An Originalist
Approach
Since 1889
Be Precise in Your Speech
- Originalism
- Non-Originalism
- Types of Claims

Originalism
“the task of constitutional interpretation is to accurately ascertain and then faithfully apply as law the objective original public meaning of the words and phrases of the constitution as a written legal instrument, that is the meaning that the words and phrases would have had to a reasonably informed speaker and reader of the English language at the time the text was adopted, considering the structure of the document and specialized uses of any terms of art.”
Michael Stokes Paulsen


Elements
The core requirements of originalism are
“(1) the meaning of a provision of the Constitution was fixed at the time it was enacted (the ‘Fixation Thesis’); and
(2) that fixed meaning ought to constrain constitutional decisionmakers today (the ‘Constraint Principle’).”
Barnett & Bernick, The Letter and the Spirit
Non-Originalism
Living Constitutionalism
Purposivism
Common Law Constitutionalism
Eclecticism

What does the Court say it is doing?
What is the Court in fact doing?
What should the Court be doing?

Originalism Best Describes How the North Dakota Supreme Court has Described Its Interpretive Method for the North Dakota Constitution

Methodology
- Avoid selection bias
- Keyword searches
- Westlaw keynote 92
- Cases most cited by ND Supreme Court
- pre- and post- 1950
Fixation Thesis
The meaning of a provision is fixed at the time of enactment
Barry v. Truax
Barry tried and convicted for premeditated murder of Mallem. Reversed on appeal. At second trial, jury hung. Judge ordered venue change to another county, which prompted petition for writ.
Fixation: "a right well known and commonly understood at the time of its adoption, and it is the right so understood which is secured by it"



Egbert v Dunseith
Gift Clause reference to article 20 was fixed at time of 1918 amendment.
The "intent and purpose of the people when they adopted the amendment" was to incorporate the substance of the referenced provision "as it existed at the time of adoption."



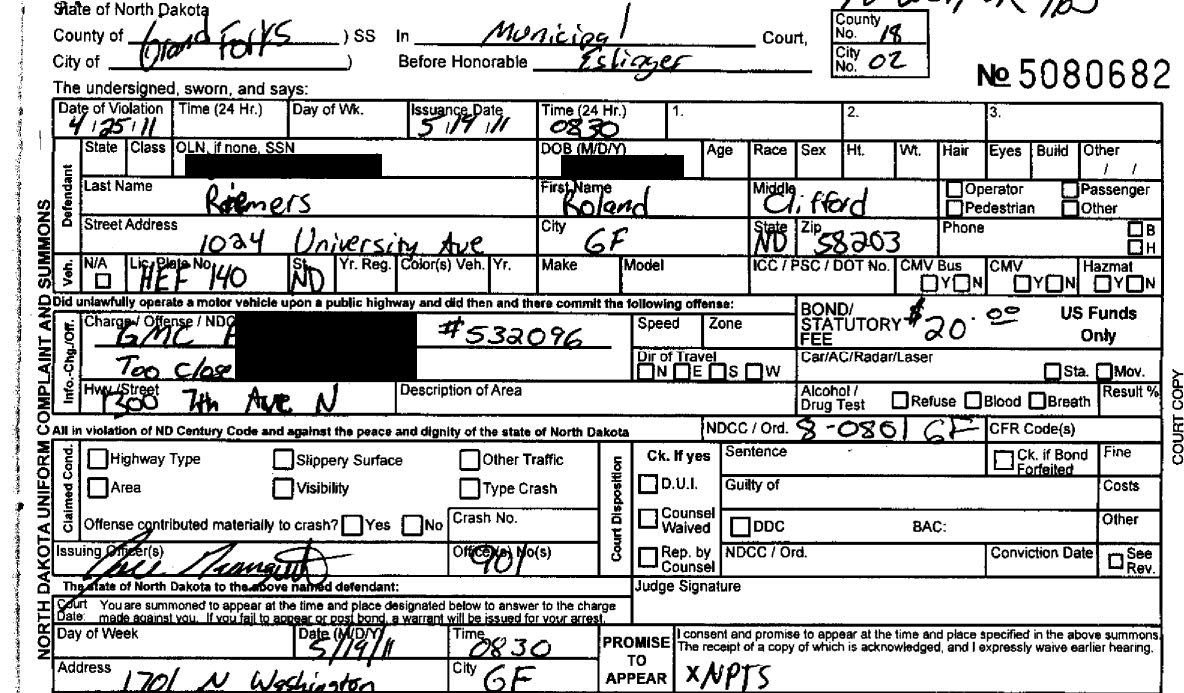
Riemers v Eslinger
We hold to our prior jurisprudence, that the right of trial by jury is determined by the laws as they existed at the time the Constitution of North Dakota was adopted. . . . The people of North Dakota may change this right if they choose.
2010 ND 76


