Parallel Software for Training Large Scale Support Vector Machines on Multiprocessor Systems
Speaker: Joanne Tseng
National Cheng Kung University
2014/12/13
Outline
- OP1 : The original QP problem
- Derivation of the decomposition matrix
- OP2 : The transformed QP problem
- Parallel Decomposition Technique (PDT) algorithm
- Parallel Gradient Projection Method (PGPM) for STEP A2 of algorithm PDT
- Parallel Gradient Updating (PGU) for STEP A3 of algorithm PDT
Define variables
- n = number of training data
- m = number of features
D=\{(x_i,y_i),i=1,...,n,x_i\in R^m,y_i\in \{(-1,1)\}\}
D={(xi,yi),i=1,...,n,xi∈Rm,yi∈{(−1,1)}}
Training Support Vector Machines (SVM) for binary classification requires to solve the convex quadratic (QP) problem.
QP problem(QP1)
min
min
F(\alpha)=\frac{1}{2}\alpha^TG\alpha-\sum_{i=1}^{n} \alpha_i
F(α)=21αTGα−∑i=1nαi
\sum_{i=1}^{n} y_i\alpha_i=0,
∑i=1nyiαi=0,
subject to
0\leq\alpha_i\leq C,i=1,...,n
0≤αi≤C,i=1,...,n
where
G_{ij}=y_iy_jK(x_i,x_j),i,j=1,...,n
Gij=yiyjK(xi,xj),i,j=1,...,n
The derivation of the decomposition matrix
QP problem(QP2)
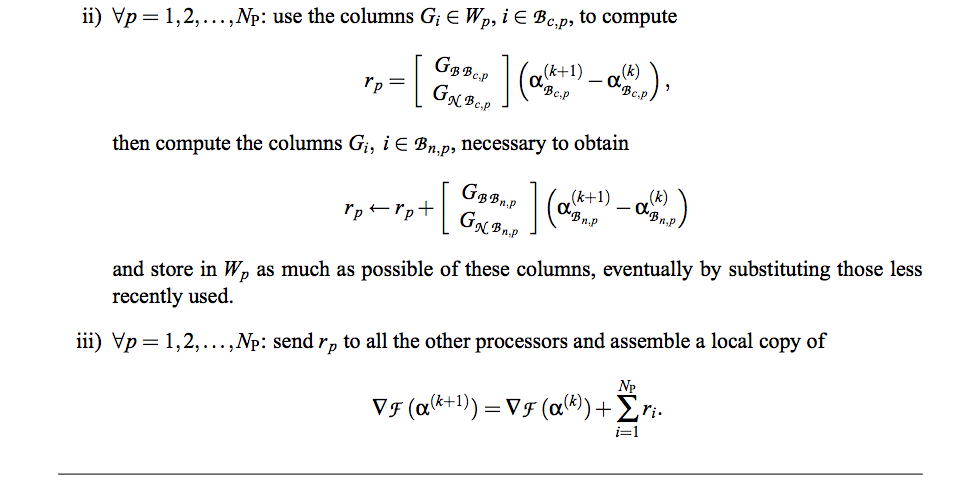
PDT Algorithm(1/2)
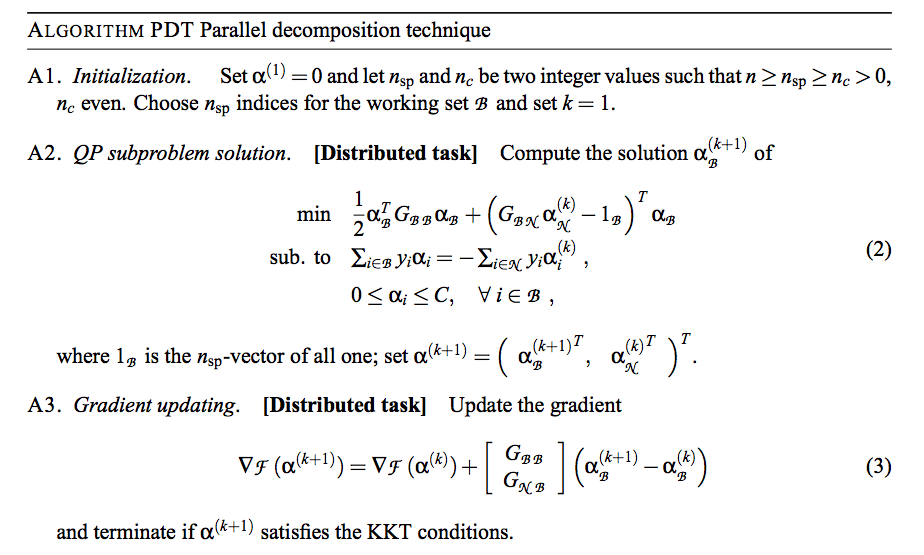
PDT Algorithm(2/2)
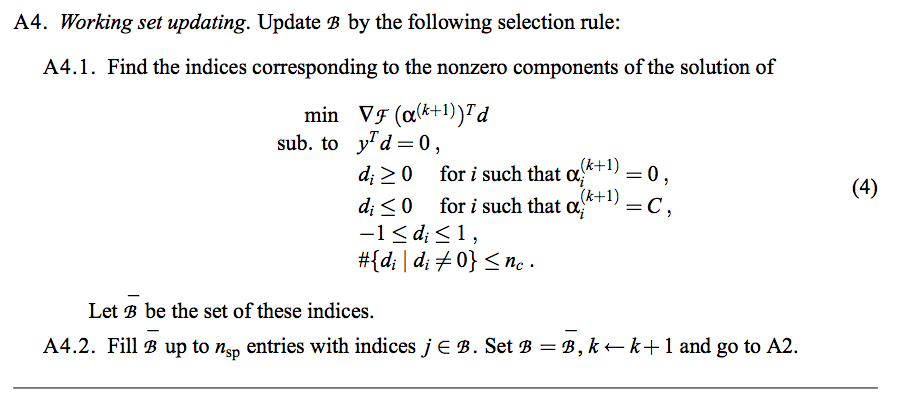
PGPM Algorithm(1/2)
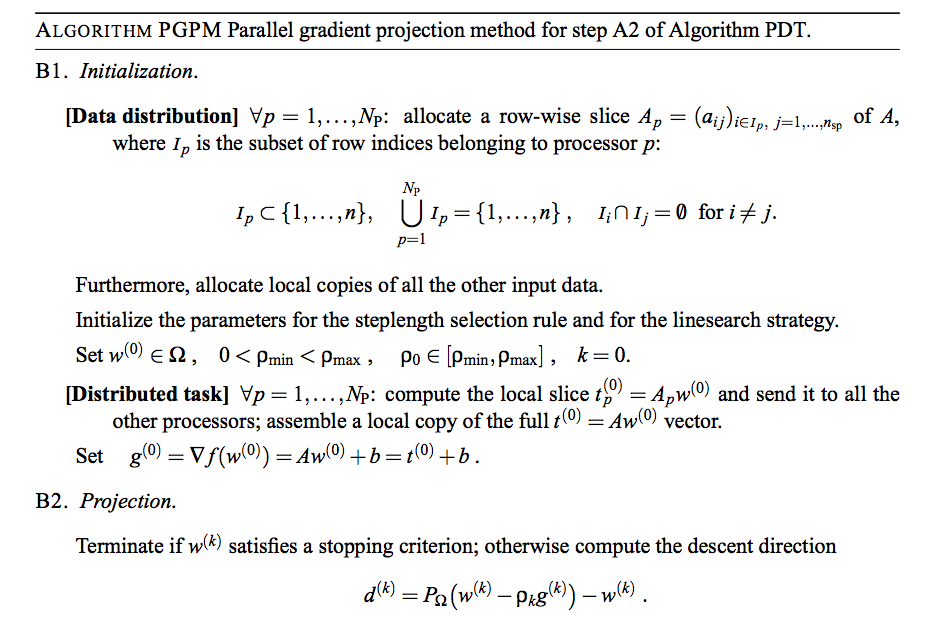
PGPM Algorithm(2/2)

PGU Algorithm(1/2)
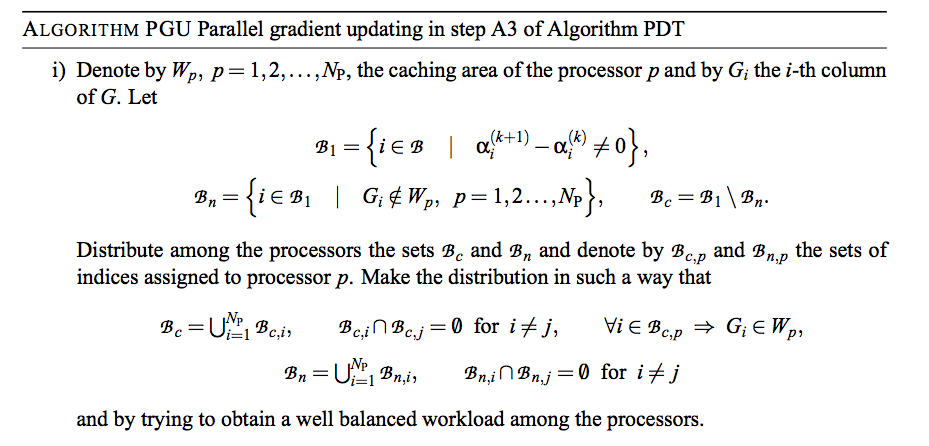
PGU Algorithm(2/2)