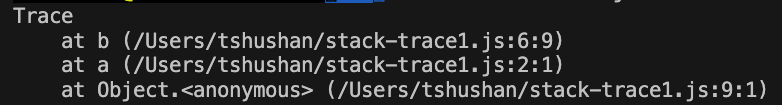
Example
function a() {
b();
}
function b() {
console.trace();
}
a();

Async Example
function a() {
setTimeout(b, 1000)
}
function b() {
console.trace();
}
a();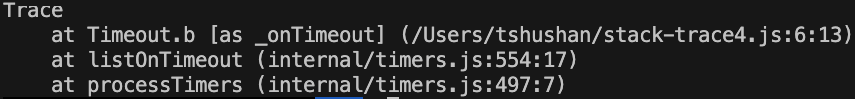

Using Promises
function a() {
b();
}
function b() {
return Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.trace()
});
}
a();


Call Stack

Async/Await
async function a() {
await b();
}
async function b() {
await Promise.resolve();
console.trace();
}
a();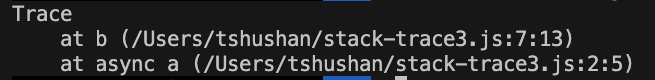


Async\await Stack Trace
Works only when using async\await all the way



What about library code?
try {
const baseURL = await discoveryClient.fetchTarget(serviceName);
return await axios.request({ ...config, baseURL });
} catch (err) {
logger.error('request error', err);
throw err;
}
try {
const baseURL = await discoveryClient.fetchTarget(serviceName);
return await axios.request({ ...config, baseURL });
} catch (err) {
err.stack = new Error().stack;
logger.error('request error', err);
throw err;
}



Transpile async\await
async function a() {
await b();
}
async function b() {
await Promise.resolve();
console.trace();
}
a();Set your tsconfig to target >= ES2017
"use strict";
var __awaiter = (this && this.__awaiter) || function (thisArg, _arguments, P, generator) {
function adopt(value) { return value instanceof P ? value : new P(function (resolve) { resolve(value); }); }
return new (P || (P = Promise))(function (resolve, reject) {
function fulfilled(value) { try { step(generator.next(value)); } catch (e) { reject(e); } }
function rejected(value) { try { step(generator["throw"](value)); } catch (e) { reject(e); } }
function step(result) { result.done ? resolve(result.value) : adopt(result.value).then(fulfilled, rejected); }
step((generator = generator.apply(thisArg, _arguments || [])).next());
});
};
function a() {
return __awaiter(this, void 0, void 0, function* () {
yield b();
});
}
function b() {
return __awaiter(this, void 0, void 0, function* () {
yield Promise.resolve();
console.trace();
});
}
a();
Summary
-
Always use async\await where you can
-
When the async flow is out of your control - create your own stack trace
-
Target >= ES2017 in your tsconfig
-
Always use async\await where you can
-
When the async flow is out of your control - create your own stack trace
-
Always use async\await where you can
-
When the async flow is out of your control - create your own stack trace