Illustrative Consistent Cases
- Newman v. Hjelle, 133 N.W.2d 549 (1965) ("the people froze into a constitutional provision a subject already covered by statute.")
- State ex rel. Twichell v. Hall, 44 N.D. 459 (1918) (stating use of term "as provided by law" would "adopt by reference for all time the existing provisions of law relative to publication")
- Board of Univ. & Sch. Lands v. Sherwood, 489 N.W.2d 584 (1992) ("In attempting to give effect to the 1912 amendment, we look first to the historical context of that amendment.")
- City of Bismarck v. Fettig, 1999 ND 193, ¶ 8 (“Our constitution must be construed in the light of contemporaneous history--of conditions existing at and prior to its adoption. By no other mode of construction can the intent of its framers be determined and their purpose given force and effect.”)
Inconsistent Cases
- State v. Norton, 64 N.D. 674 (1934) ("The constitution is a living, breathing, vital instrument, adaptable to the needs of the day, and was so intended by the people when adopted.")
- Ferch v. Housing Auth. Cass Co. (1953) ("As governmental activities increase with the growing complexity and integration of society, the concept of 'public use' naturally expands in proportion.")
- Tormaschy v. Hjelle, 210 N.W.2d 100 (1973) ("The terms and provisions of constitutions are constantly expanded and enlarged by construction to meet the advancing affairs of men." (quoting Ramsey, 151 Neb. 333)
- Andrews v. O'Hearn, 387 N.W.2d 716 (1986) ("this court once stated that the provision must be interpreted in light of the 'superior rights of the public and the necessities of the occasion'")
Silent cases

Cooley
"What a court is to do, therefore, is to declare the law as written, leaving it to the people themselves to make such changes as new circumstances may require.
The meaning of the constitution is fixed when it is adopted, and it is not different at any subsequent time when a court has occasion to pass upon it."
Const. Lim. at 67-68 (5th ed. 1883)
The Constraint Principle
Constitutional actors, including judges, must act consistent with original meaning.
Land Bd. v. McMillan
“When the Constitution speaks, its voice is supreme, and its mandates are to be obeyed by all departments and all officers of the state government.”
The 'true rule': "Contemporary construction can never abrogate the text; it can never fritter away its obvious sense; it can never narrow down its true limitations; it can never enlarge its natural boundaries." 12 N.D. 280 (1903)

N.W. Bell v. Wentz
The constitution of the state is its paramount law. It is a self-imposed restraint upon the people of the state in the exercise of their governmental sovereign power, either by themselves through the initiative or by their agency, the legislature.
103 N.W.2d 245, 252 (N.D. 1960)

State v. Strom
2019 case involving embezzlement of $690,000 from oil field services company and order for restitution in that amount
The Court read the 2016 victims rights amendment as impliedly repealing or abrogating inconsistent statutes limiting restitution by defendant's ability to pay.

Consistent Cases
- Standish v. Nomland (1893) ("If the legislature in any act disregard the mandate, it is the duty of this court to nullify the act, and the fact that the abortive legislation may be highly beneficial and salutory in its nature can in no manner control that duty.")
- State v. Taylor (1911) ("[C]onstitutions are a means employed by the sovereign people to limit the powers of their agents, especially those of the legislative department.")
- Langer v. Olson (1920) ("The Constitution ... is ... equally obligatory upon the court, and upon the legislature. It is the duty of this court to uphold the Constitution in its plain words and meaning, so long as this court has imposed upon it the sworn duty to uphold the Constitution.")
- Riemers v. Eslinger (2010) ("This provision deprives the legislature and courts of all authority to destroy by legislation or by judicial construction any of the substantial elements of the right of jury trial.")
Inconsistent Cases
-
State v. Norton, 64 N.D. 675 (1934) ("[The constitution] was not a hard and fast piece of legislation, but a declaration of principles of government for the protection and guidance of those upon whose shoulders the government rested.")
[echoes of Cooley's advice, Journal 66-67] - McCarney v. Meier, 286 N.W.2d 780 (1979) ("under the circumstances of this case, substantial compliance with the constitutional mandate is sufficient").
What is the meaning of meaning?
meaning, intent, purpose, means vs. ends, and a failure to communicate
Framers
Adopters


The Law of Interpretation
- Drafters, Adopters, or both
- Read as a Legal Instrument
- Structure and Reading as a Whole
- Terms of Art, Context
- Rules or Standards, vs. Expected Applications
Baude & Sachs, The Law of Interpretation 130 Harv. L. Rev. 1079

Not what what do these words mean, but what law did this instrument make?
Miller v. Taylor
"The intent of the convention is not controlling in itself; but, as its proceedings were preliminary to the adoption by the people of the Constitution, the understanding of the convention as to what was meant by the terms of this provision goes a long way toward explaining the understanding of the people when they ratified it."

"How shall we reasonably assume the people, in ratifying the Constitution, understood it?"
RECALLND v. Jaeger
- "intent and purpose of the people adopting the constitutional statement"
- "plain, ordinary, and commonly understood meaning"
- "We must interpret what is actually contained in the Constitution, not what the parties would prefer it contained."

Effective Advocacy

Preservation
- Raise isue
in the trial court - Facial challenges to statute must satisfy Rule 44 and
N.D.C.C. § 32-23-11.

Start With the Text
"When interpreting the Constitution, it is our overriding objective to give effect to the intent and purpose of the people adopting the constitutional statement. Such intent and purpose are to be found in the language of the constitution itself."
City of Bismarck v. Fettig, 1999 ND 193, ¶ 8

Dictionaries
Which dictionary?
Which among several definitions?



Terms of Art
"right of trial by jury"
"general superintending control"
"normal school"

Treatises
Constitutional Convention
Both the Proceedings and Debates and the Journal of the 1889 Convention are sparse.
Committee work unrecorded.
Secret sources.
Some press coverage.

Historical Context
Publicity pamphlets were published until 1965.
Bill of Rights incorporated against the states through Fourteenth Amendment.
Court may look to history of time when provision was enacted to consider prior law, mischief, and remedy.

Caution
Avoid:
- Unadorned request to exercise will, not judgment.
- Arguments based in policy not traceable to original meaning.

Looking Forward
References
Jerod Tufte, The North Dakota Constitution: An Original Approach Since 1889, 95 N.D. L. Rev. 417 (2020). (link)
Sources and materials available at ndconst.org
Other Examples
- Single Subject Rule
NDPERS v NDLEG, 2023 ND 185 - Constitutional dialog between NDLEG and NDSC
RRWC v. Wrigley, 2025 ND 26 - Statutory dialog
NDCC 12.1-32-07(6) & State v. McGinnis, 2022 ND 46
NDCC 29-05-20; Jesser, 2019 ND 287; Schulz, 2020 ND 154
